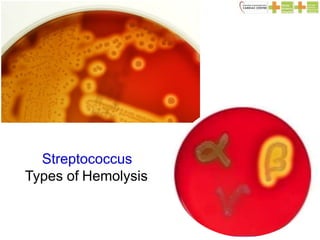
Rheumatic fever is an autoimmune disease that can occur weeks after a Group A streptococcal (GAS) infection such as a sore throat. It is characterized by migratory arthritis, heart inflammation (carditis), abnormal movements (Sydenham's chorea), skin nodules, and rash. If not properly treated, it can cause long-term damage to the heart valves known as rheumatic heart disease. Treatment involves antibiotics to treat the initial strep infection, anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin to reduce symptoms, and ongoing preventative antibiotics to reduce the risk of recurrent episodes and further heart damage.




























![Chronic RHD
• Characterized by organization of acute
inflammation and subsequent fibrosis
• Valves show thickening, commissural fusion and
shortening,
• Cordae tendinae shows thickening and shortening
• Mitral valve: MS [Button hole, Fish mouth]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rhdtalk-190729033529/85/Rhd-31-320.jpg)








