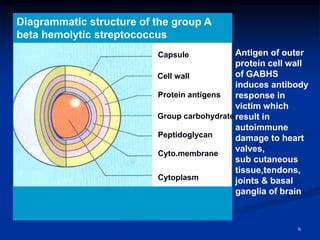
1. Acute rheumatic fever is a non-suppurative sequelae that occurs 1-3 weeks after a Group A streptococcal infection of the throat, and results in immune-mediated damage to connective tissues, especially the heart valves.
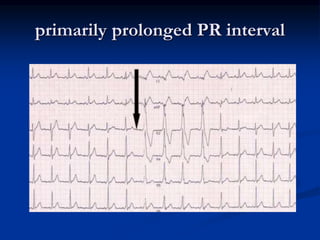
2. It most commonly affects children between 5-15 years of age, and is diagnosed based on the modified Jones criteria which looks for major manifestations like carditis, polyarthritis, chorea or minor manifestations along with evidence of a prior streptococcal infection.
3. Treatment involves antibiotics to treat the initial strep infection, anti-inflammatory drugs like aspirin and steroids to reduce inflammation, and long-term antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent