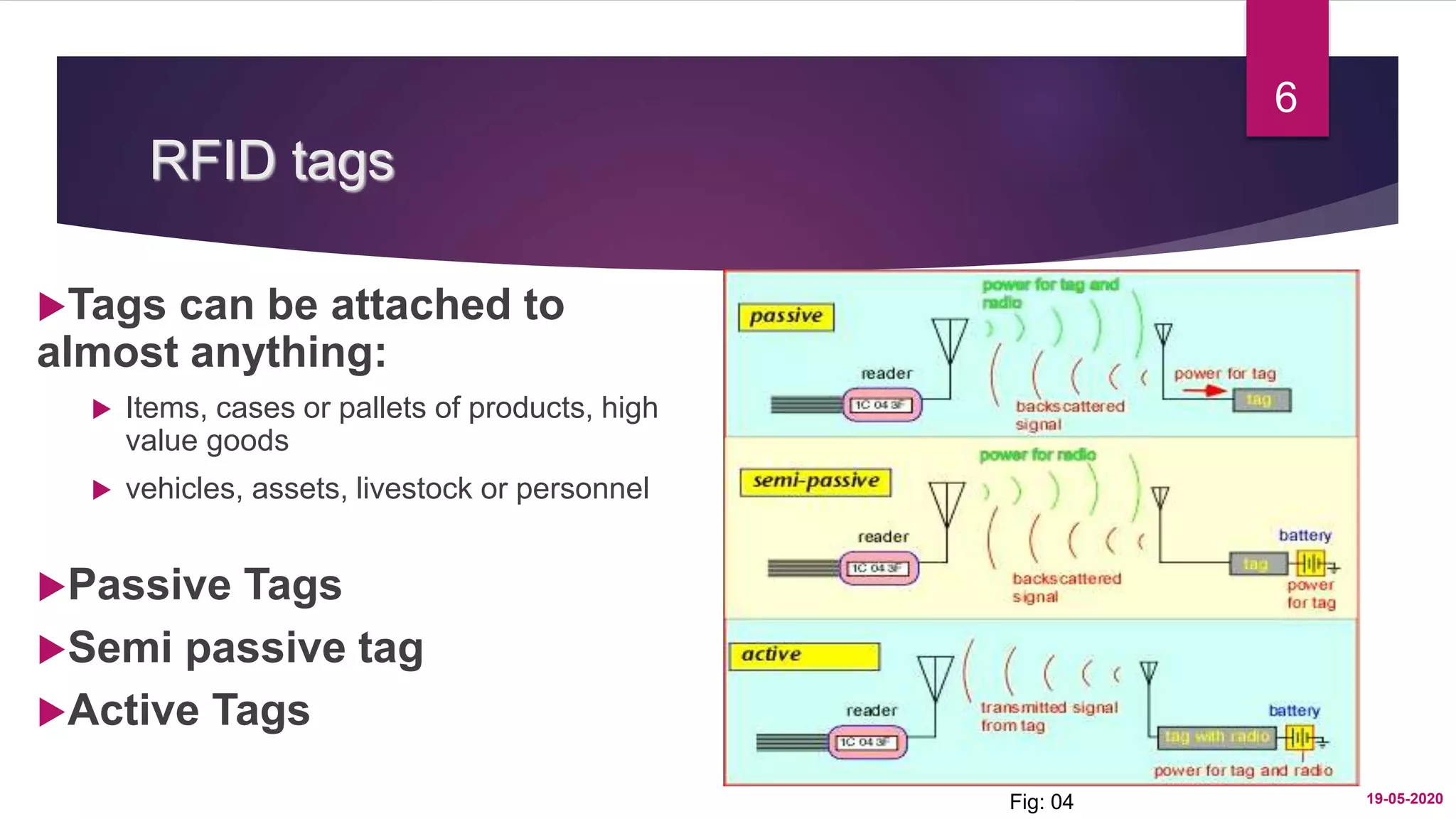
RFID technology uses radio waves to identify objects without physical contact or line of sight. An RFID system consists of RFID tags attached to objects, RFID readers that can read tag data, and a host computer system. RFID tags contain antennas to receive and respond to radio-frequency queries from RFID readers, and some tags are passive while others are active. RFID provides advantages over barcodes by allowing multiple items to be identified simultaneously without scanning each item. Common applications of RFID include supply chain management, asset tracking, and automated payment systems.