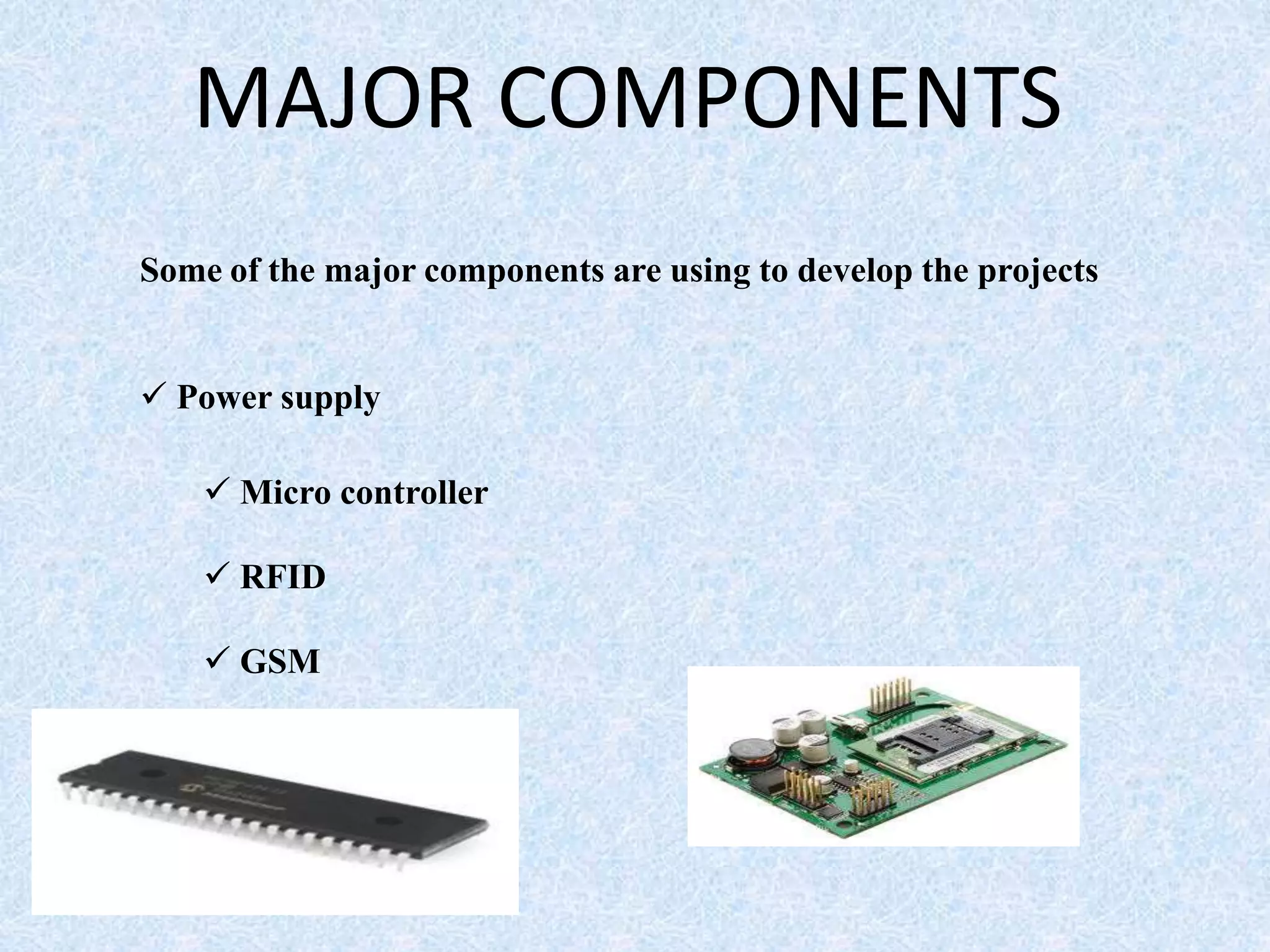
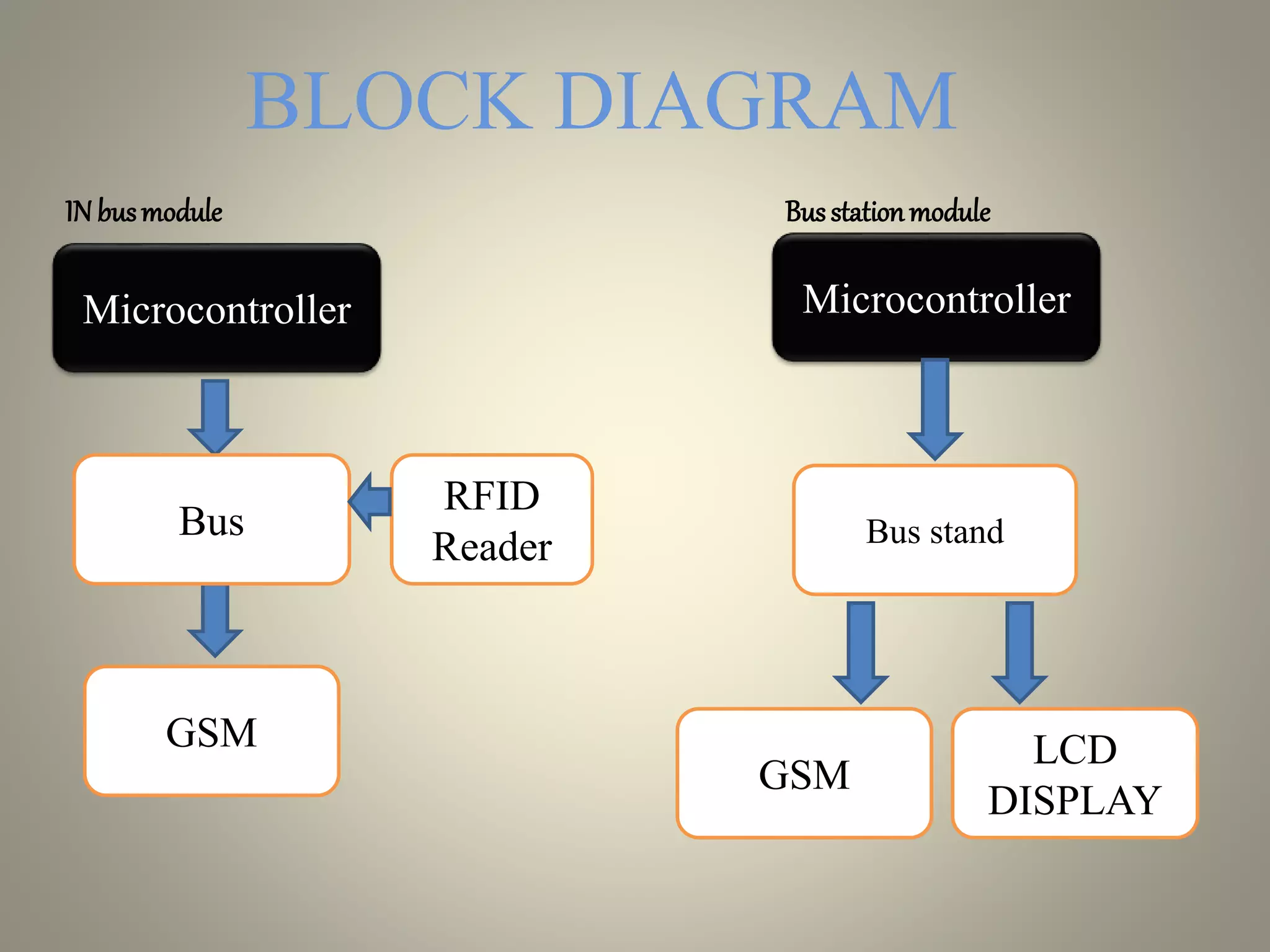
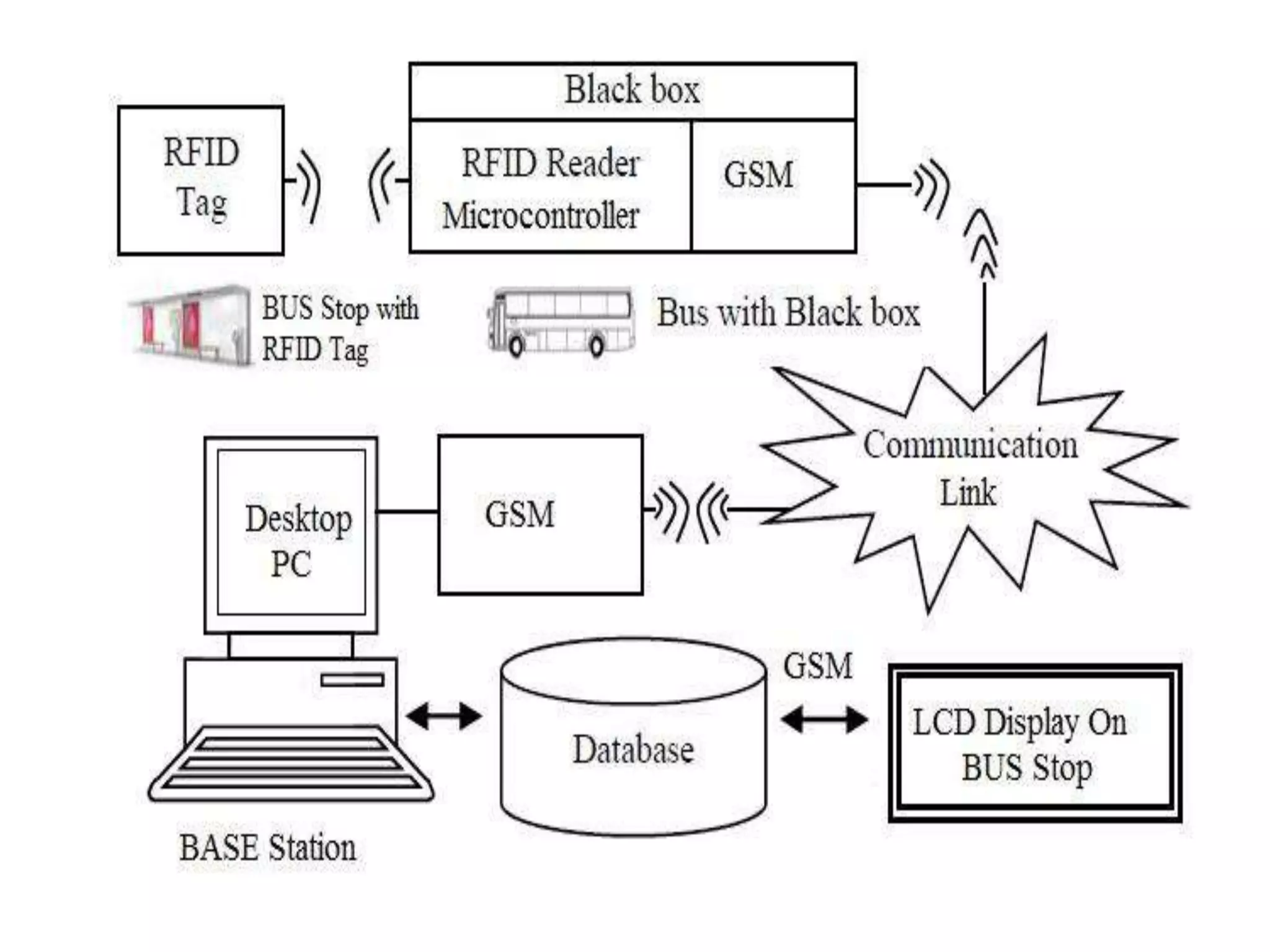
The document describes a transportation management system that uses RFID and GSM technologies. It consists of RFID tags on buses that are read by readers located at bus stops and stations. The readers send data about bus locations to a central server via GSM. An LCD display at bus stops and stations then shows estimated arrival times to users (3 sentences).