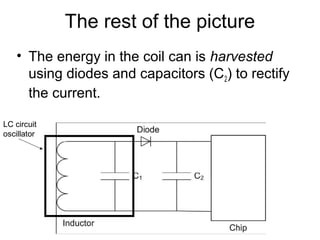
The document provides an overview of RFID system characteristics including operating frequency, method of coupling, transmission range, data storage capacity, power supply, and transmission types. It describes two main methods of coupling - inductive coupling and electromagnetic backscatter. Inductive coupling uses magnetic flux between coils to transmit data over short ranges under 1 meter, while electromagnetic backscatter reflects signals to transmit data over longer ranges greater than 1 meter.