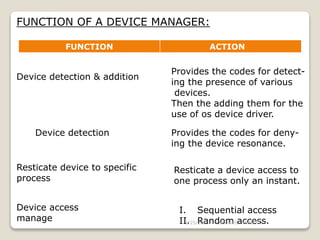
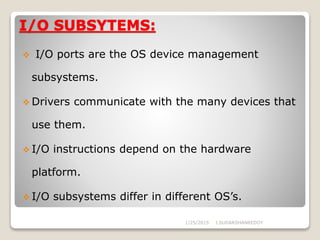
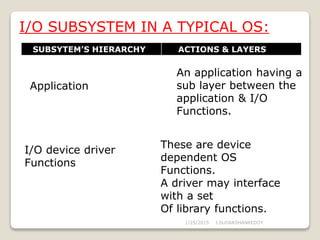
1) A device manager, either inside or outside the kernel, coordinates communication between applications, drivers, and devices by managing I/O requests and interrupt queues.
2) The device manager creates a kernel interface and API to control devices by activating their register-specific actions.
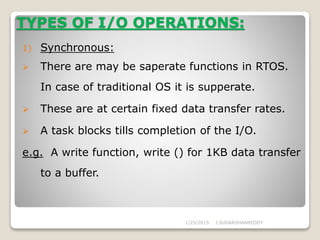
3) Device management involves polling, interrupts, and DMA and supports various I/O approaches including programmed, interrupt-driven, and DMA-driven I/O.