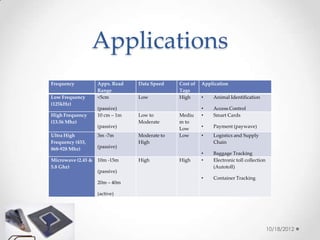
This document discusses RFID technology, including its components, types of tags, applications, and future development. It provides details on passive, semi-passive, and active tags. Common applications mentioned are payment systems, logistics/supply chain, toll collection, and access control. The document also describes an online survey on SME opinions of RFID and a conclusion that highlights benefits like contactless reading but notes high costs and developing standards.