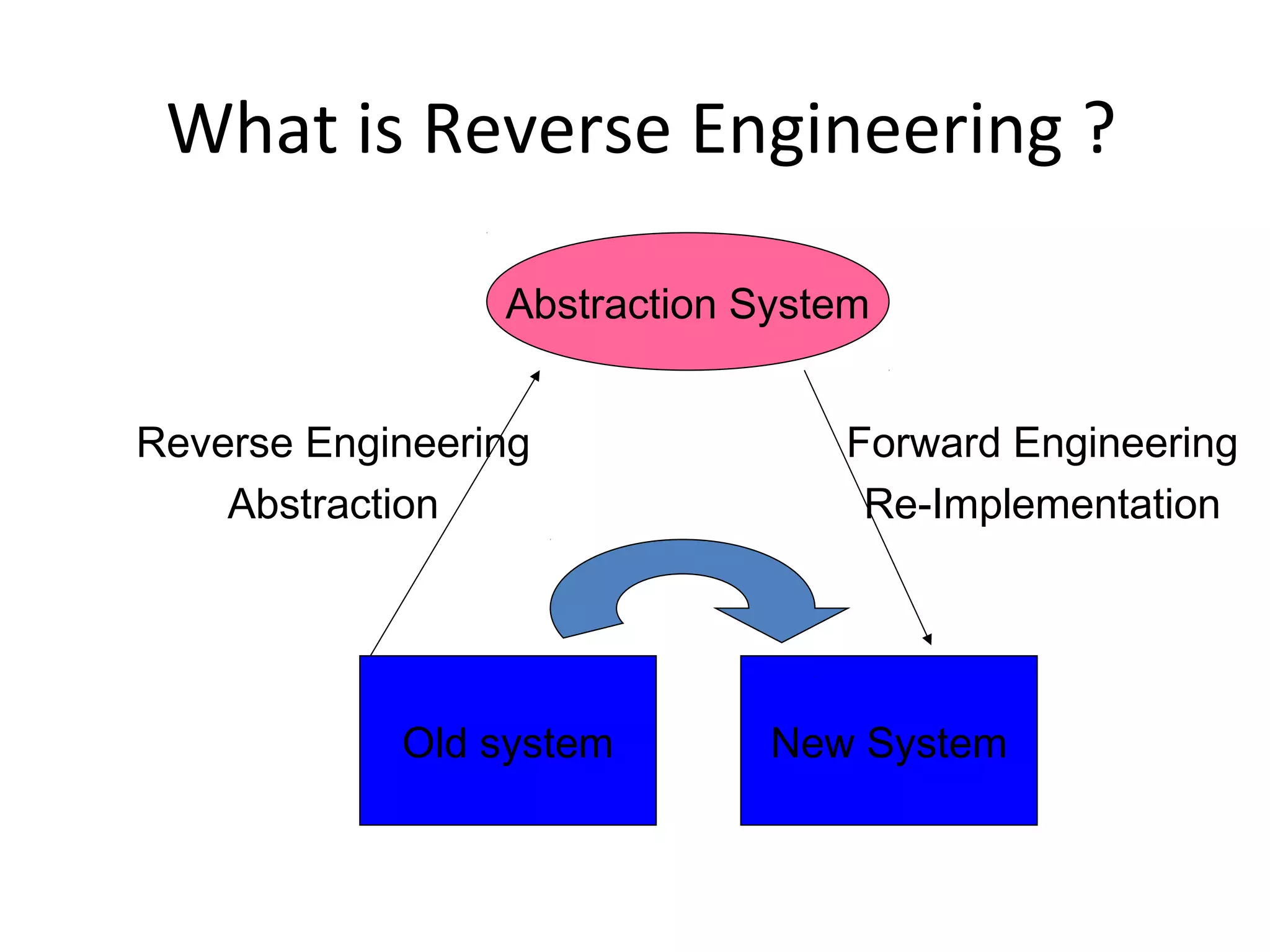
Reverse engineering is the process of analyzing a system to understand how it works in order to recreate or re-implement the system. It involves determining the system's components, architecture, and algorithms by working backwards from its executable form. Reverse engineering is used to recover lost information, assist with maintenance, migrate systems to new platforms, and facilitate software reuse. It requires discovering the system's abstraction levels and mapping between its problem domain and implementation. Common reverse engineering tasks include program understanding, redocumentation, component identification, and abstraction discovery.