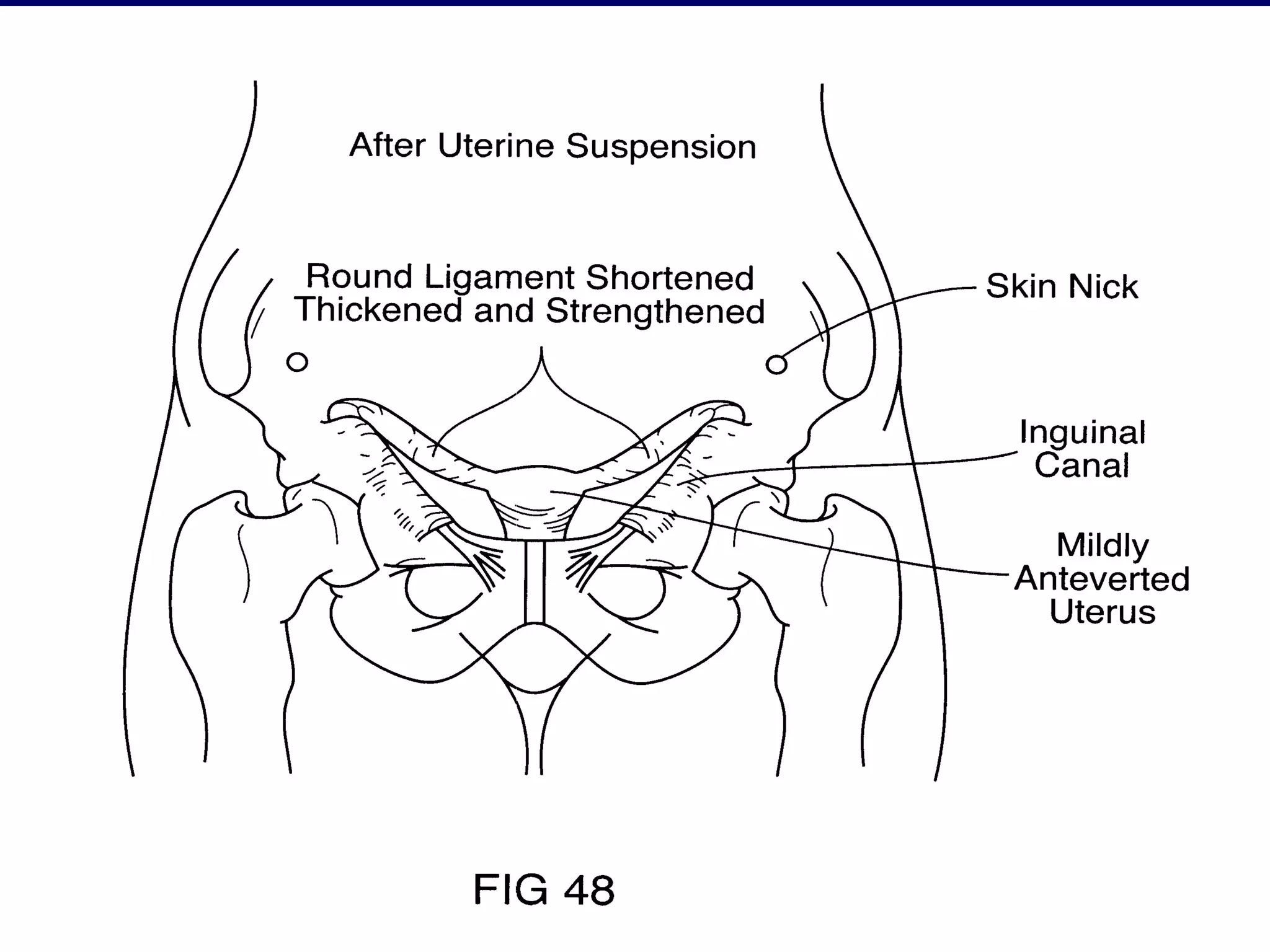
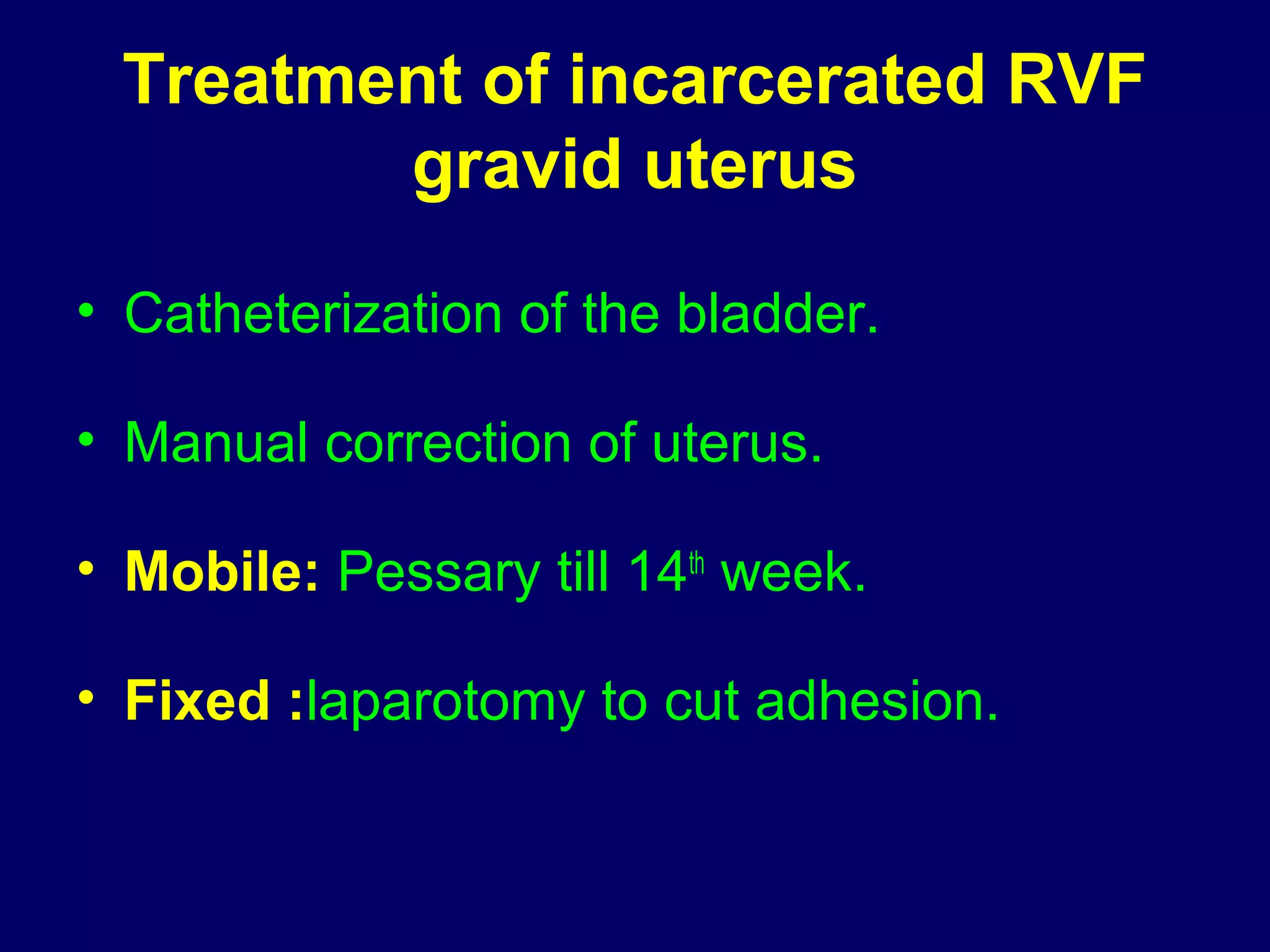
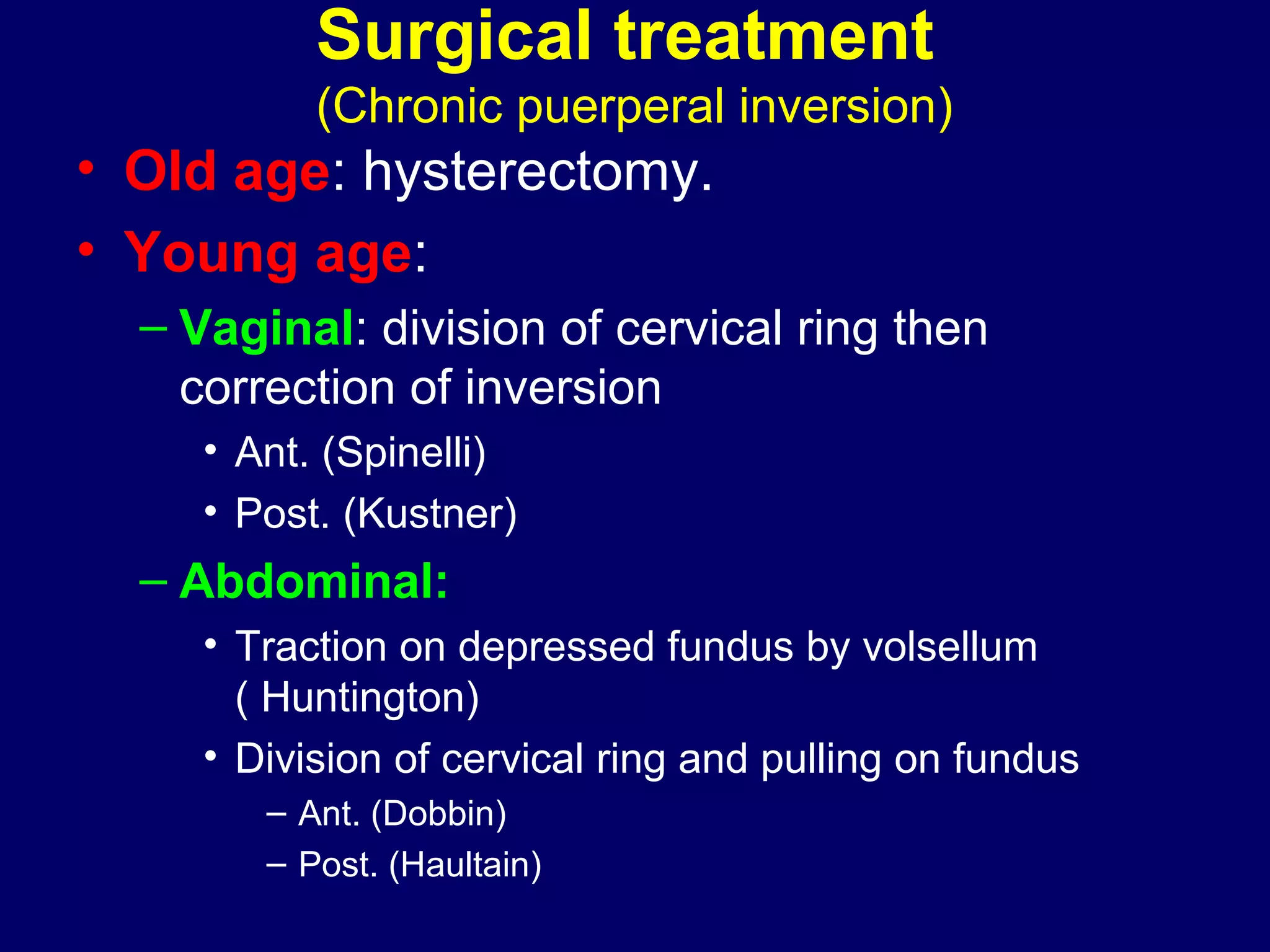
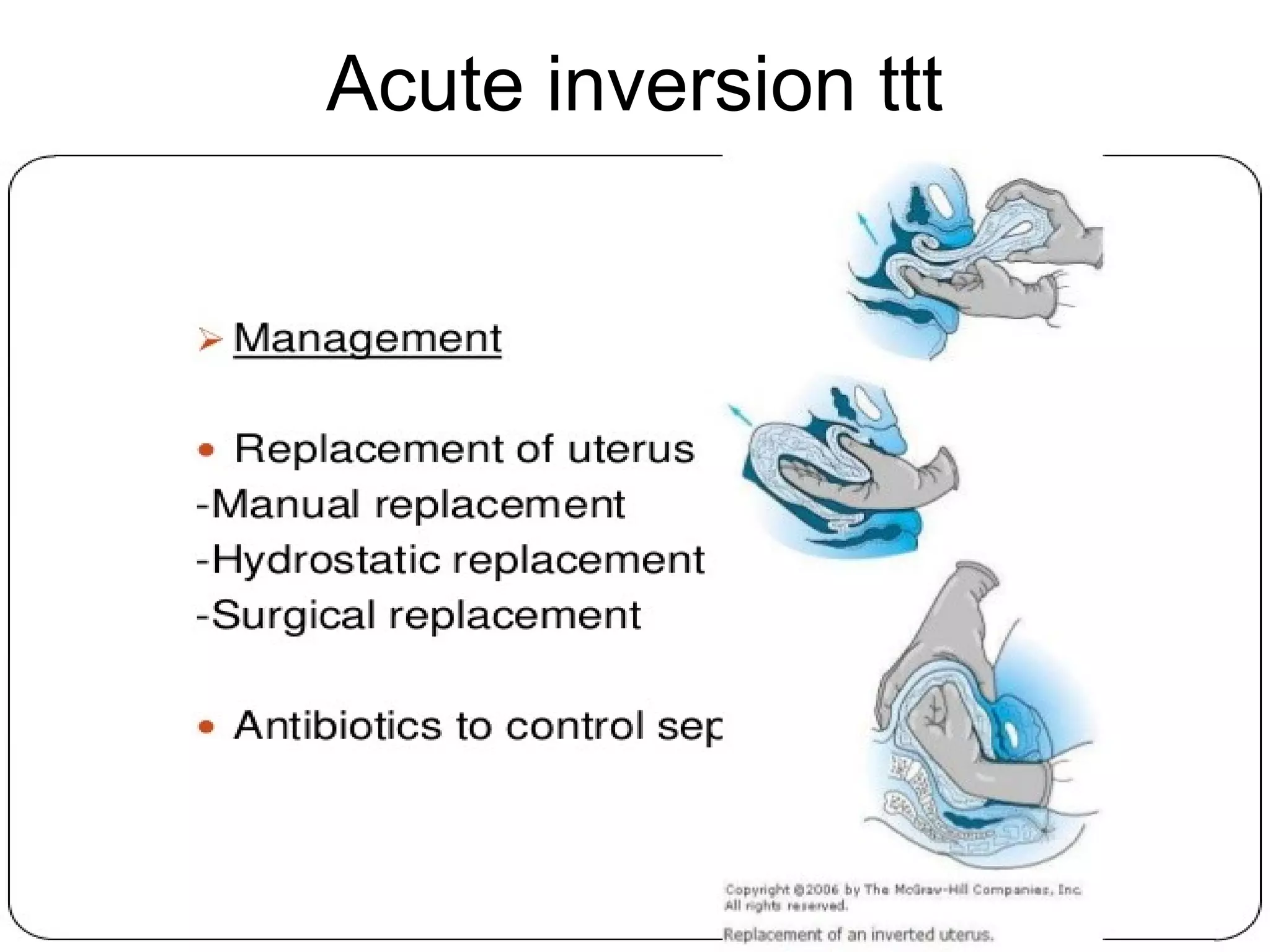
This document summarizes information about retroverted and retroflexed uteruses (RVF) including:
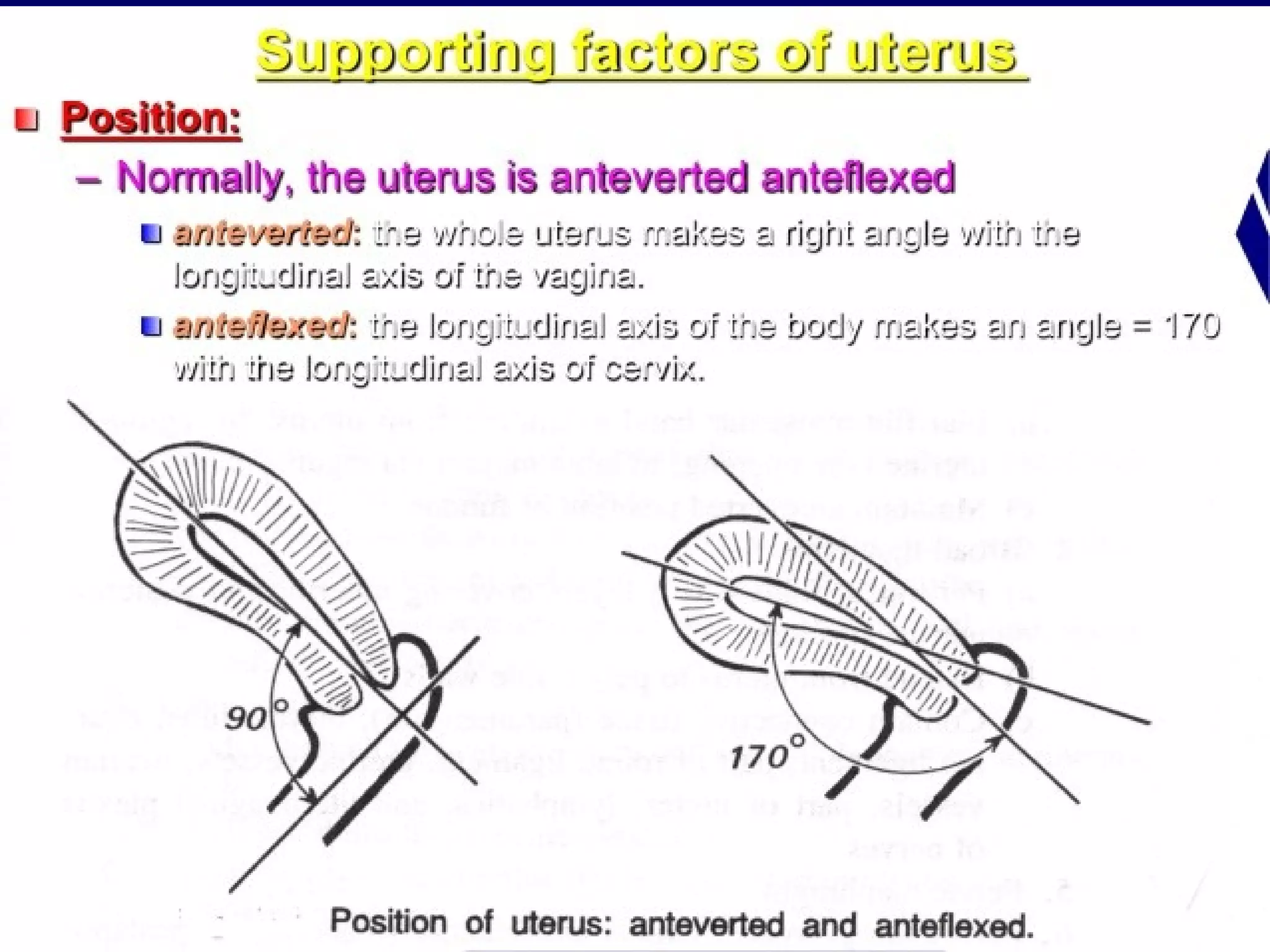
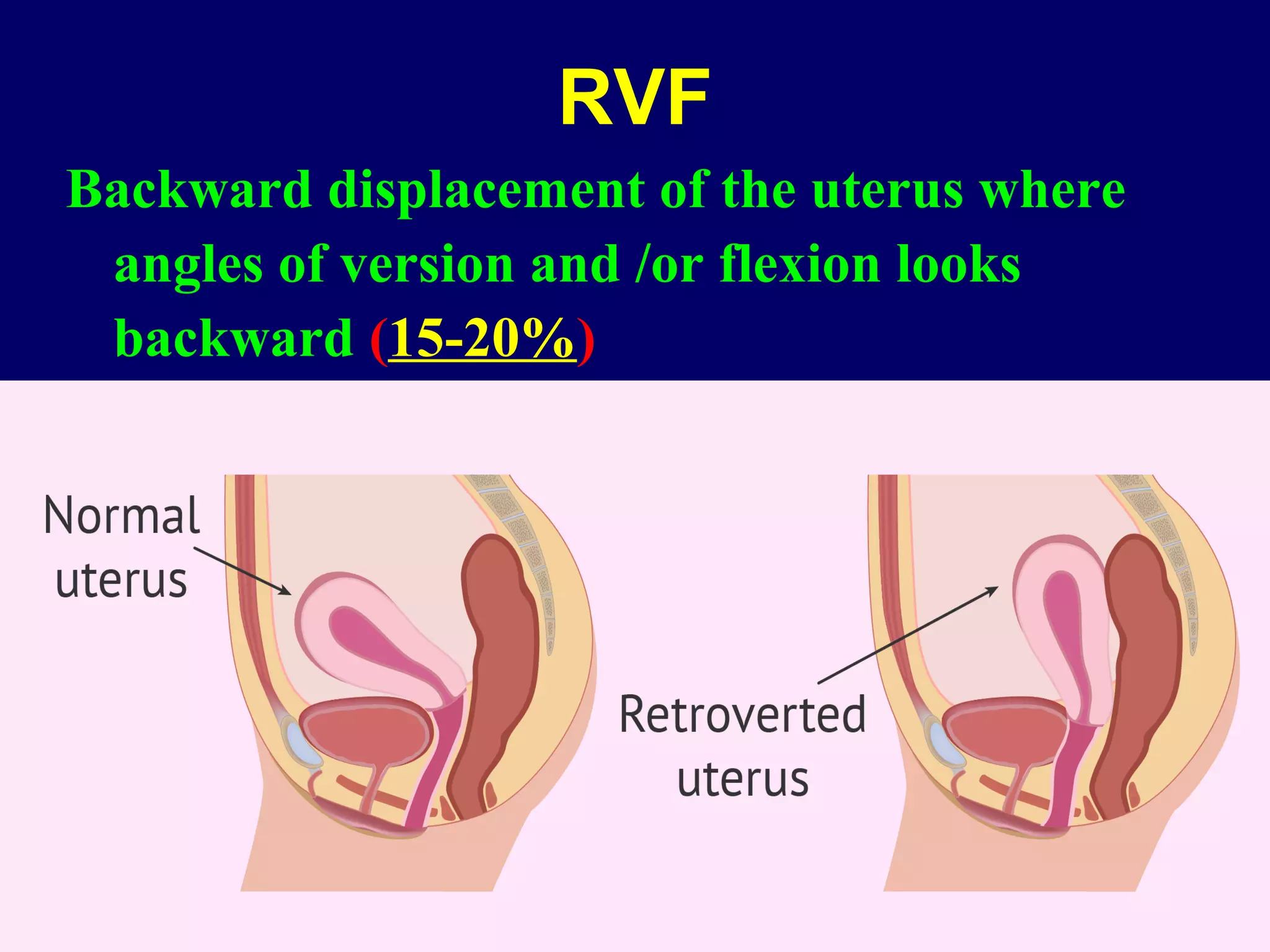
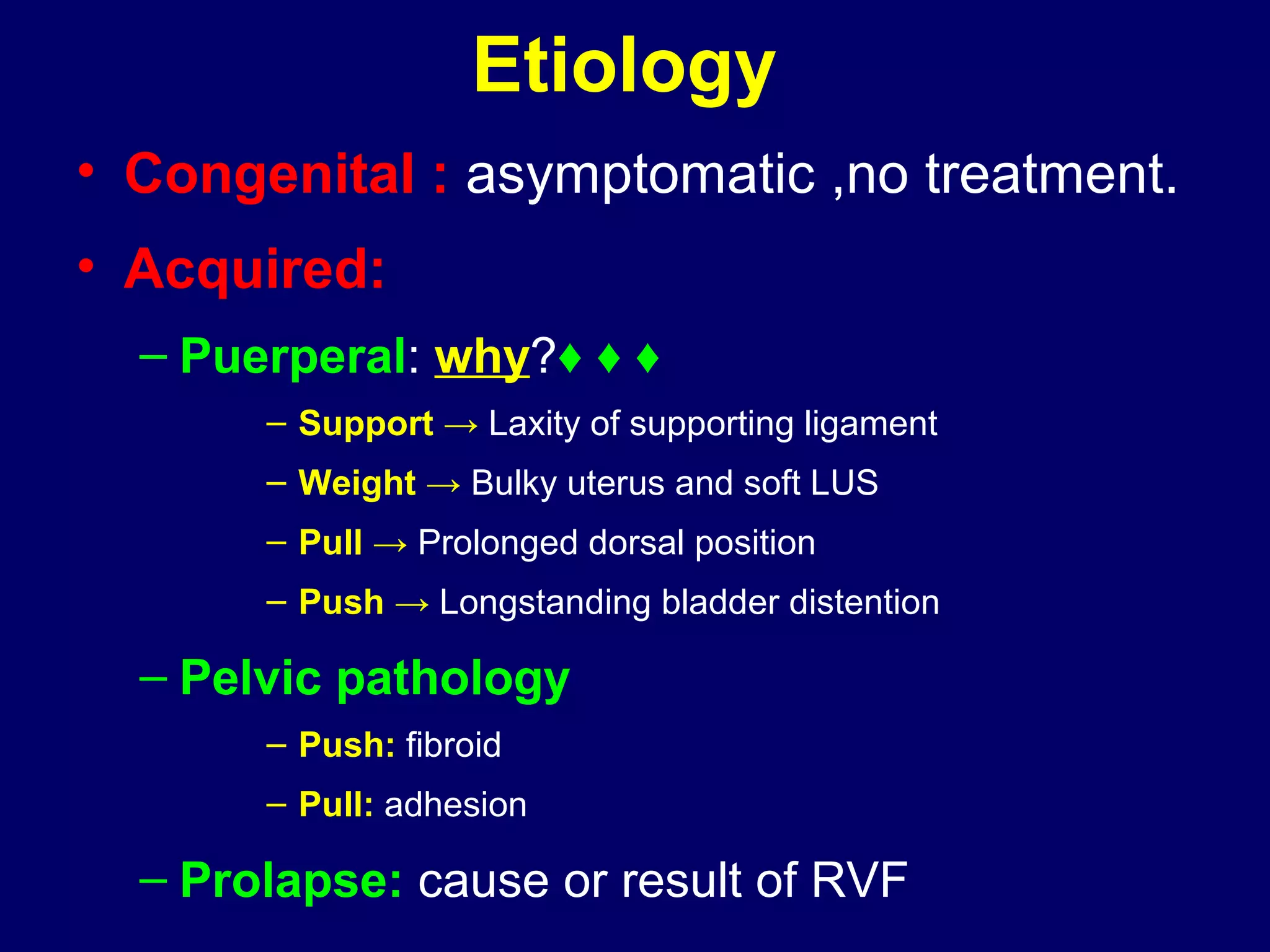
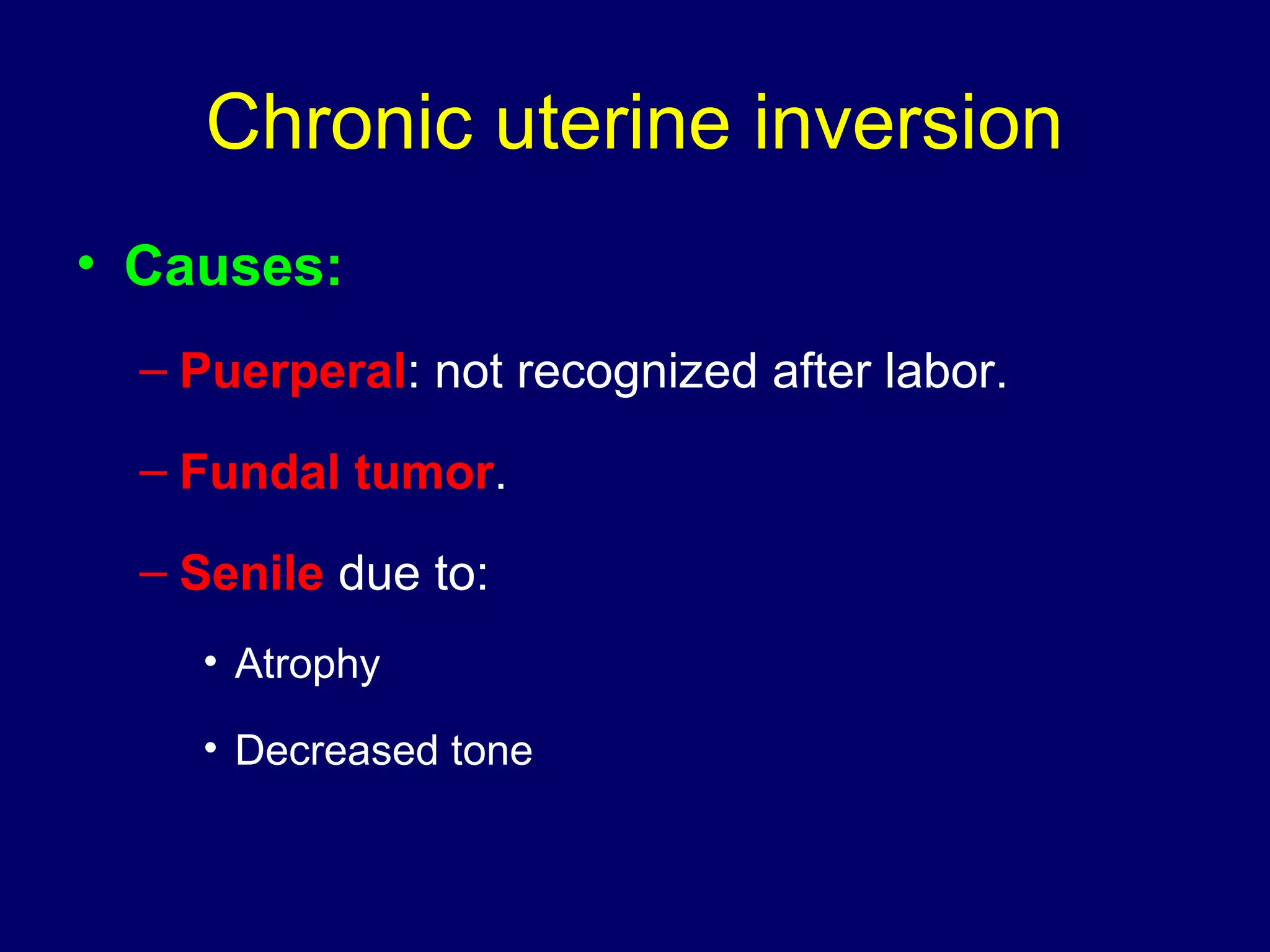
1) RVF occurs when the uterus is displaced backwards, with the angles of version and flexion directed posteriorly. It can be congenital and asymptomatic or acquired due to factors like childbirth, ligament laxity, uterine weight, prolonged dorsal positioning, or pelvic pathology.
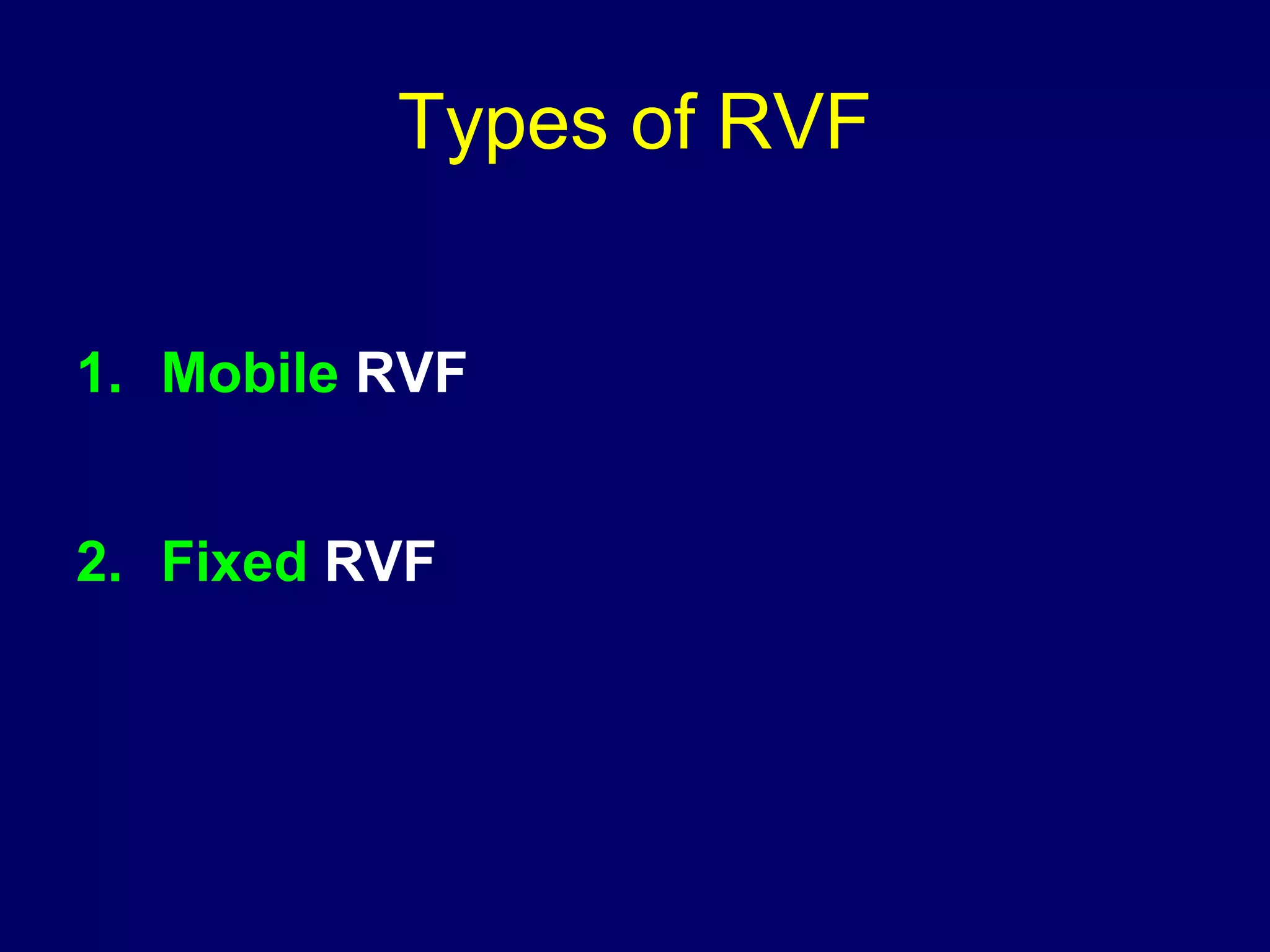
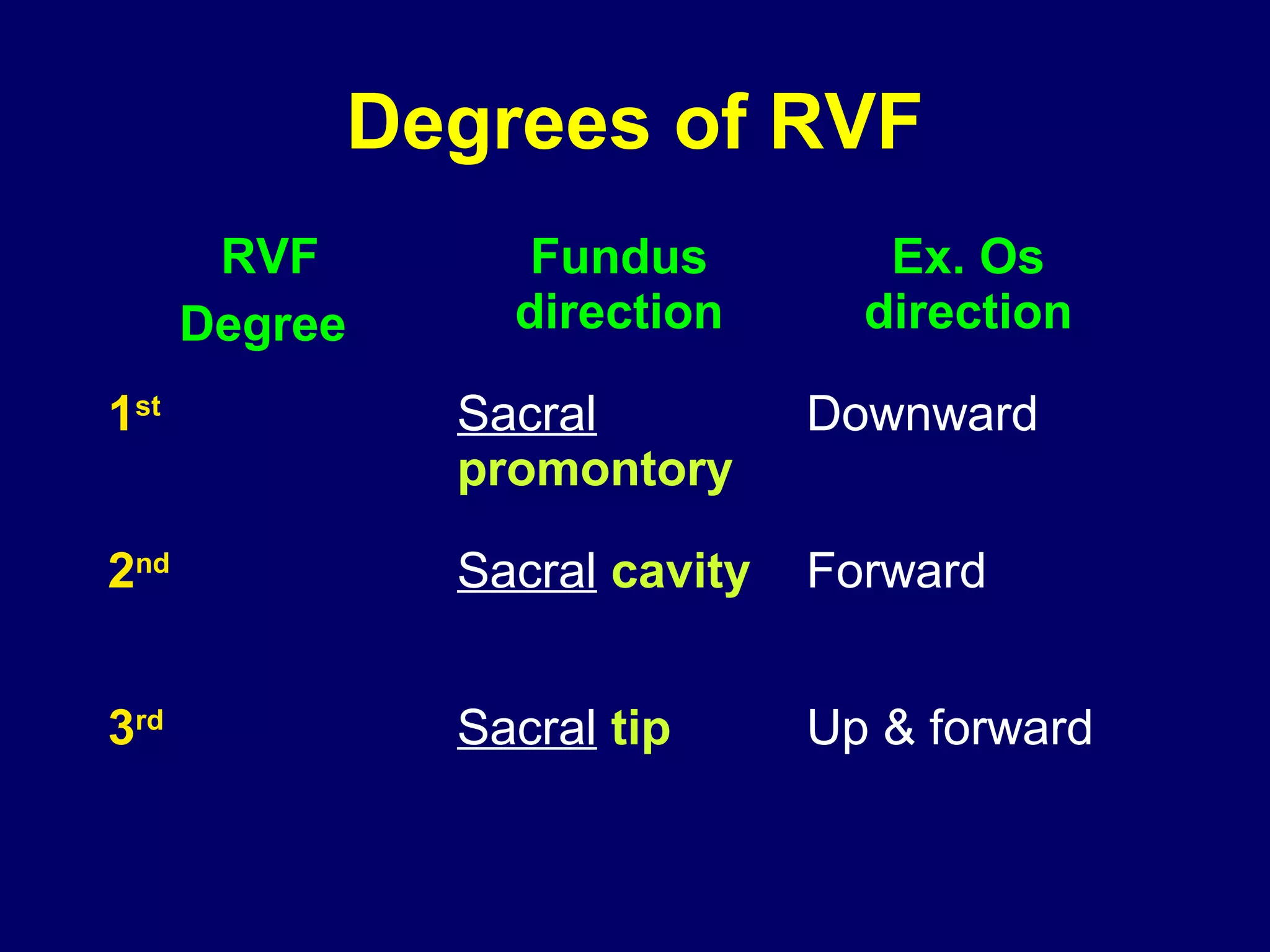
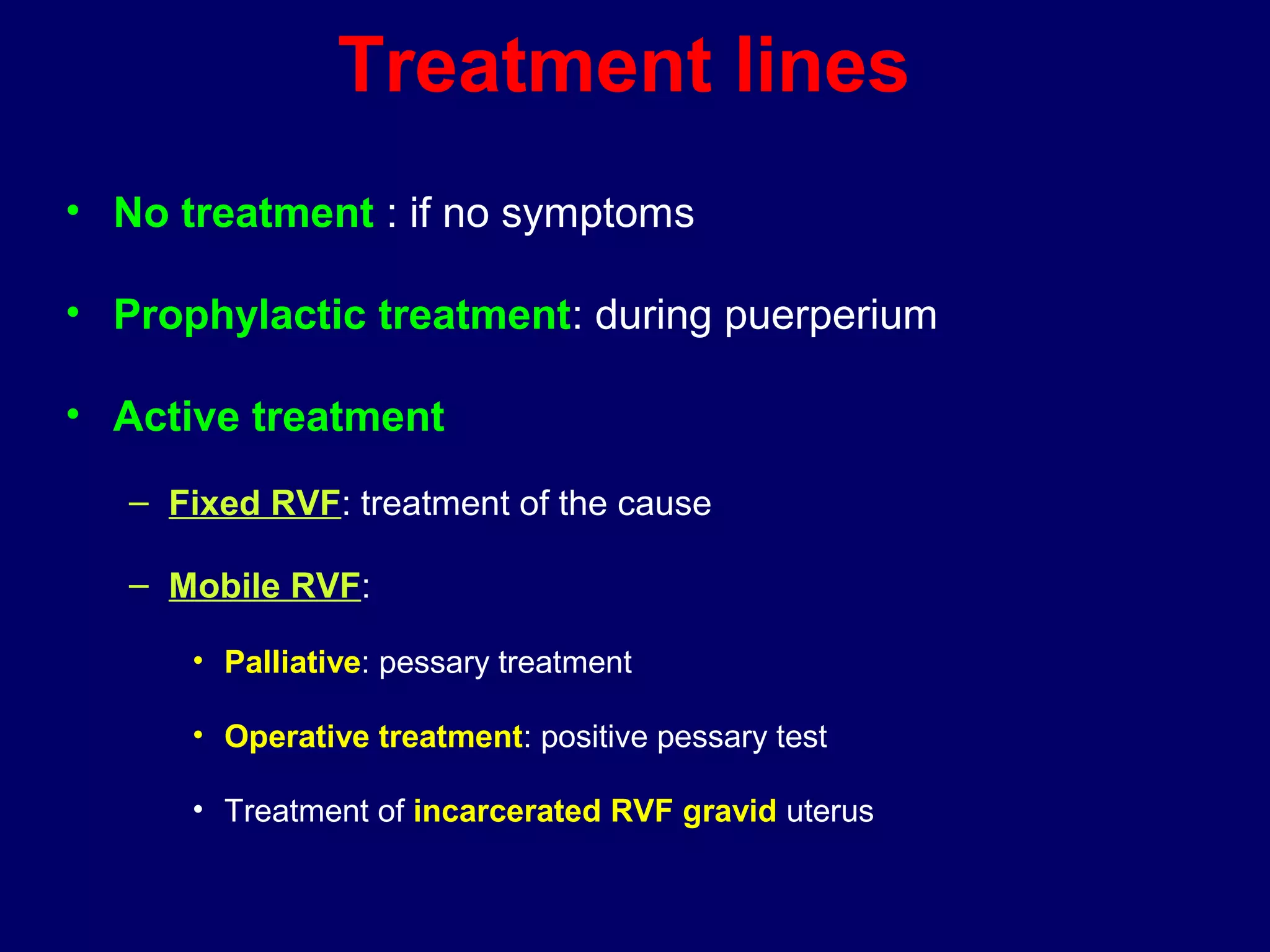
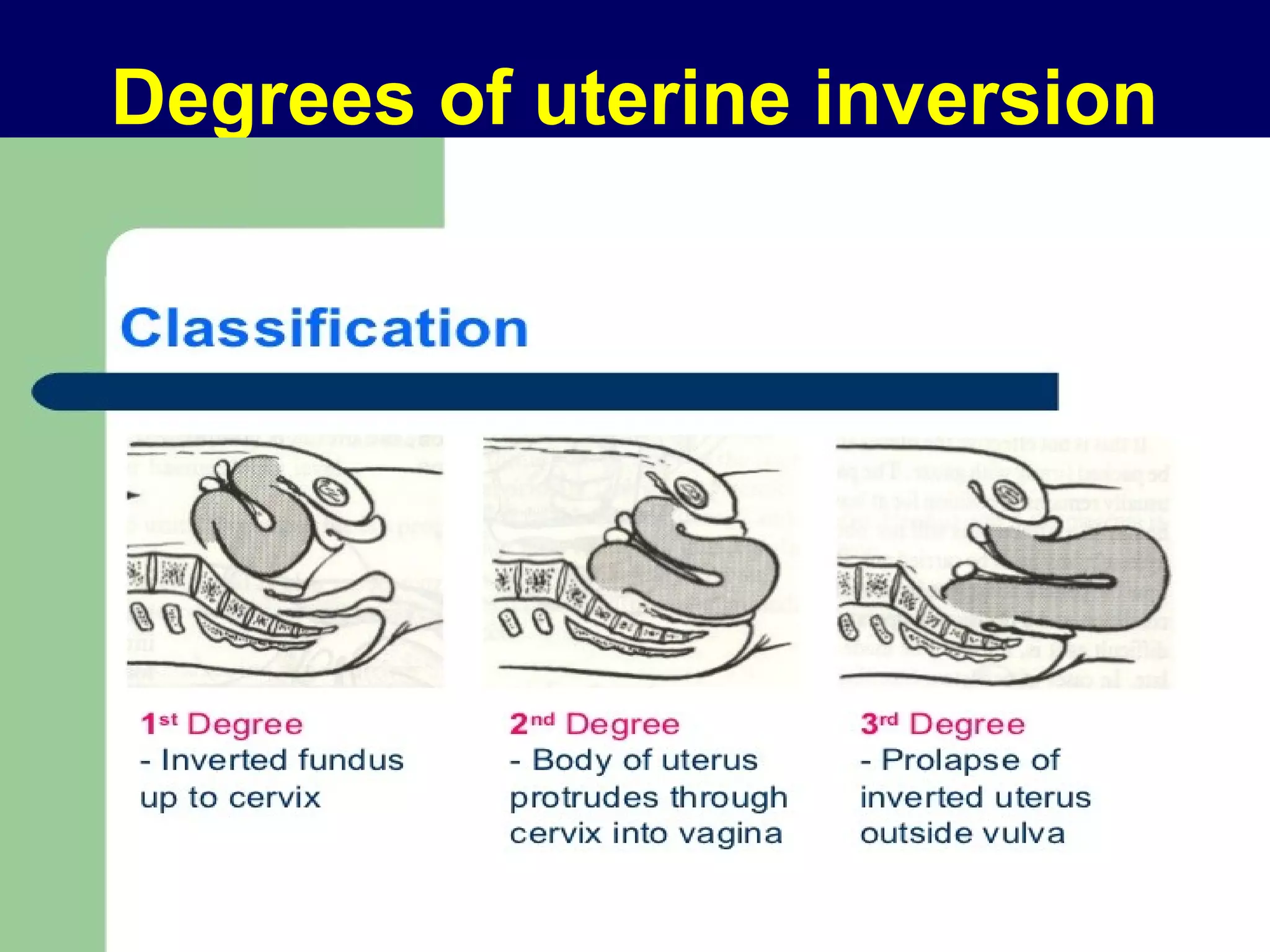
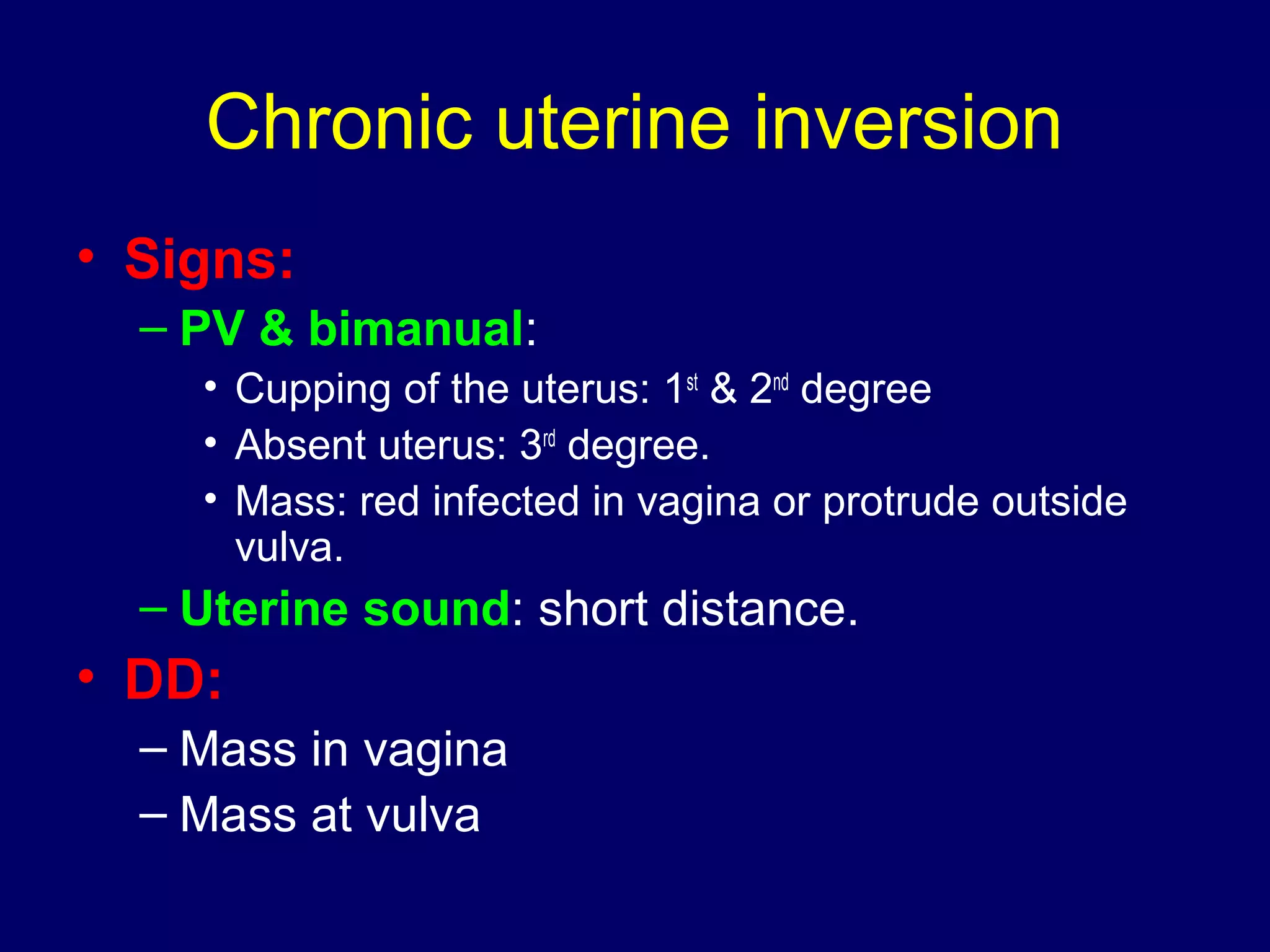
2) RVF is classified as mobile or fixed, and has degrees from the 1st degree where the fundus is directed downward to the 3rd degree where it is directed upward and forward into the sacral cavity.
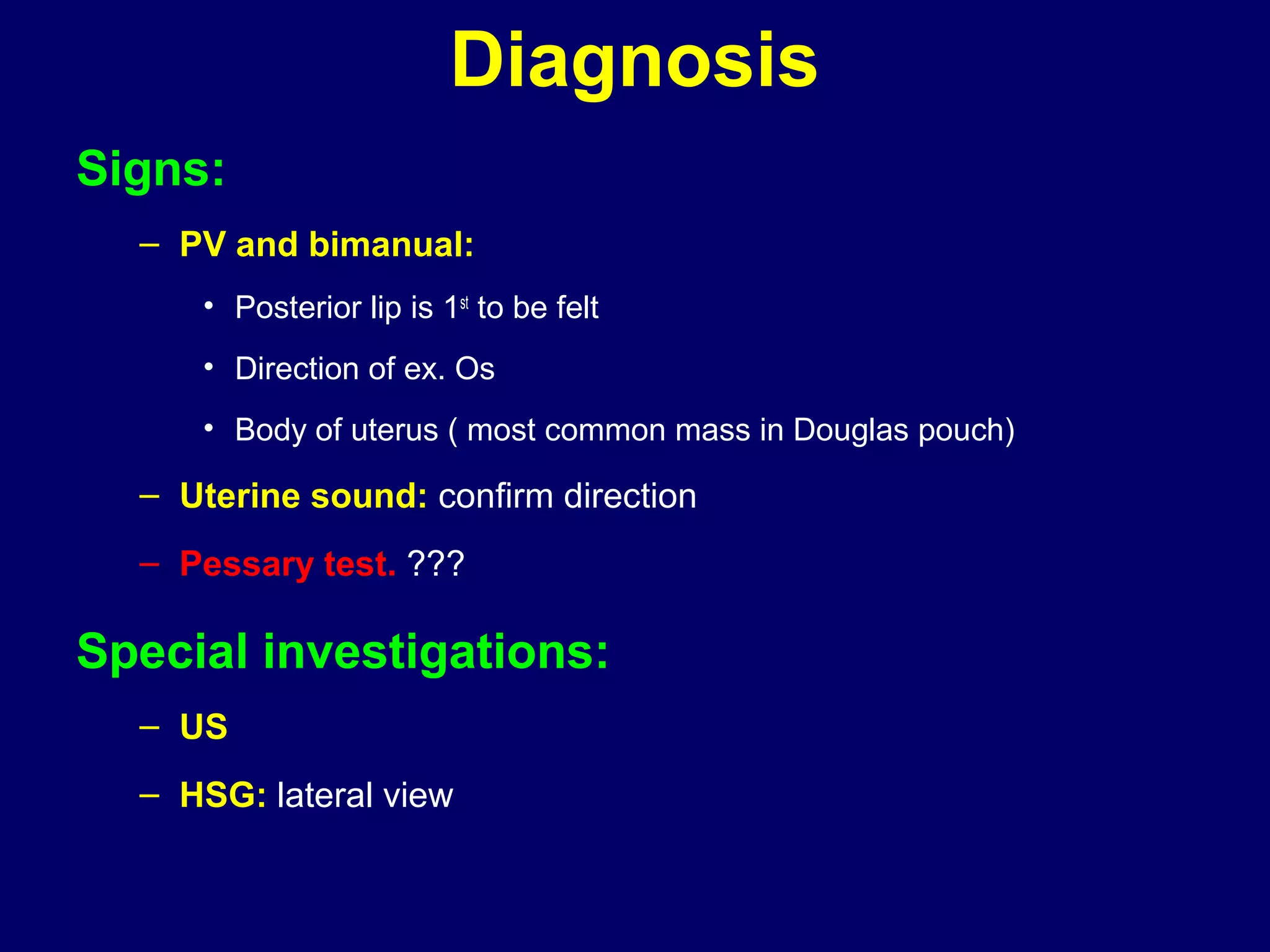
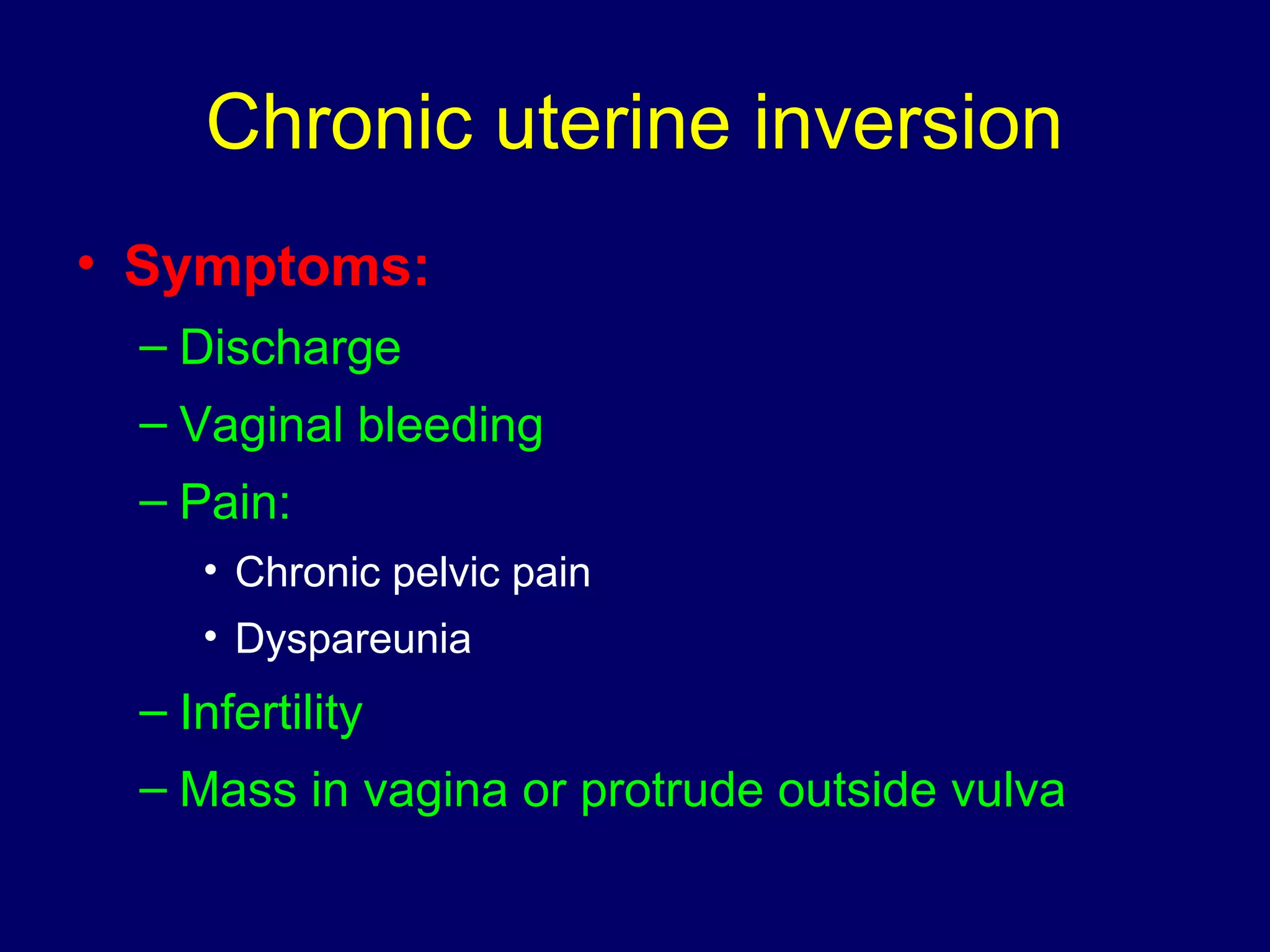
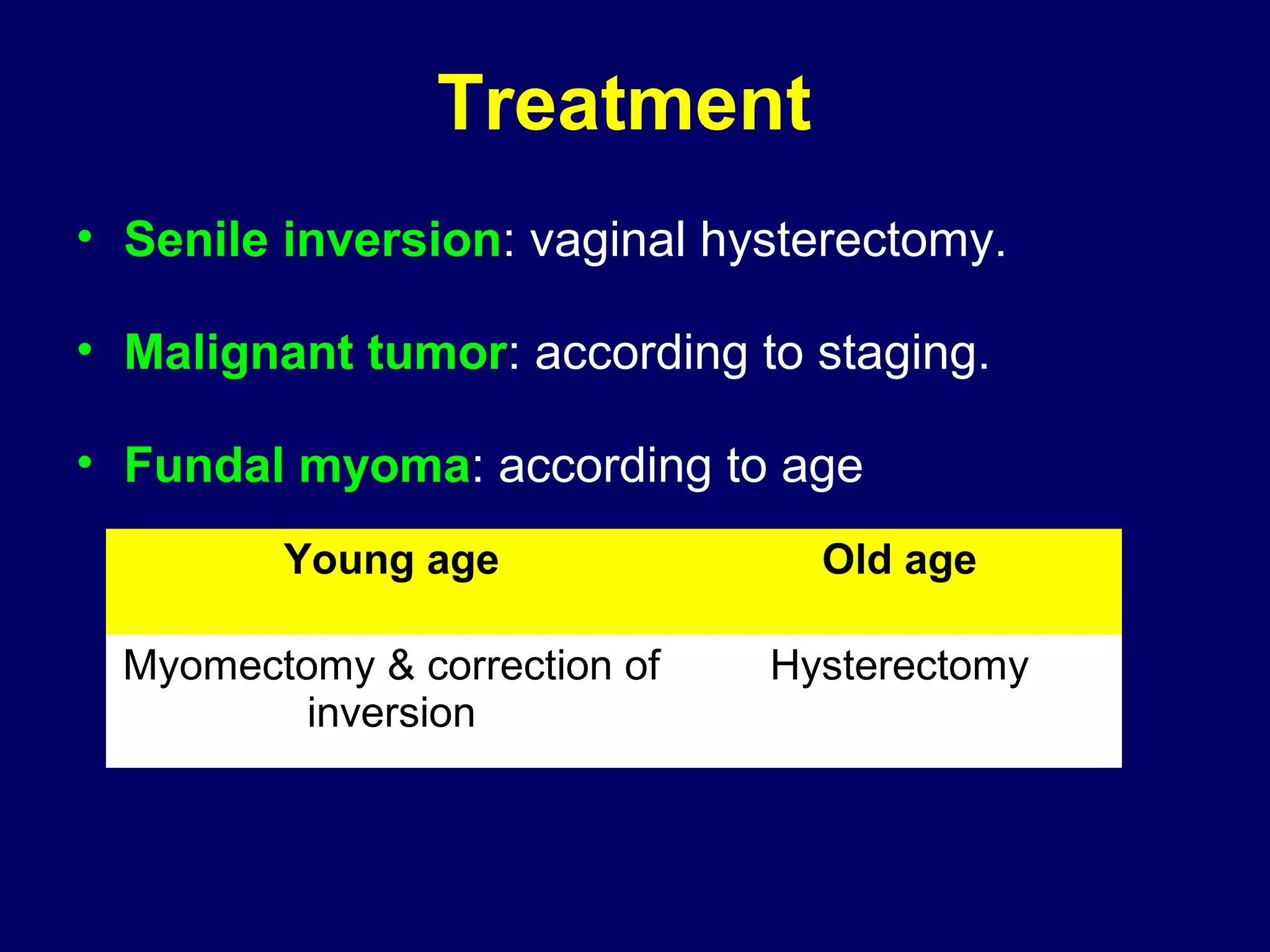
3) Diagnosis involves symptoms, signs on examination, ultrasound, and hysterosalpingography.