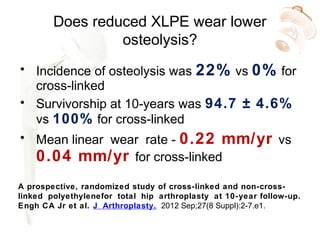
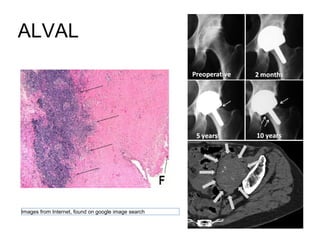
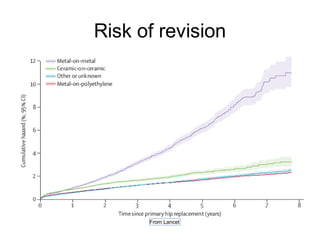
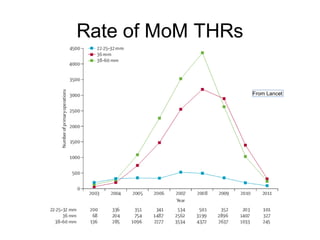
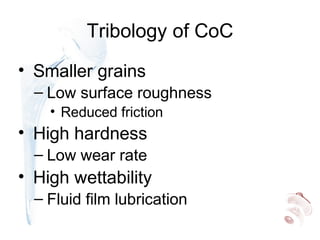
Highly cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) has been shown to reduce wear rates compared to conventional polyethylene in hip replacements. This reduced wear is associated with lower rates of osteolysis. XLPE appears compatible with large diameter heads, though thin liners may be at increased risk of early failure. Fatigue properties of XLPE are favorable though long-term data is still needed. Ceramic-on-ceramic bearings have the lowest wear rates of any bearing surface but can fracture, though modern designs have low fracture risks. Ceramic generates fewer inflammatory particles than other bearings and may have the best long-term durability without osteolysis. Metal-on-metal bearings are no longer recommended due to high revision rates