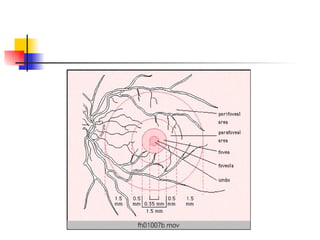
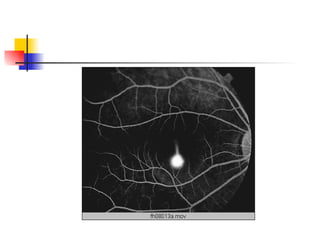
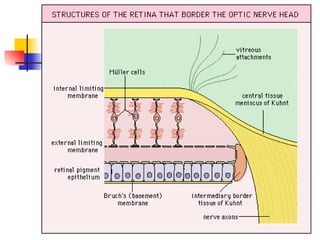
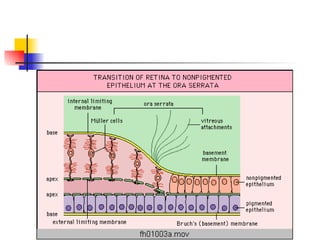
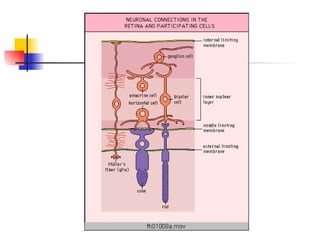
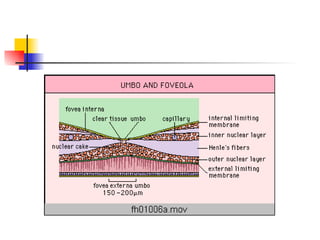
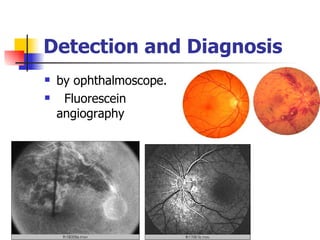
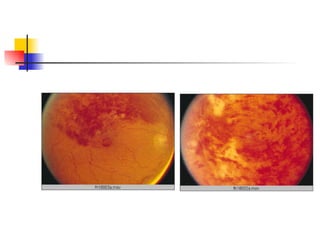
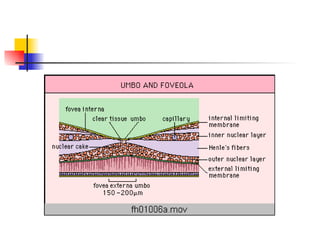
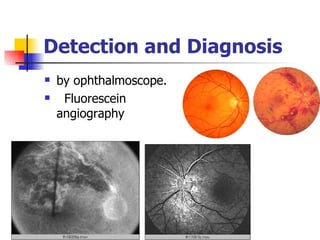
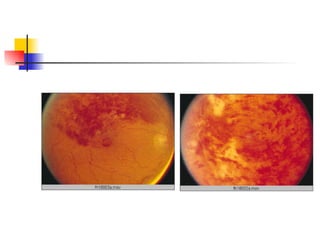
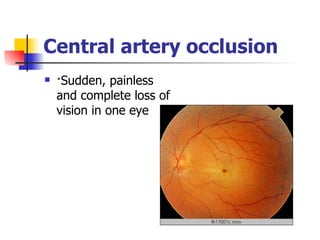
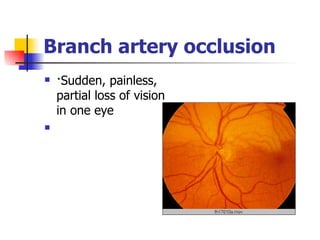
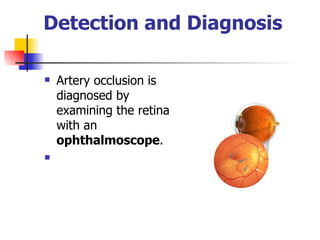
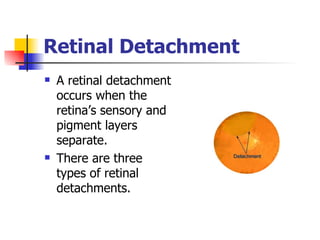
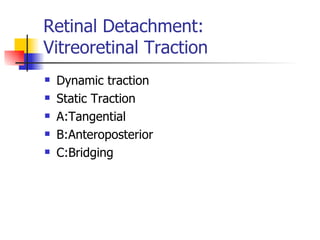
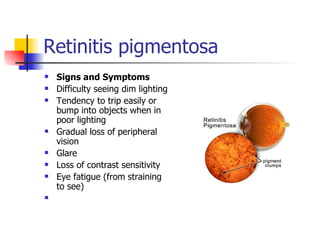
The document summarizes various retinal diseases including retinal vein occlusion, retinal artery occlusion, retinal detachment, and retinitis pigmentosa. It describes the symptoms, risk factors, detection methods, and potential treatments for each condition. The diseases can cause blurred or lost vision and are typically diagnosed via examination of the retina using an ophthalmoscope. While treatments aim to address complications, restoring full vision loss is often not possible depending on the severity and type of condition. Research continues on developing treatments and potential prosthetics to help treat retinal diseases.