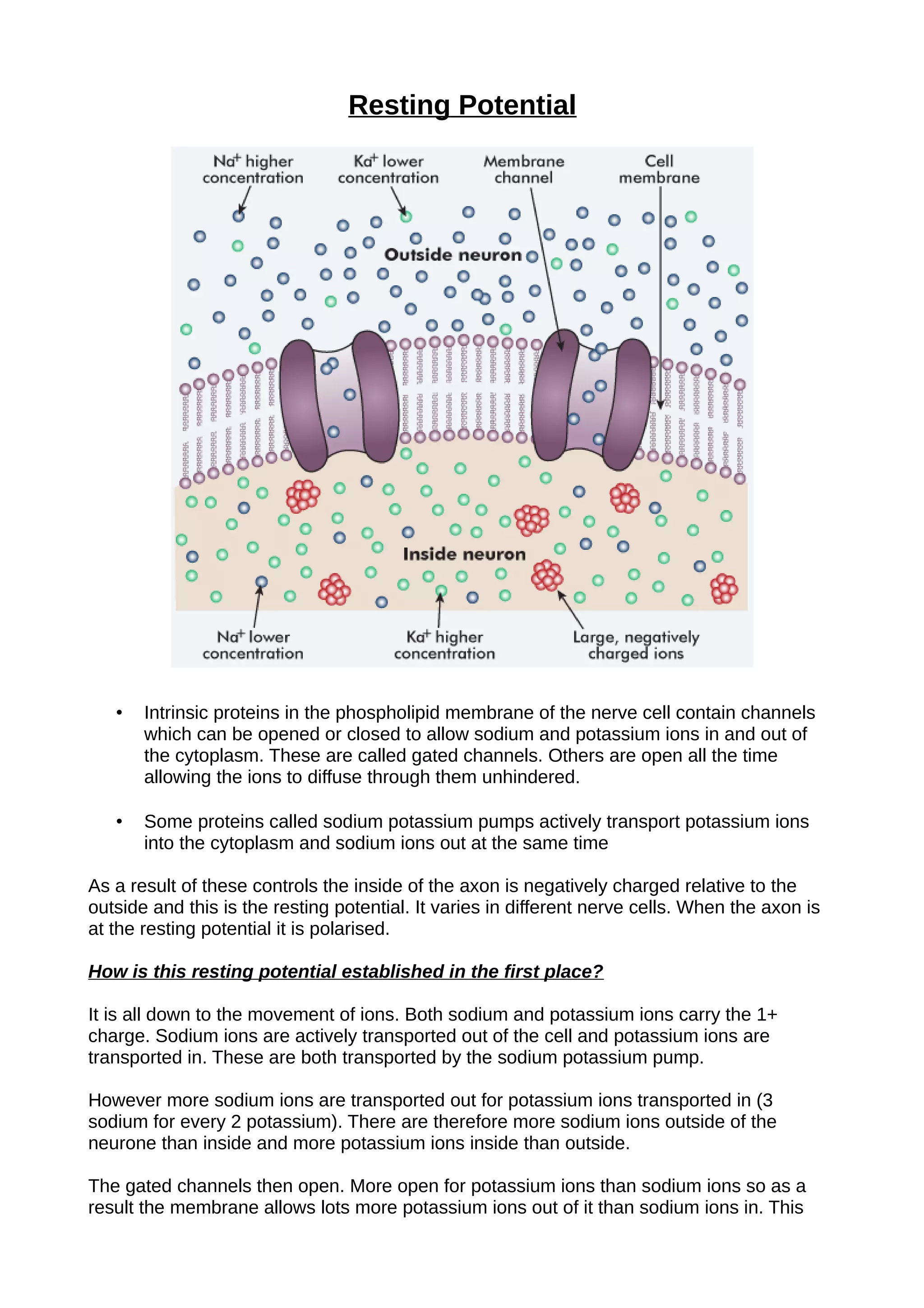
The resting potential of nerve cells is established by the movement of ions across the cell membrane. Sodium-potassium pumps actively transport sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell. More sodium ions are transported out than potassium ions transported in, making the outside of the cell more positive than the inside. Gated channels then allow more potassium ions to diffuse out of the cell than sodium ions into the cell, further increasing the charge difference between the inside and outside of the cell. This electrical gradient causes potassium ions to be attracted to the inner cytoplasm and repelled from the outer fluid, resulting in no net movement of ions and establishing the cell's resting potential.