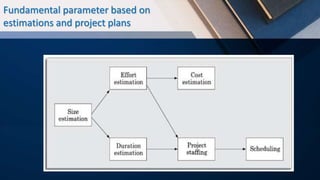
The document discusses software project management. It identifies the main goal of software project management as enabling developers to work effectively towards project completion. It also identifies several factors that contribute to the complexity of managing software projects, such as invisibility, changeability, and the intellect-intensive nature of the work. The responsibilities of a software project manager are divided into project planning and project monitoring and control. Project planning involves estimating characteristics like cost, duration, and effort and developing schedules, staffing plans, and risk management plans. The key skills for software project managers are knowledge of project management techniques, decision-making capabilities, and experience managing similar projects.