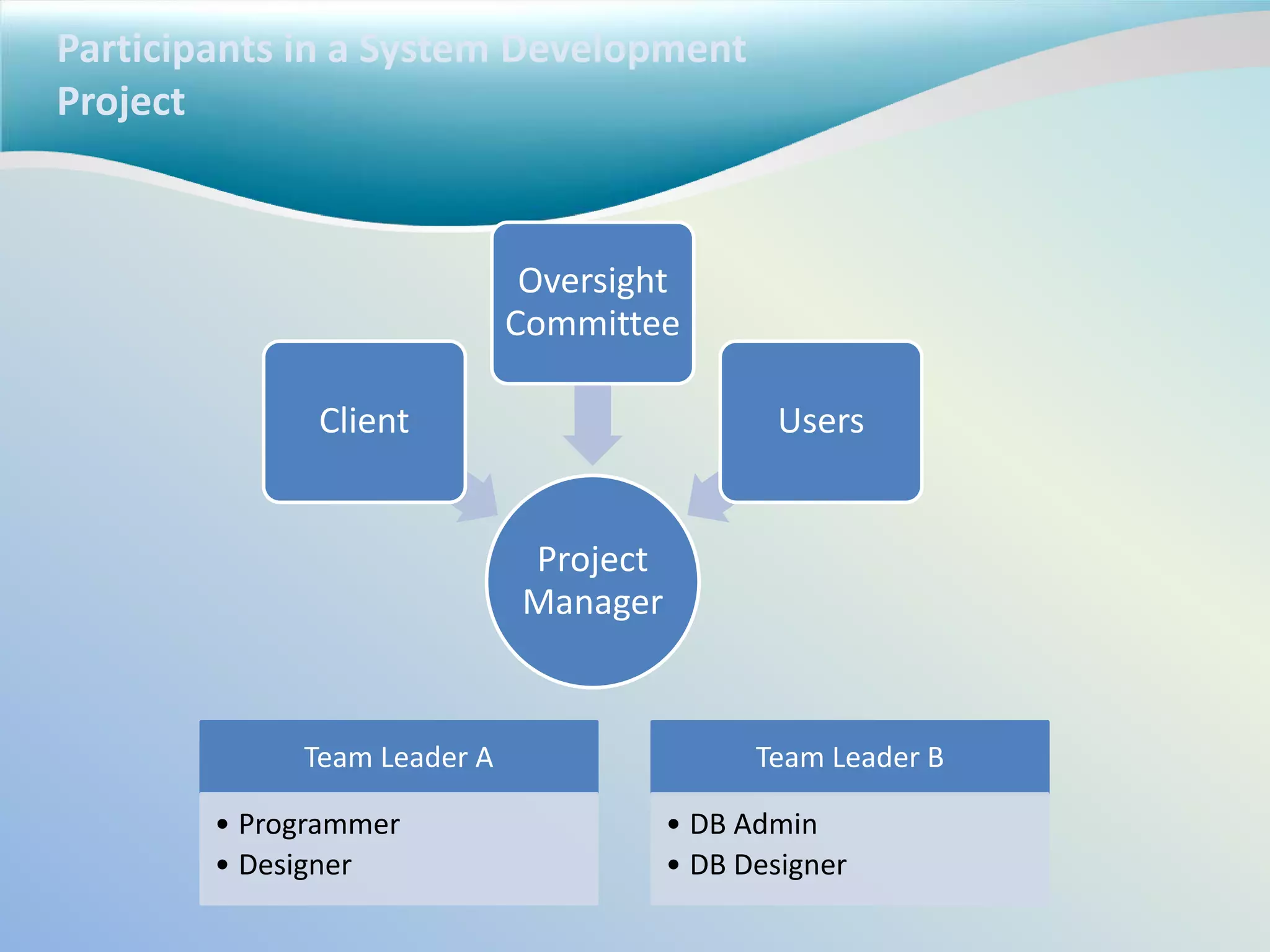
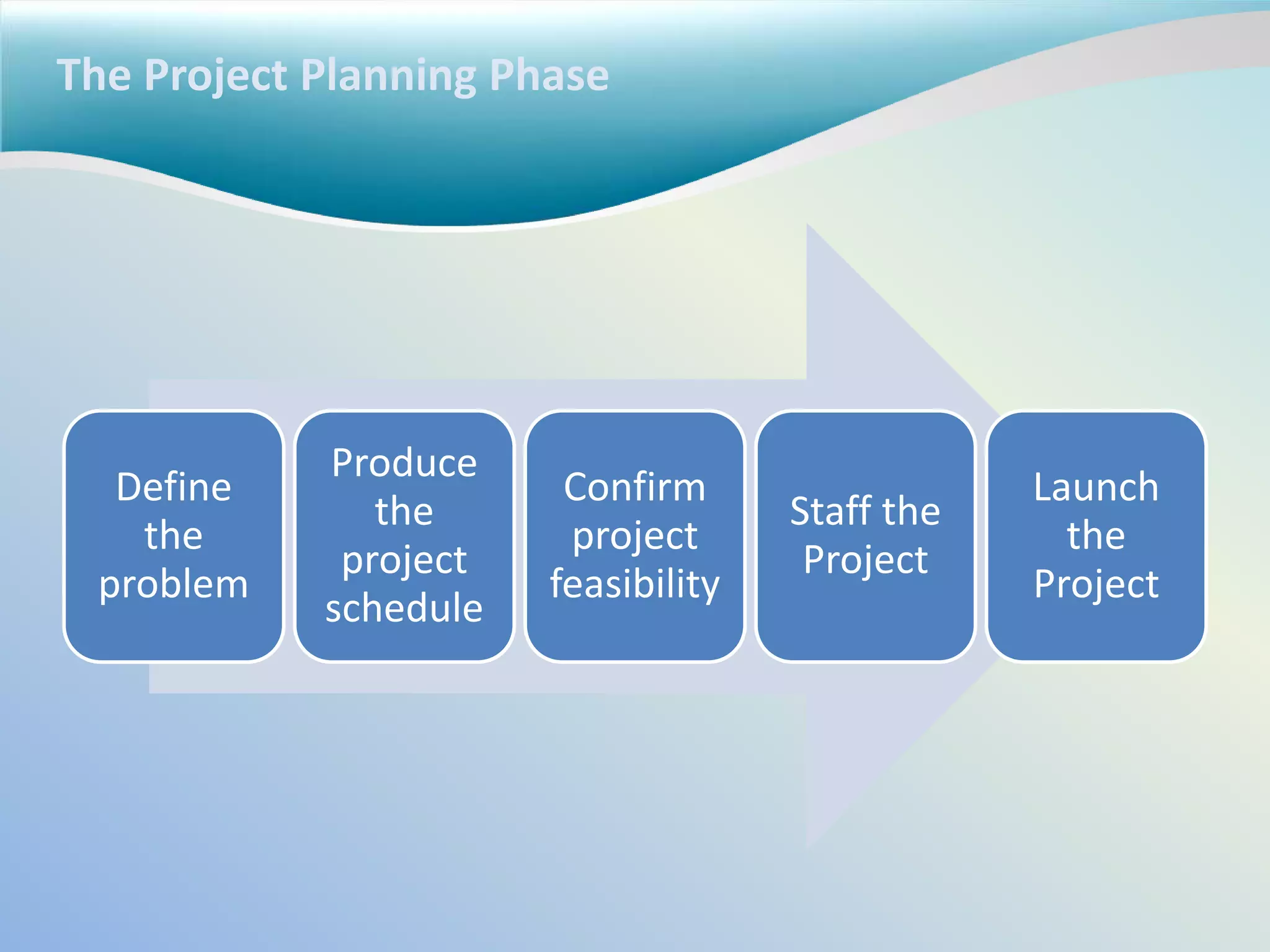
The document discusses reasons why IT projects fail and succeed. It fails due to incomplete requirements, lack of user involvement, poor planning and unclear objectives. It succeeds with clear requirements, user involvement, management support, thorough planning and realistic schedules. The role of the project manager is to organize tasks, develop schedules, assign team members, monitor progress and quality, and report status. Project planning involves defining problems, scheduling tasks, confirming feasibility through risk assessment and cost/benefit analysis.