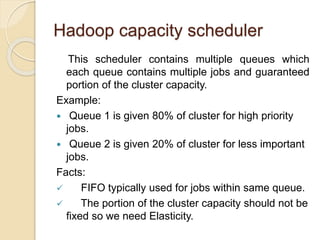
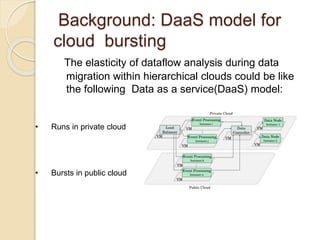
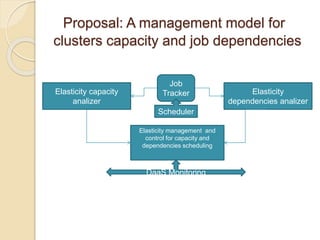
The document discusses resource scheduling techniques for cloud computing including single processor scheduling algorithms, cloud scheduling approaches for multi-tenant systems like the Dominant Resource Fairness scheduler, and Hadoop schedulers like the fair scheduler and capacity scheduler. It also proposes a management model for analyzing elasticity of cluster capacity and job dependencies to enable data bursting between private and public clouds.