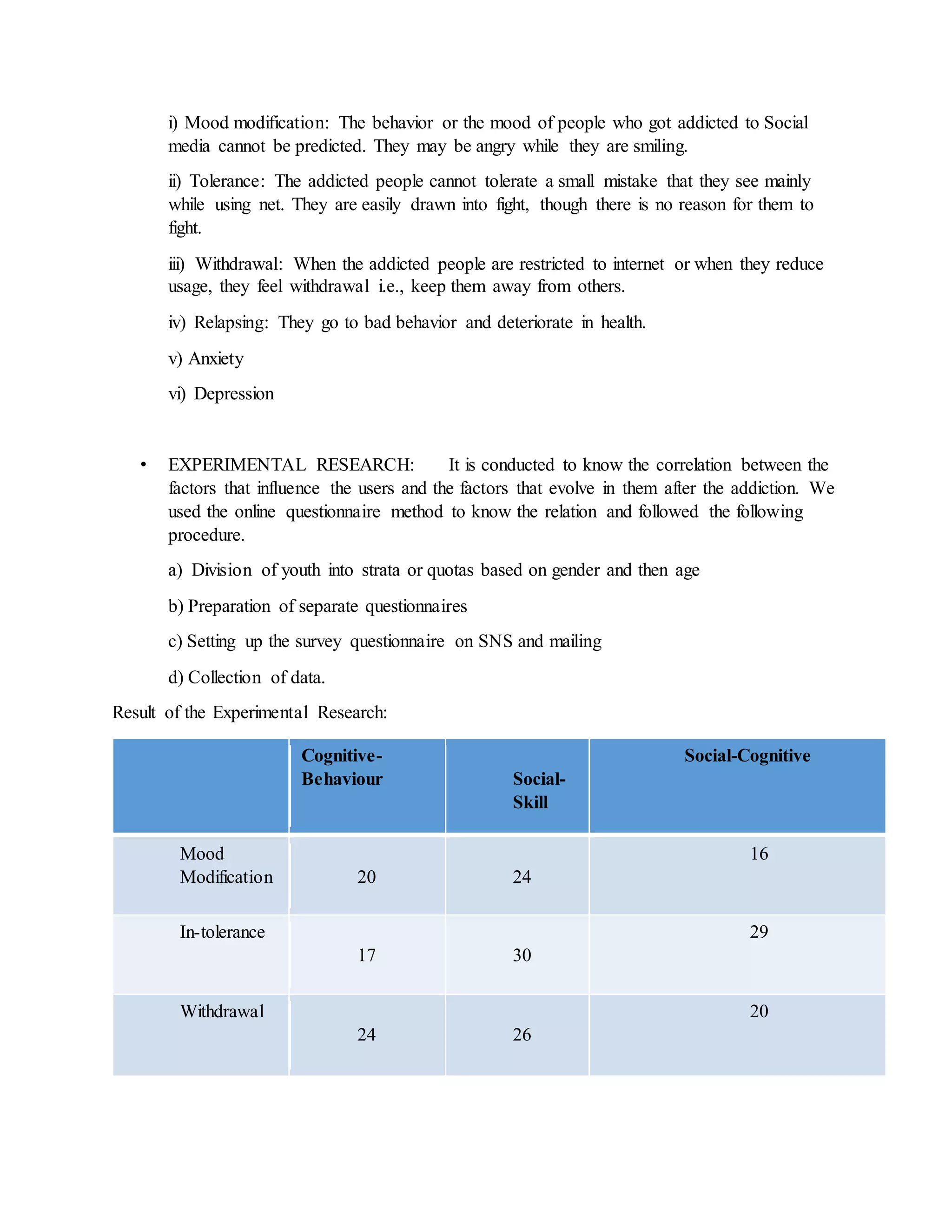
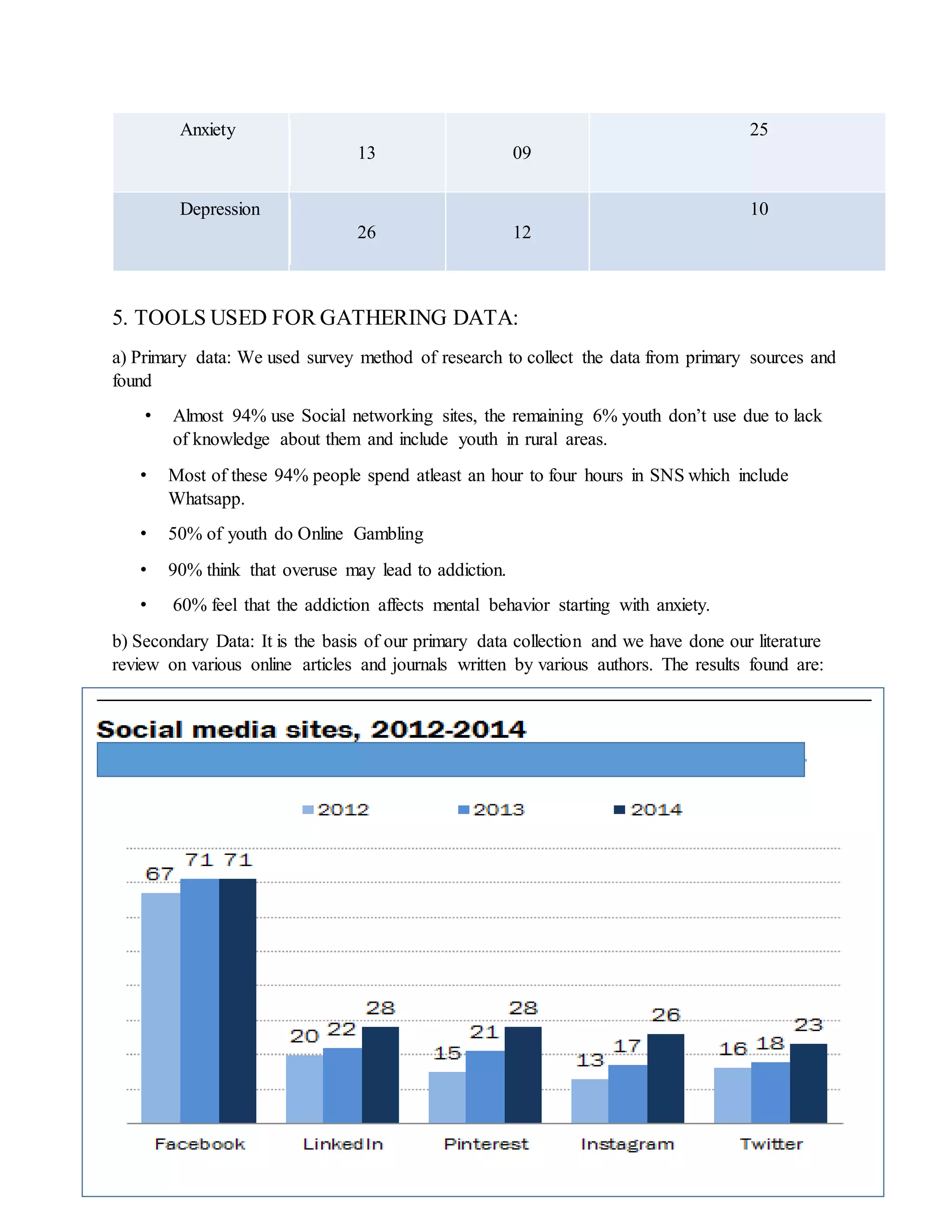
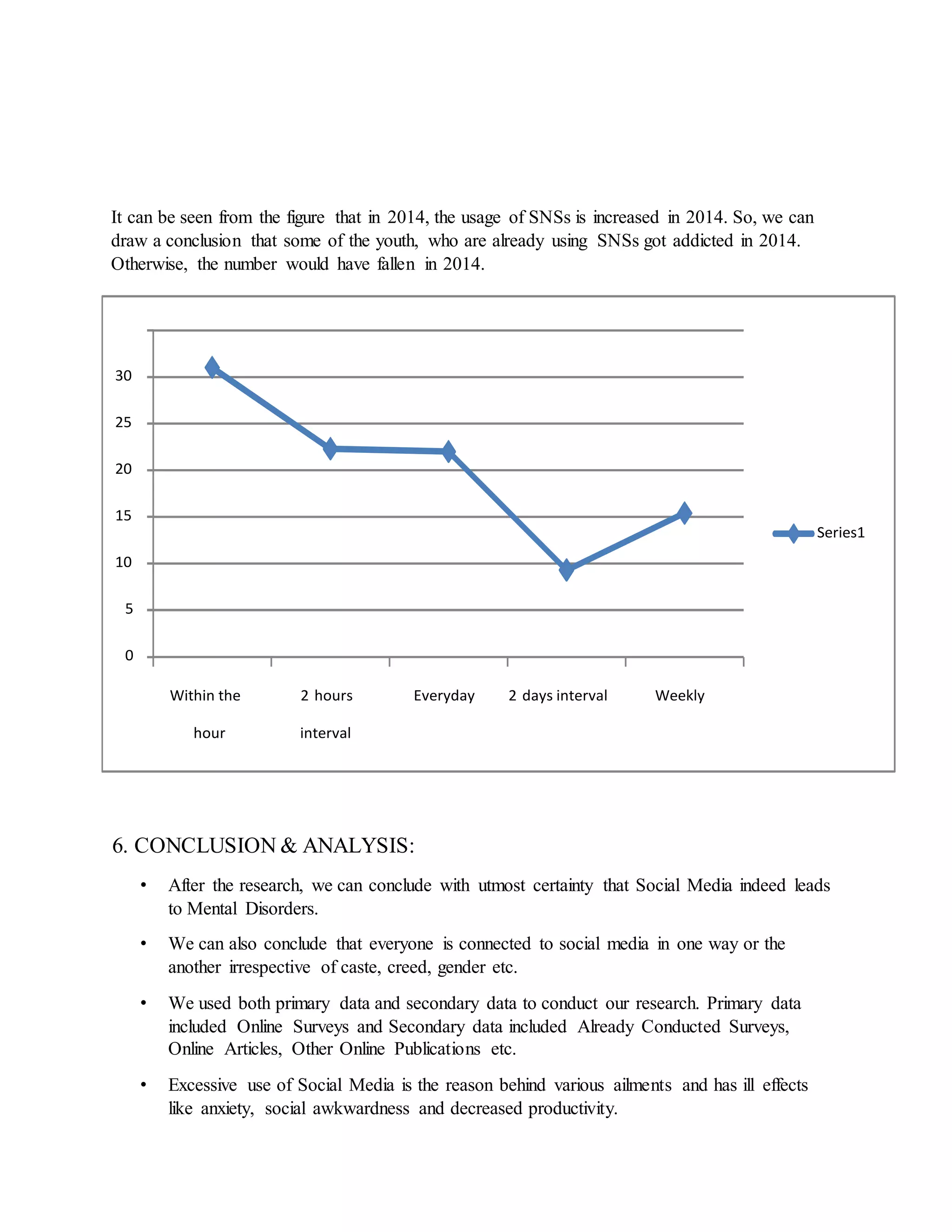
This document explores the relationship between excessive use of social networking sites (SNSs) and the development of addictive behaviors and mental health issues among youth, particularly focusing on Bangalore. Findings suggest that excessive SNS usage is linked to various negative outcomes, including anxiety, decreased academic performance, and social awkwardness, with personality traits such as low conscientiousness and high narcissism correlating to higher usage. The research concludes that while social media aims to foster connectivity, its overuse poses significant risks to mental well-being and productivity.