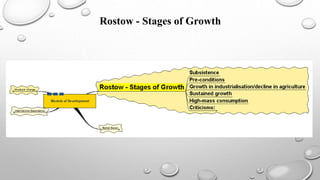
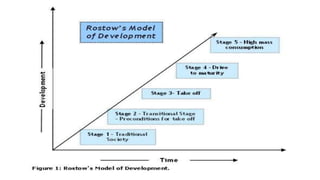
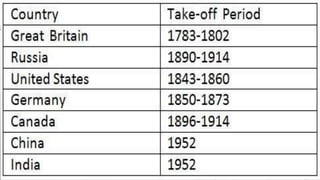
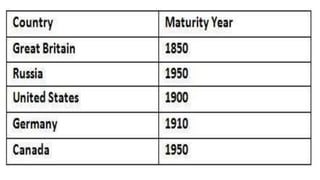
Rostow's stages of economic growth model outlines 5 stages of development:
1. Traditional society dominated by subsistence agriculture.
2. Preconditions for take-off with emerging infrastructure and trade.
3. Take-off stage where industrialization increases and workers move to manufacturing.
4. Drive to maturity where the economy diversifies and innovation increases.
5. Age of mass consumption where the economy focuses on mass production for consumers.