Nursing research is important to develop the scientific foundation of clinical practice and provide evidence-based care. The scientific method involves asking questions, conducting background research, developing hypotheses, experimentation, analysis of data, and communication of results. Nursing research helps build standards of care, scientific knowledge, and high quality evidence-based practice. Identifying a clear research problem is the first step in the scientific research process.
![Defination [1].Research is define as systematic and scientific process
to answer the question about fact and relationship .
[2]. Meaning of Research Research is defined as the scientific
investigation of phenomena which includes collection, presentation,
analysis and interpretation of facts that lines an individual’s
speculation with reality.
Nursing research
Nursing research develops knowledge to:
Build the scientific foundation for clinical practice
Prevent disease and disability
Manage and eliminate symptom caused by illness
Enhance end-of-life and palliative care
Need of nursing research
Development a good standered of nursing care
Developed a scientific knowledge
Provide evidance based nursing care](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/research-140203065621-phpapp01/85/Research-notes-B-sc-nursing-4rth-year-919887888167-1-320.jpg)
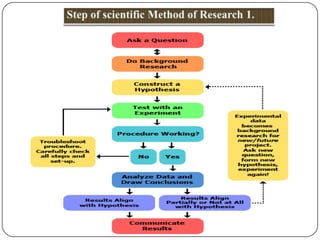

![Do Background Research: Rather than starting from scratch
in putting together a plan for answering question,want to
be a sarvy scientist using library and Internet research to
help find the best way to do things and insure that don't
repeat mistakes from the past.
Construct a Hypothesis: A hypothesis is an educated guess
about how things work:
"If _____[I do this] _____, then _____[this]_____ will
happen." must state hypothesis in a way that can easily
measure, and of course, hypothesis should be constructed in
a way to help answer , original question.
Test Hypothesis by Doing an Experiment: experiment tests
whether hypothesis is supported or not. It is important for
experiment to be a fair test.conduct a fair test by making
sure that change only one factor at a time while keeping all
other conditions the same.repeat experiments several times
to make sure that the first results weren't just an accident.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/research-140203065621-phpapp01/85/Research-notes-B-sc-nursing-4rth-year-919887888167-4-320.jpg)








