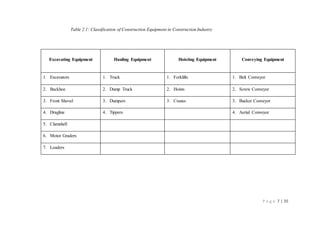
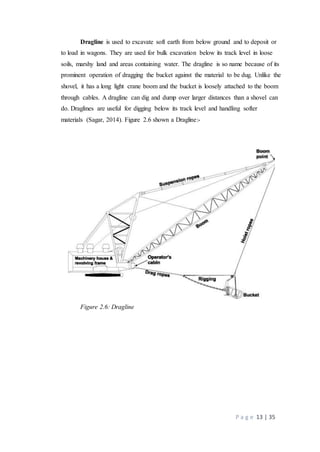
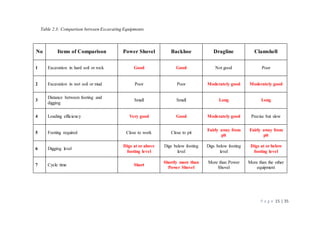
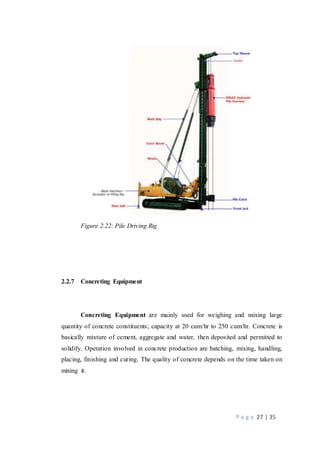
The document provides information about machinery used in the construction industry. It discusses different types of excavating equipment like excavators, backhoes, front shovels, draglines, and clamshells. It also discusses hauling equipment like trucks, dump trucks, and tippers. Hoisting equipment discussed includes forklifts, hoists, and cranes. The roles and uses of this machinery in construction processes are described over multiple pages. Tables and figures are provided to classify and illustrate the different types of equipment.