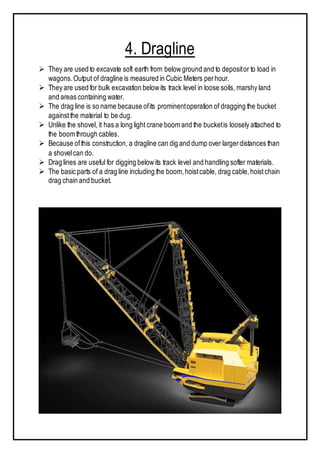
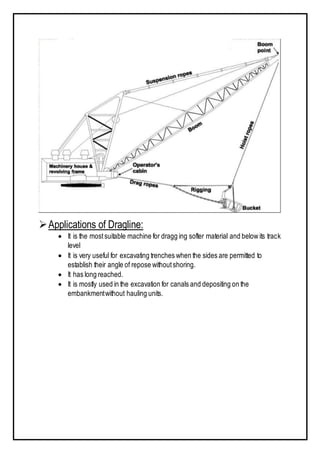
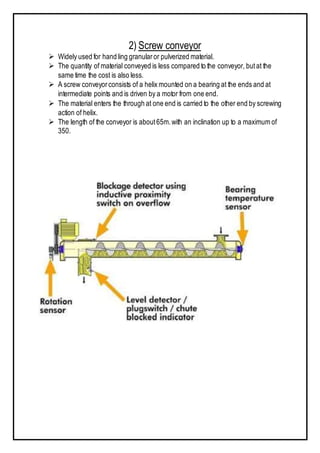
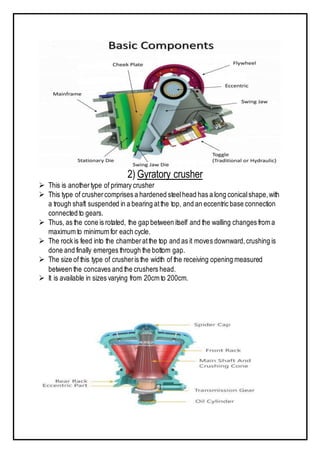
The document discusses various types of equipment used in construction projects. It describes earth-moving equipment such as excavators, backhoes, front shovels, draglines, clamshell buckets, and bulldozers. Excavators are used for digging trenches, holes and foundations. Backhoes are commonly used to dig holes and trenches. Front shovels are mounted on tracks and used for digging and loading earth or rock. Draglines excavate soft earth below ground level, while clamshell buckets lift material vertically. Bulldozers push large quantities of soil and rubble. The document provides details on the uses and applications of these important pieces of heavy construction equipment.