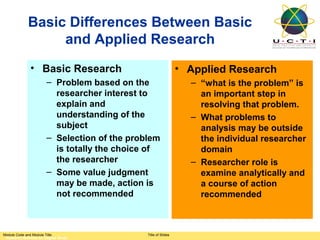
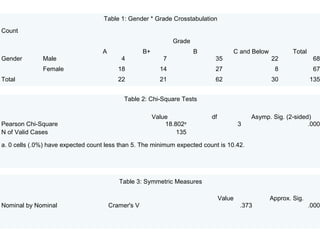
Based on the tables provided, here is a summary of the key findings:
1. A chi-square test of independence found a significant association between gender and grade (p < 0.01).
2. Most male students (83.9%) received grades of B or lower, while most female students (88.1%) received grades of A or B+.
3. This suggests that female students generally performed better than male students.
4. The Cramer's V value of 0.373 indicates a moderate strength of association between gender and grade.
In summary, the results show that gender is significantly related to grade, with female students tending to achieve higher grades.

















![Answer
1. A chi-square test of independence was conducted to assess
whether the grade received by students (A, B+, B, C and
below) is related to their gender (male and female)
2. The finding of crosstabs analysis for grade and gender was
found to be correlated or related [Pearson χ2 (3, N = 135) =
18.802, p≤ 0.01]
3. A close inspection of Table 1 for pattern of relationship
reveals that the majority (83.9%) of the male students
obtained grades between “B” to “C and below”, while the
majority (88.1%) of female students obtained grade between
A to B
4. This suggests that, in general, the female students
performed better in the test compared to male
5. The Cramer’s V value obtained (V = 0.373) indicates that
the strength or magnitude relationship between grade and
gender is at moderate level](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/researchmethodfinal-121031030614-phpapp01/85/Research-method-final-25-320.jpg)
