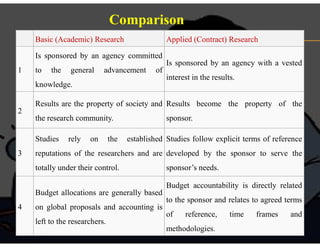
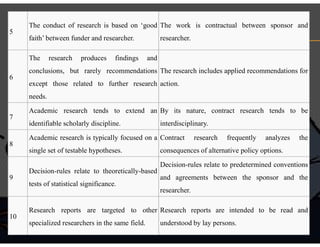
This document defines research and discusses the key differences between basic (academic) research and applied (contract) research. It provides Creswell's definition of research as a process using steps to collect and analyze information to increase understanding of a topic. It also outlines 10 aspects of educational research by Gray Anderson, including using research to solve problems, gather new data, develop generalizations, and carefully record and report findings. The document then explains that basic research, also called pure or fundamental research, focuses on discovering truth or developing theories without practical goals in mind. Applied research deals with solving real-world problems and testing theories. Key differences between basic and applied research are discussed, such as ownership of results and focus on layperson versus specialized