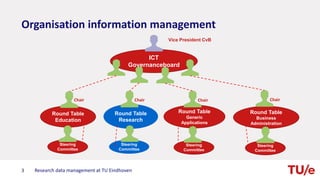
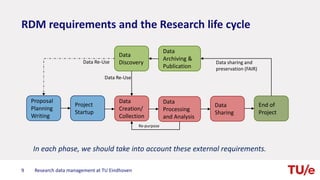
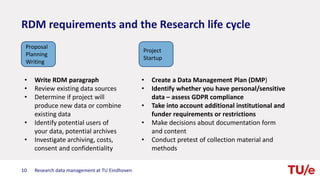
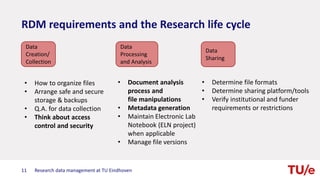
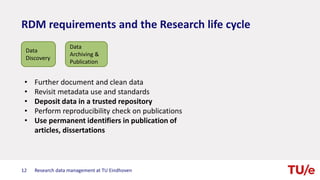
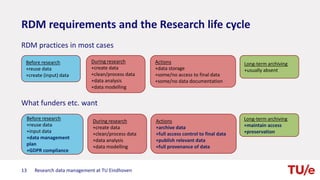
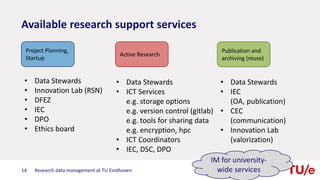
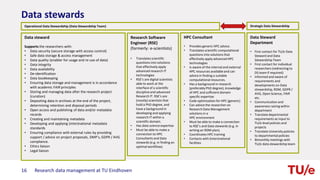
The document discusses research data management at TU Eindhoven. It outlines the long process of developing RDM practices since 2008. It describes the current organization and governance structure for RDM. Key external requirements for RDM from funders, regulations, and integrity standards are also summarized. The document concludes by outlining RDM support services available and the benefits of good RDM practices.