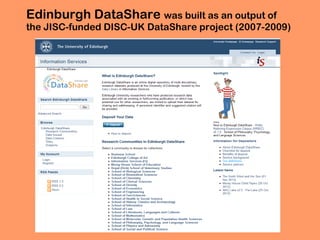
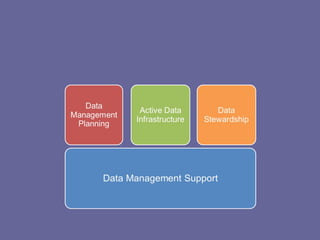
The document summarizes the activities of EDINA and the Data Library at the University of Edinburgh related to research data management. It describes EDINA as a national data center that provides online resources for education and research. The Data Library assists university researchers with discovering, accessing, using and managing research datasets. It also outlines several projects the Data Library is involved in to develop training, policies and services to support best practices in research data management according to funder requirements. This includes developing an institutional research data management roadmap to help the university meet funder expectations by 2015.