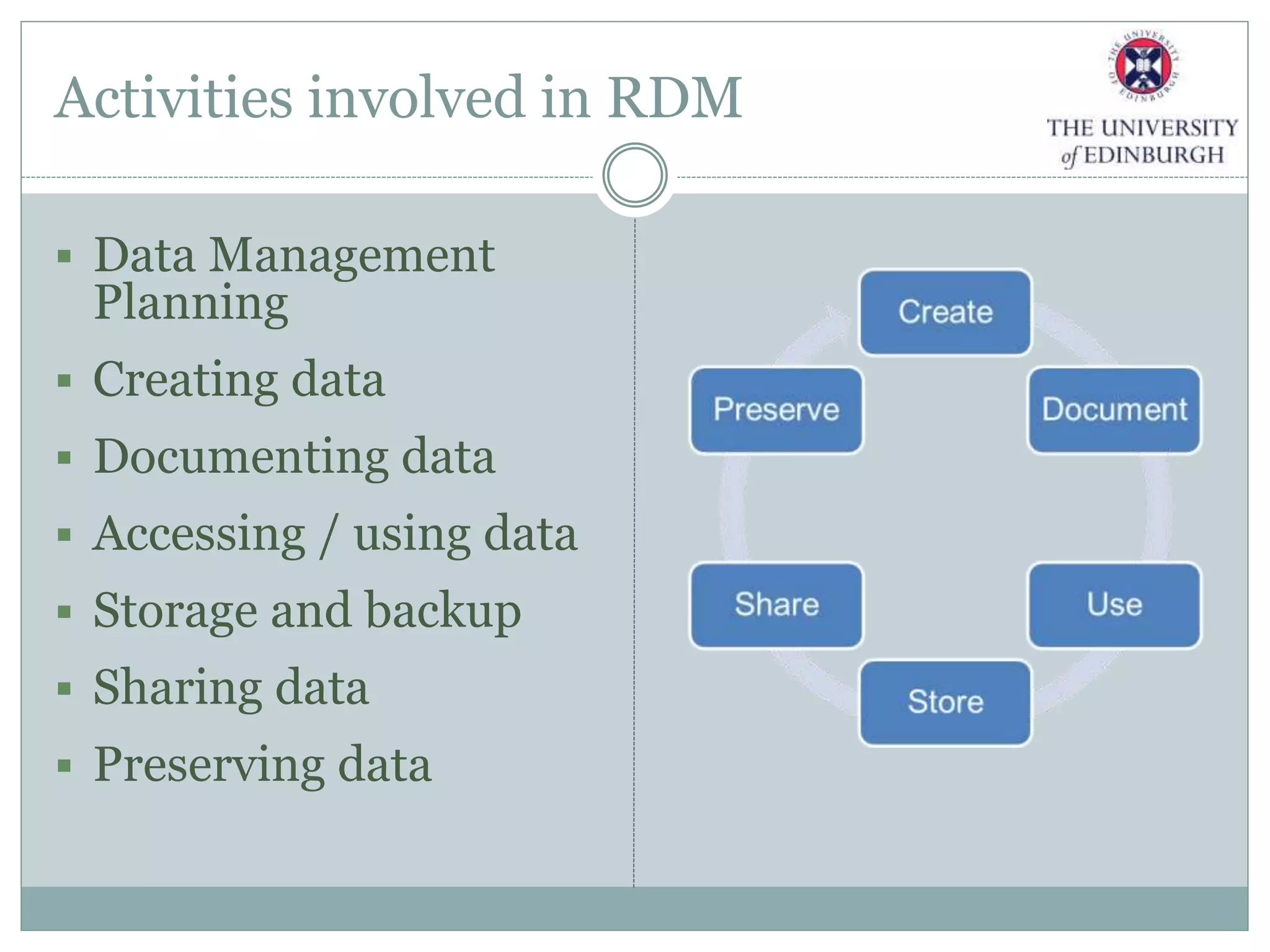
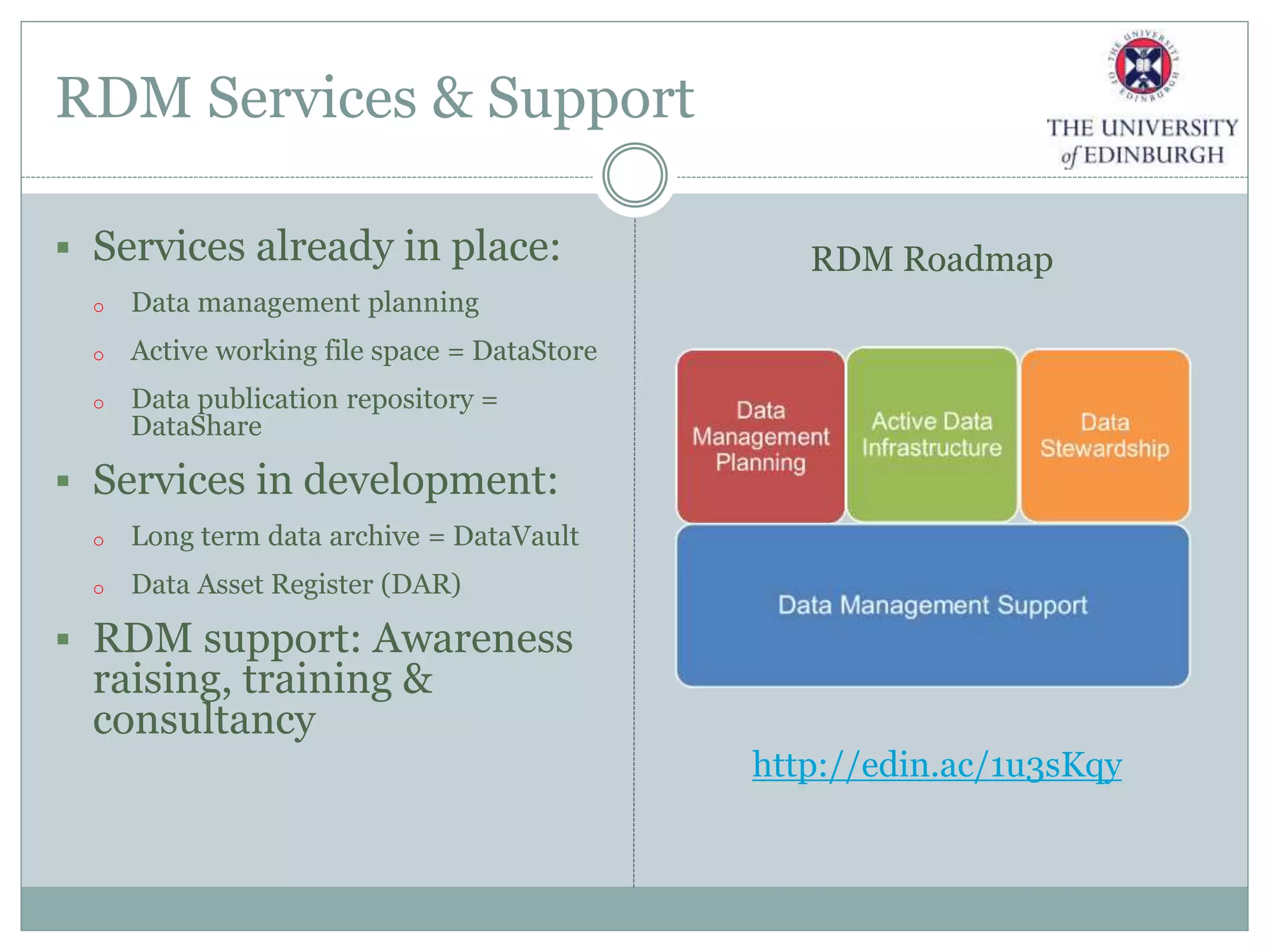
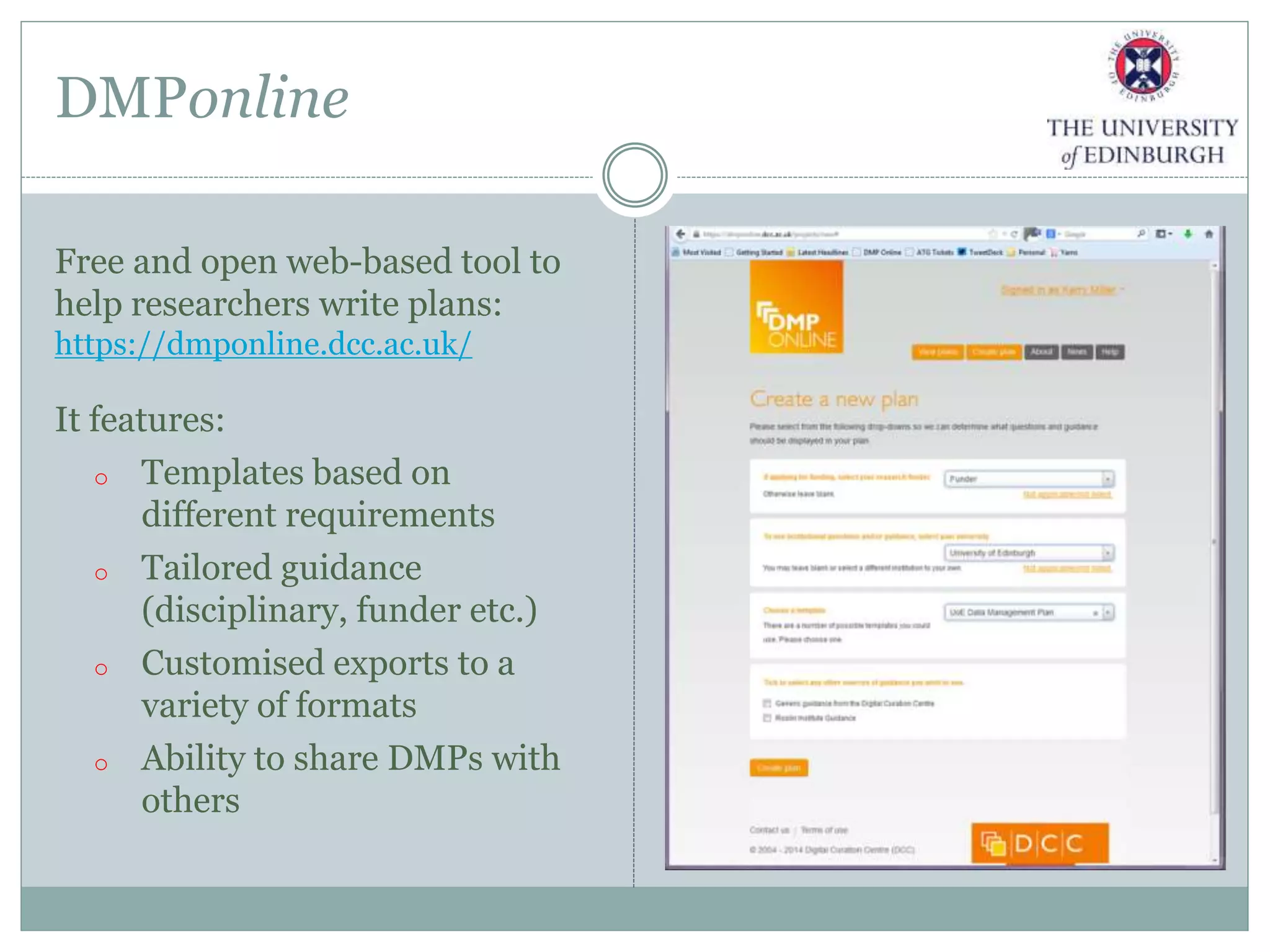
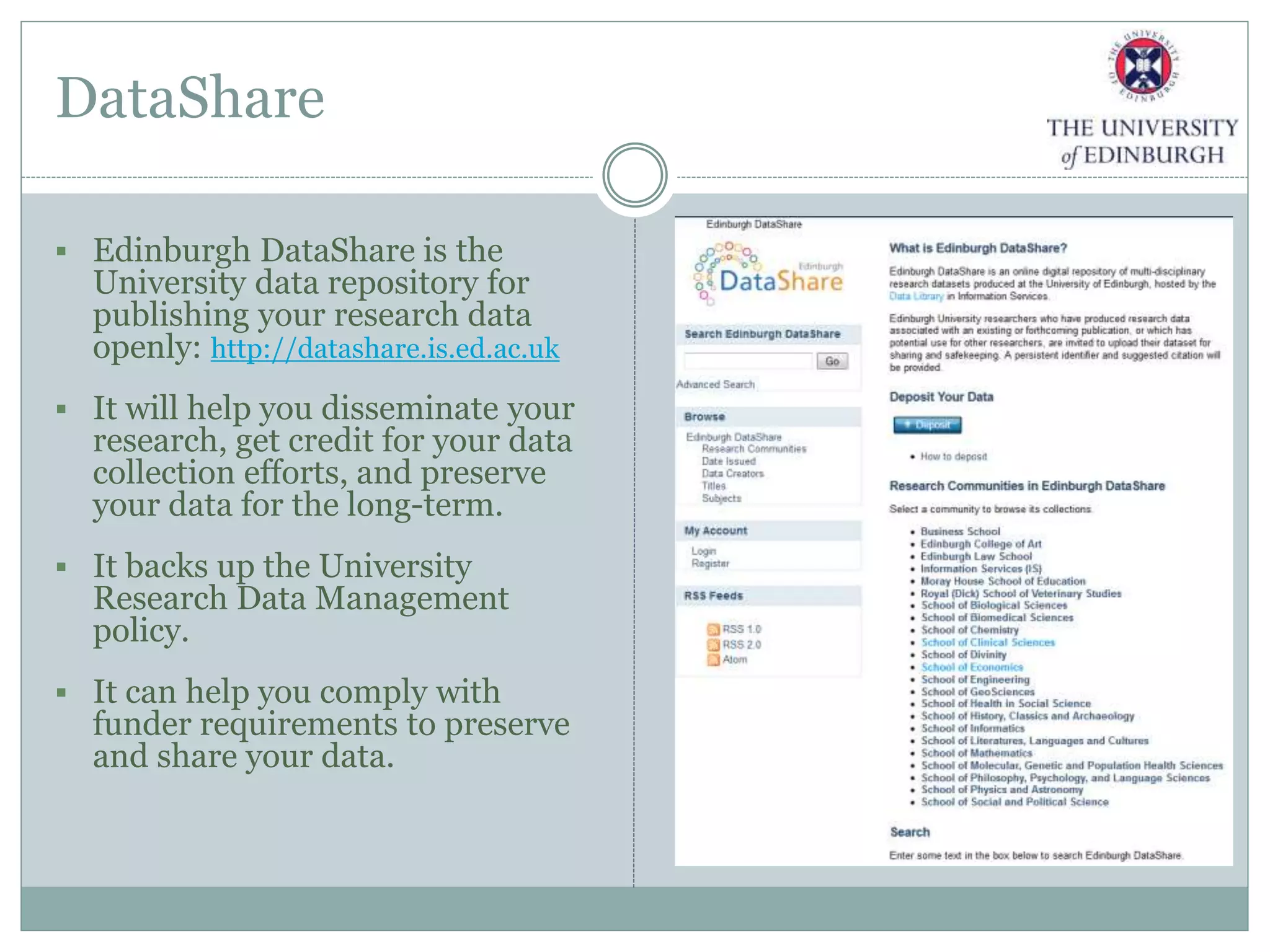
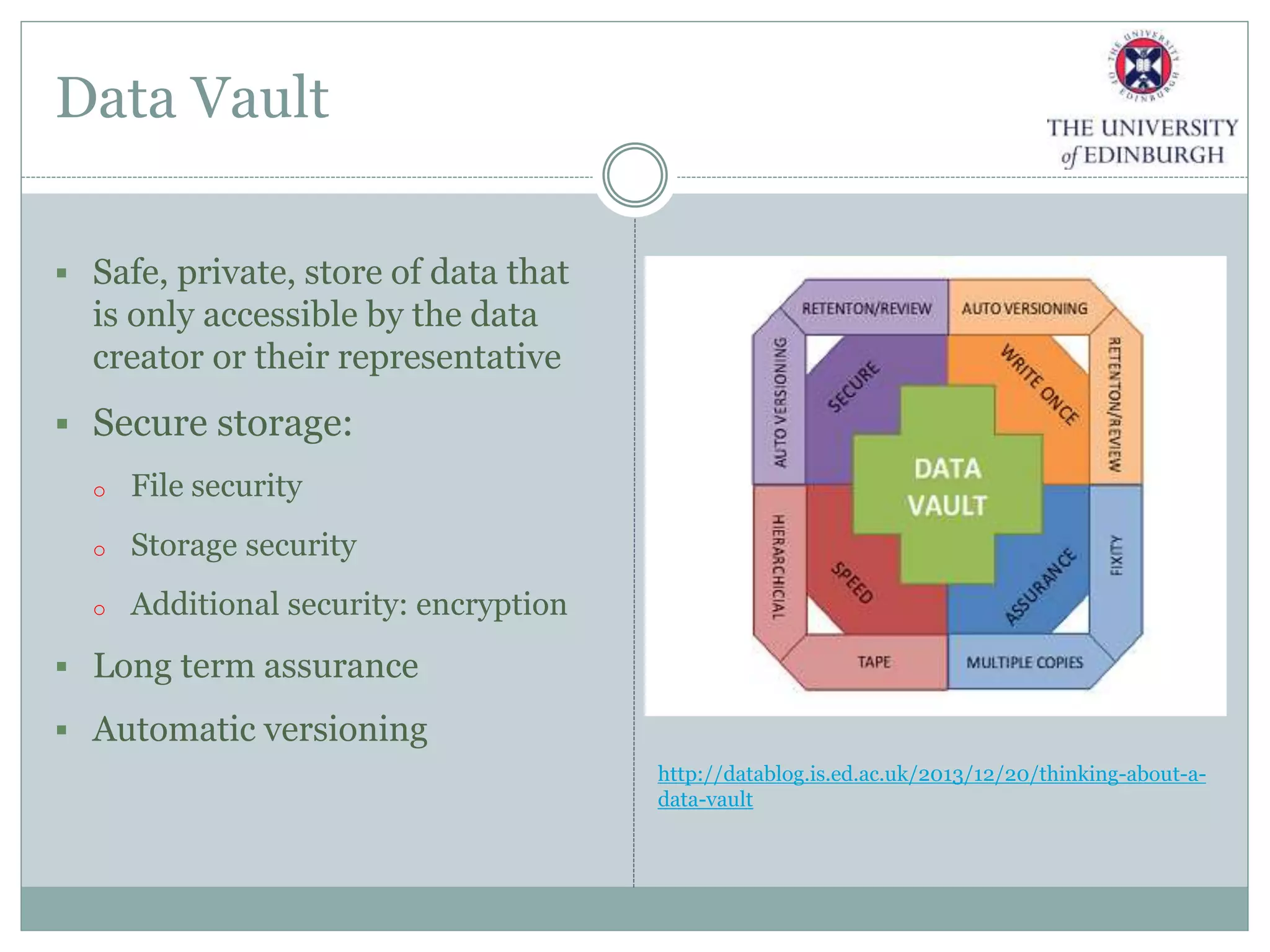
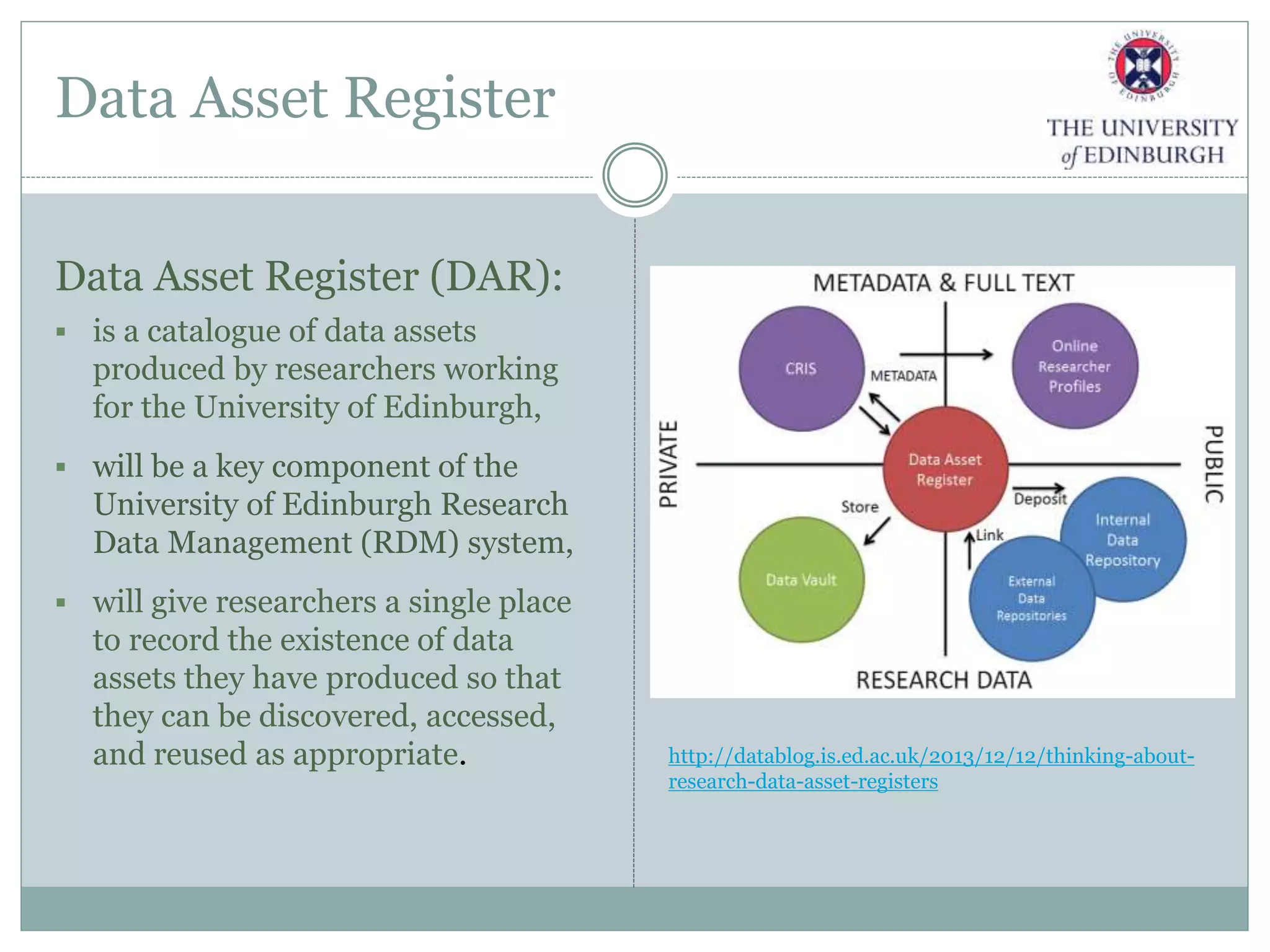
The University of Edinburgh has implemented a comprehensive research data management (RDM) policy aimed at caring for, preserving, and providing access to research data throughout its lifecycle. Services like data management planning, data sharing, and a long-term data archive are being developed to support researchers, while training programs are in place to promote adherence to good research practices. The initiative also includes tools and resources like a data repository and a data asset register to facilitate data management and compliance with funder requirements.