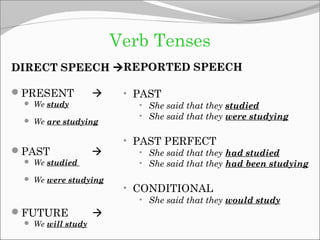
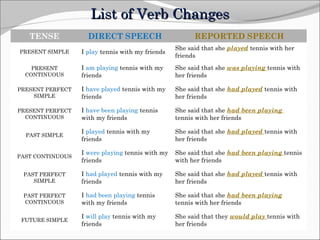
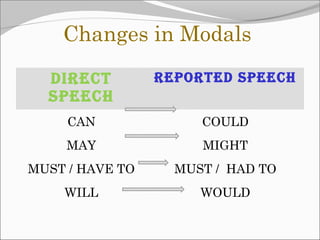
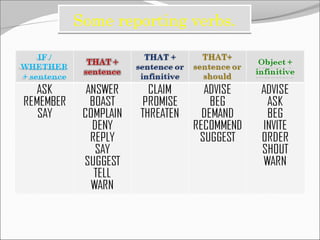
The document discusses reported (indirect) speech and the changes that are made when reporting what someone said. It provides examples of direct quotes and how they are changed in reported speech by altering verb tenses, pronouns, time/place expressions, and question/command structures. The key changes that occur in reported speech include changing present tenses to past tenses, changing pronouns, and adjusting time/place adverbials. Various reporting verbs are also discussed that can be used to introduce reported statements, questions, suggestions, promises and threats.