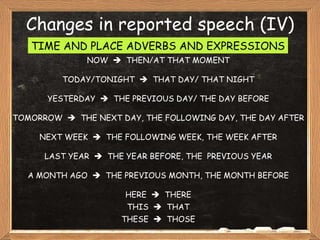
This document provides an overview of how to change direct speech into reported or indirect speech. It discusses how to change verb tenses, pronouns, time and place expressions, and other elements when moving from direct to reported speech. Reporting verbs are categorized based on whether they are reporting statements, questions, commands, suggestions, or advice. Verb tense changes and exceptions are also outlined.