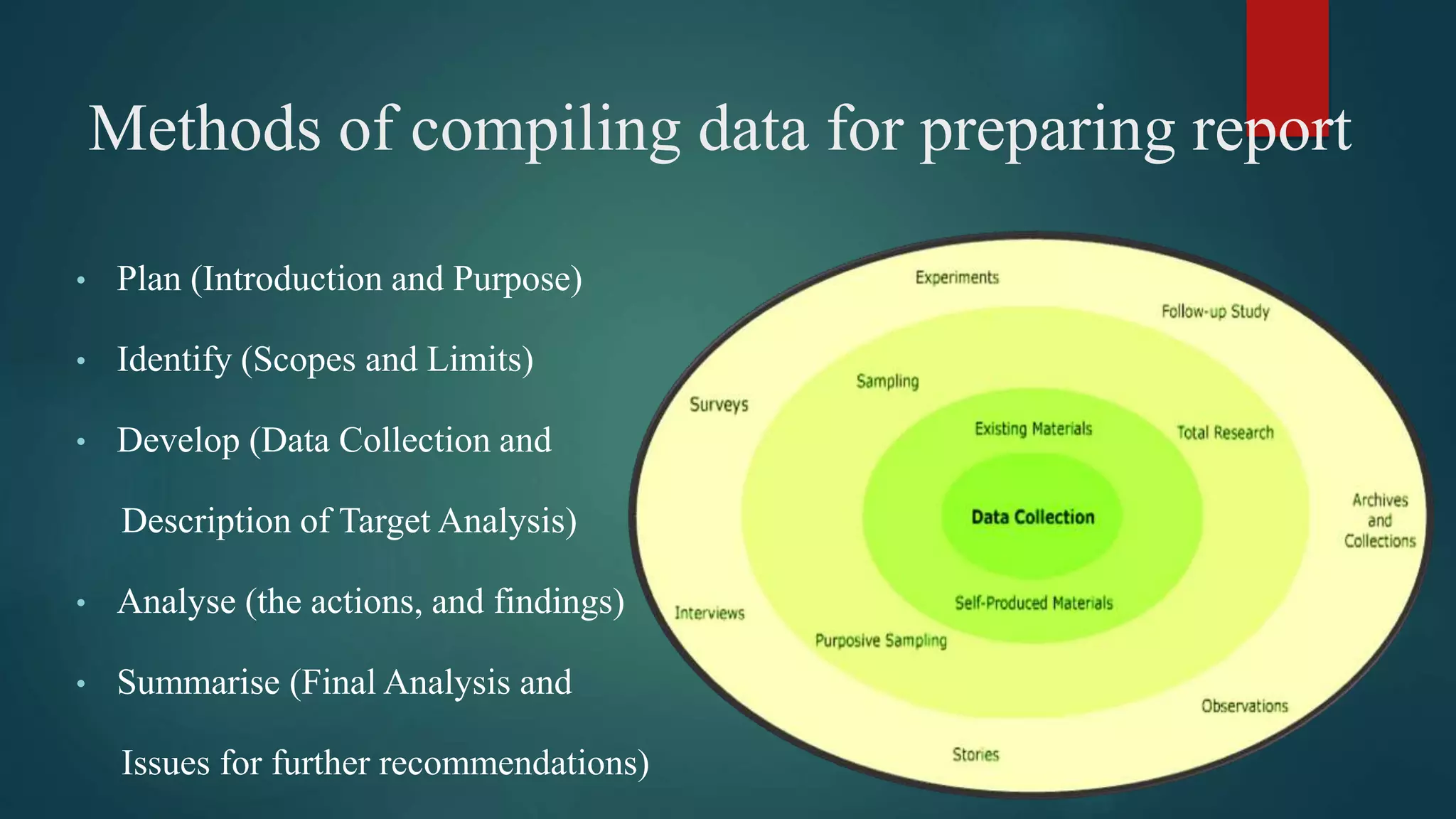
This document discusses various aspects of report writing, including definitions, qualities, types, formats, and methods of compiling data. It defines a report as an official document providing an account of information gathered from investigation or consideration. Reports have qualities of clarity, completeness, conciseness, compactness, correctness, and concreteness. The main types of reports are research reports, business reports, scientific reports, routine reports, and investigation reports. Common report formats include memo reports, letter reports, and project reports. Memo reports are used for internal communication, while letter reports are for external use. Project reports follow a detailed format with sections for introductions, descriptions, conclusions, and recommendations. The document also outlines methods for compiling data which include