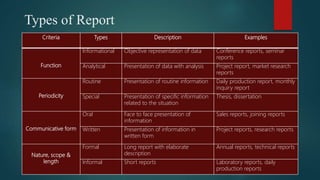
This document provides an overview of report writing, including the concept, objectives, characteristics, types, formats, and structure of reports. It defines a report as a factual account of a specific business or professional activity that aims to present data, record events, describe problems and solutions, and analyze situations. The document outlines the key characteristics of reports as being precise, factual, relevant, reader-oriented, clear, compact, and concrete. It also categorizes reports based on their function, periodicity, communicative form, nature, scope, and length. Finally, the document describes the typical parts of a formal report, including the preface, main body, and supplementary sections.