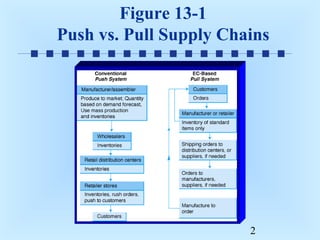
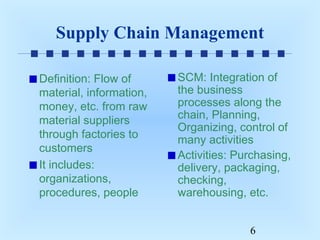
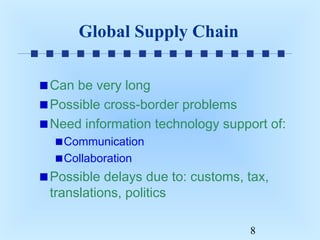
This document discusses order fulfillment, logistics, and supply chain management. It defines key terms like logistics and supply chain management. The steps of order fulfillment include payment clearance, packaging, shipping, and insuring. Supply chain management involves integrating business processes along the supply chain from raw materials to customers. Benefits include reducing uncertainty, proper inventory levels, and minimizing delays. Global supply chains can experience cross-border problems and delays. Areas for opportunities within supply chains include manufacturing, warehousing, transportation, and inventory management. Electronic commerce solutions can automate processes to decrease costs and cycle times. Software supports tracking activities throughout the supply chain.