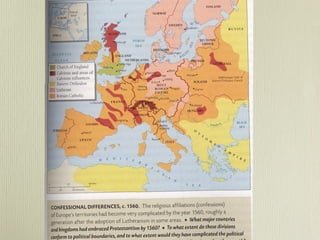
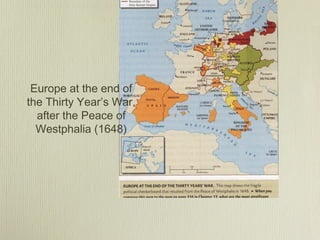
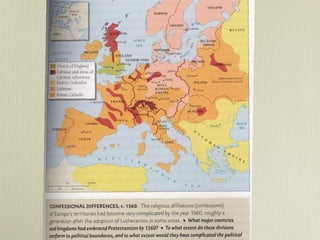
The document provides an overview of religion, warfare, and sovereignty from 1540-1660. It discusses the key events and figures of the Renaissance, Reformation led by Luther and Calvin, and the devastating Thirty Years War. It also briefly mentions the Edict of Nantes, which was conceived in this time period to offer protections to French Protestants, known as Huguenots.












![Calvinist Ordinances
• Drunkenness:
That no one shall invite another to drink under penalty of 3 sous.
That taverns shall be closed during the sermon, under penalty that the tavern-keeper
shall pay 3 sous, and whoever may be found therein shall pay the same amount
If anyone be found intoxicated he shall pay for the first offence 3 sous and shall be
remanded to the consistory [church governing body]; for the second offence he shall
be held to pay the sum of 6 sous, and for the third 10 sous and be put in prison
Songs and Dances.
If anyone sings immoral, dissolute or outrageous songs, or dance the virollet or other
dance, he shall be put in prison for three days and then sent to the consistory.
(source: Hunt 433)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rennaisancelutherreligiouswars-130307082146-phpapp01/85/Rennaisance-luther-religious-wars-14-320.jpg)