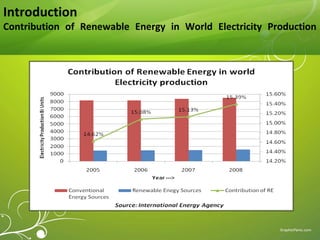
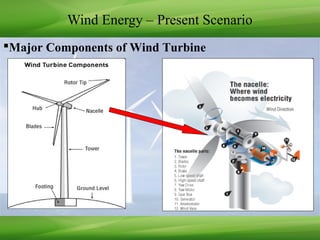
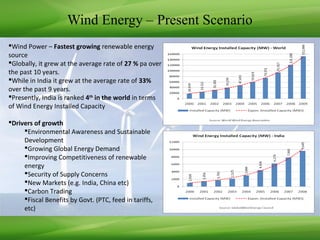
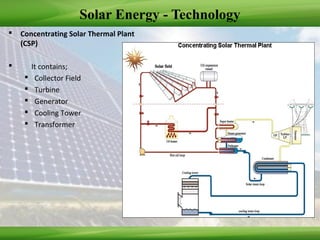
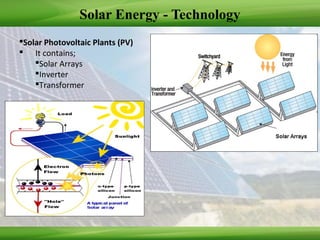
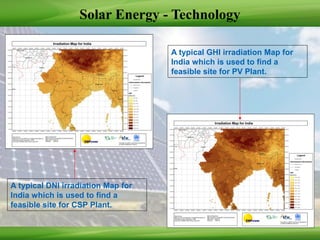
This document provides an overview of renewable energy technologies used for power generation, focusing on wind and solar energy. It discusses how wind turbines convert wind force into torque to generate electricity, and the typical power load factors for wind farms. It also explains the two main solar power generation technologies: concentrating solar thermal plants and photovoltaic plants. Concentrating solar plants use collectors and turbines to generate electricity from heat, while photovoltaic plants use solar arrays and inverters. The document concludes with current installed capacities of wind and solar power in India.