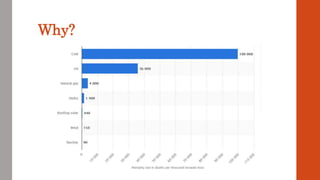
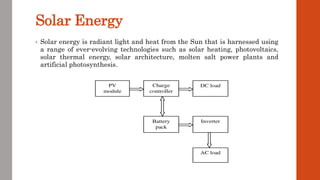
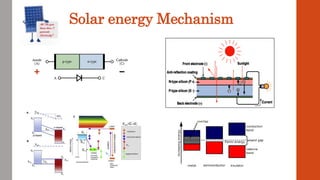
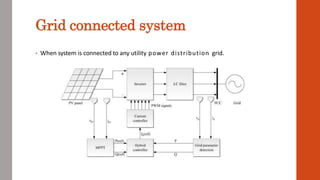
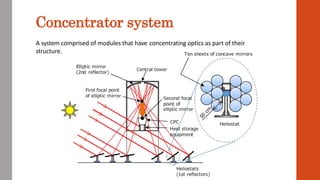
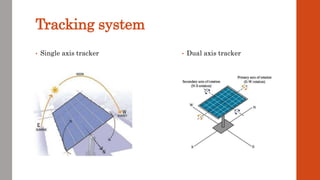
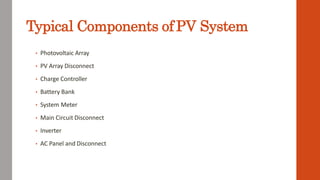
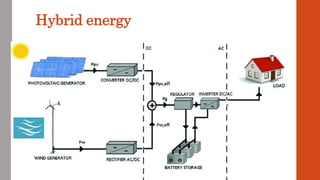
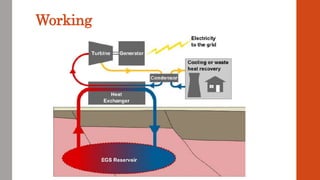
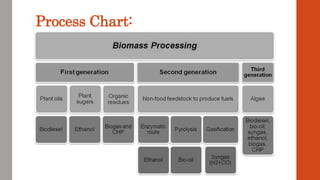
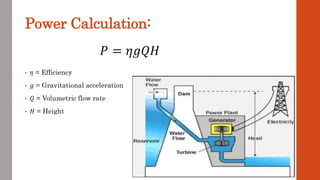
This document discusses various renewable energy sources including solar, wind, geothermal, bioenergy, hydropower, and ocean energy. It provides details on each type of renewable energy such as the mechanisms, advantages, calculations, and typical components involved. Renewable energy sources are defined as natural resources that constantly replenish themselves and have lower environmental impact than fossil fuels. The document highlights that renewable energy facilities require less maintenance than traditional generators and are sustainable sources that will never run out.