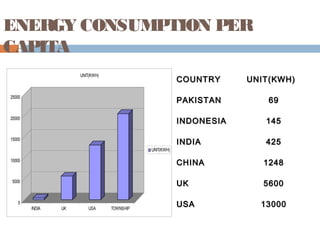
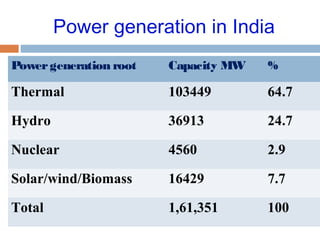
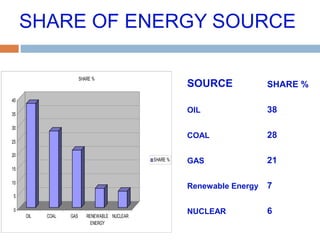
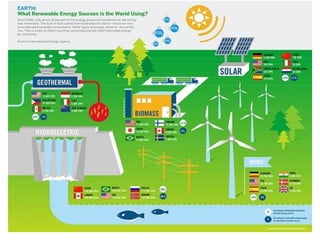
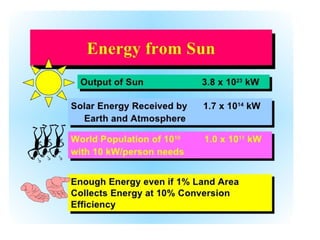
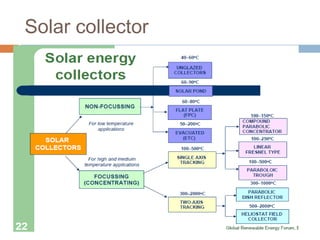
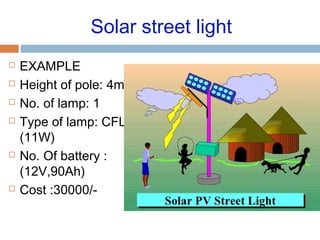
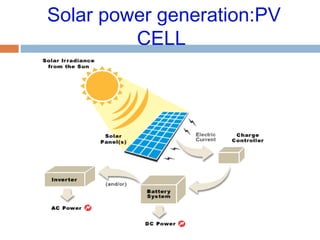
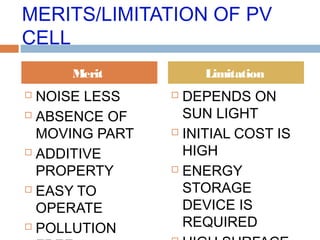
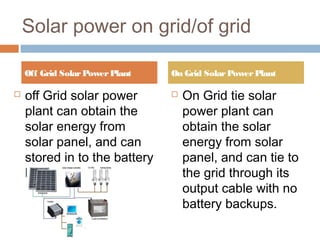
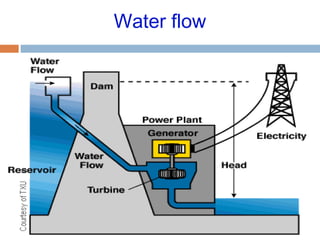
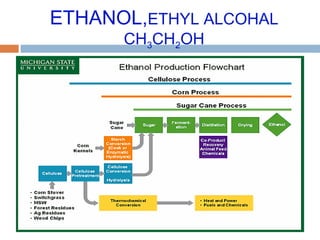
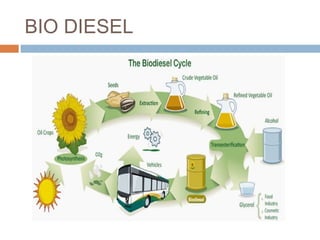
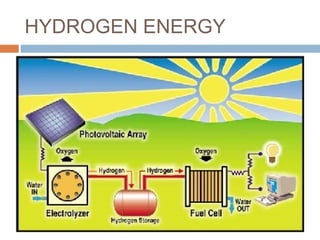
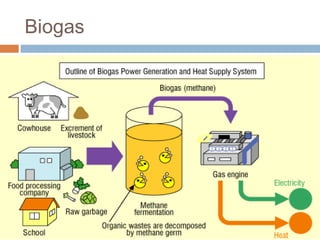
This document summarizes renewable energy sources. It discusses various renewable sources like wind, solar, hydroelectric, tidal, and geothermal energy. It provides information on non-renewable sources like coal, LPG, natural gas and nuclear energy. It also shares data on energy consumption per capita in different countries and the share of different energy sources in India's total power generation. The document further describes various solar energy applications like solar panels, solar collectors, solar street lights and their merits and limitations. It concludes with providing facts about other renewable sources like hydroelectric, biomass, biogas, ethanol and hydrogen energy.