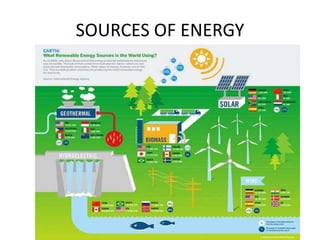
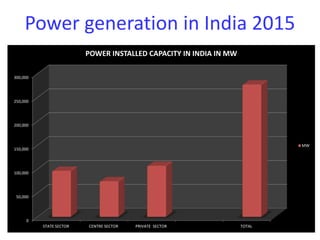
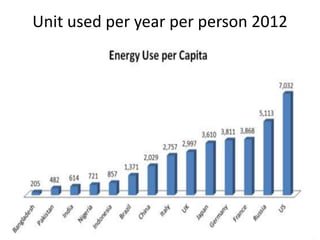
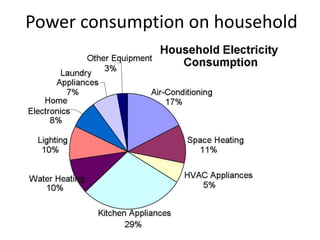
This document discusses energy conservation in India. It summarizes that in 2015, thermal power generation made up 64.7% of India's total installed capacity of 161,351 MW. The document outlines various sources of energy in India, both renewable and non-renewable. It provides statistics on household power consumption and discusses practical methods for energy conservation like installing LED lights, fixing air leaks, and using energy efficient appliances.