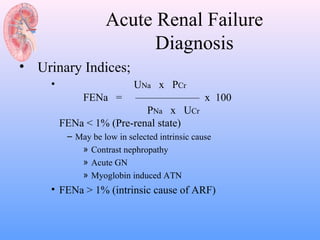
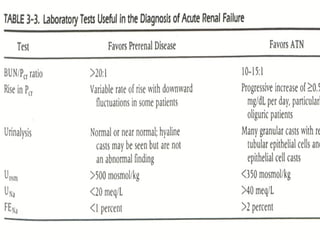
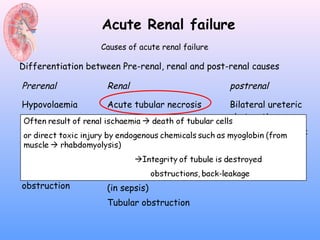
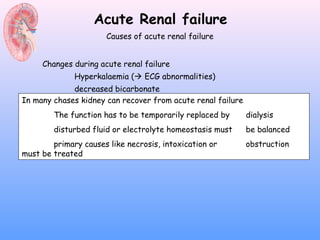
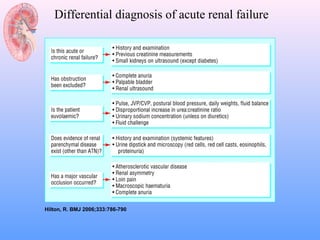
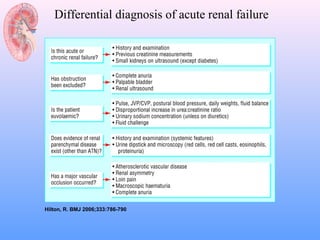
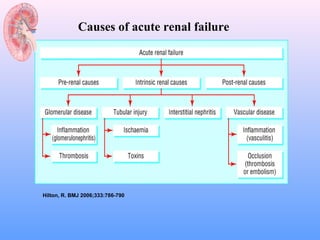
This document discusses acute renal failure (ARF), also known as acute kidney injury (AKI). It defines ARF, discusses its epidemiology and causes. The main causes of ARF are pre-renal (decreased blood flow/volume), renal (damage within the kidneys), and post-renal (obstruction of urine flow). The most common form of intrinsic ARF is acute tubular necrosis, often due to ischemia or nephrotoxins. Diagnosis involves lab tests of kidney function and urine analysis. Treatment focuses on identifying and reversing the underlying cause, maintaining fluid/electrolyte balance, and potentially initiating renal replacement therapy like dialysis.




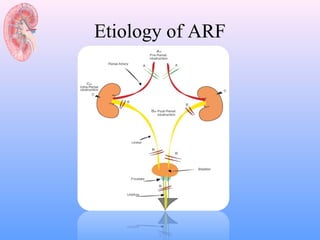

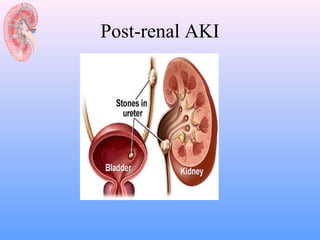
![Post-renal AKI
– Ureteric obstruction
• Stone disease,
• Tumor,
• Fibrosis,
• Ligation during pelvic surgery
– Bladder neck obstruction
• Benign prostatic hypertrophy [BPH]
• Cancer of the prostate
• Neurogenic bladder
• Drugs(Tricyclic antidepressants, ganglion blockers,
• Bladder tumor,
• Stone disease, hemorrhage/clot)
– Urethral obstruction (strictures, tumor)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acuterenalfailure2-130207032508-phpapp01/85/Acute-renal-failure-2-10-320.jpg)