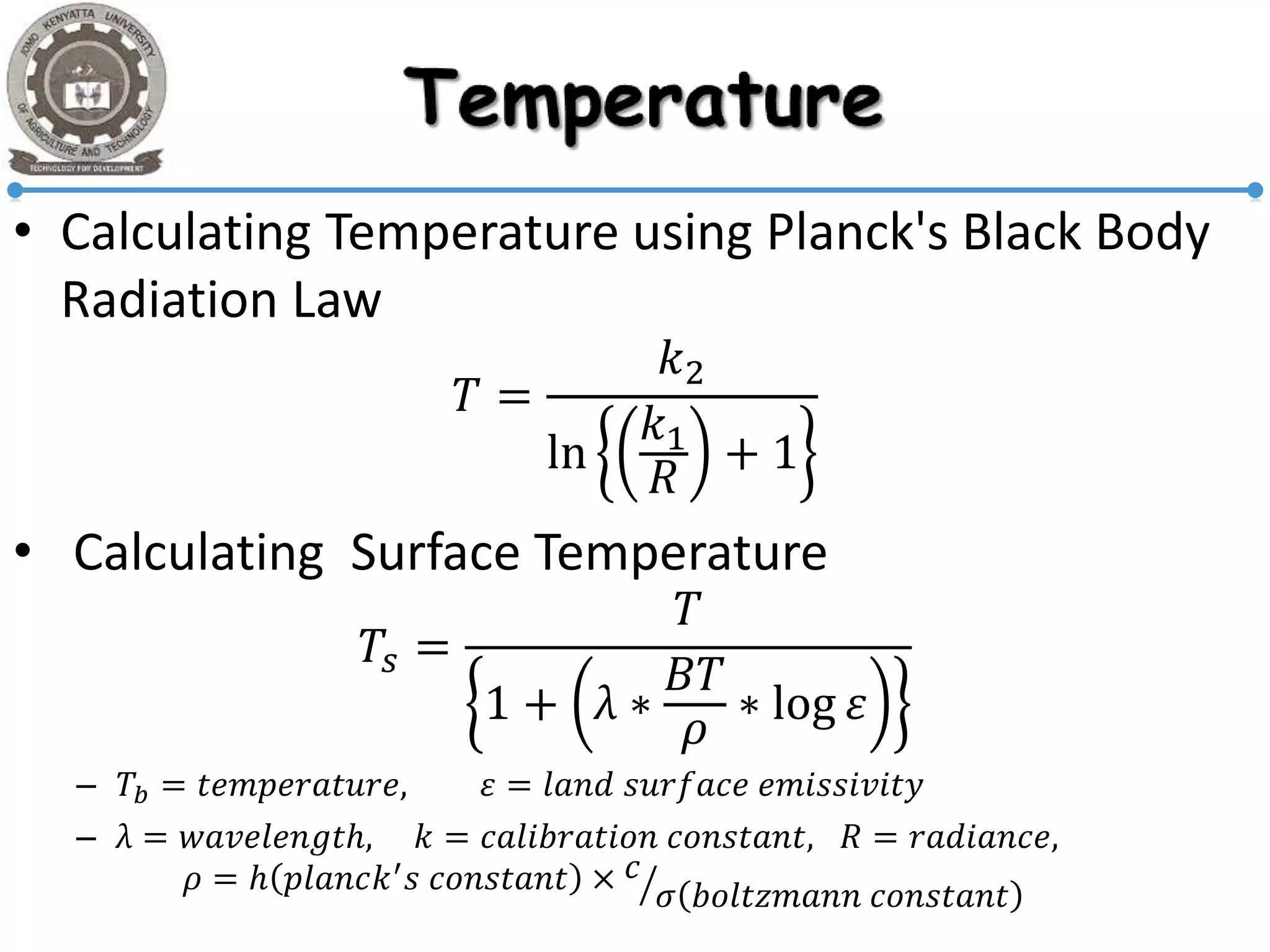
This document discusses remote sensing applications and seminar. It summarizes key concepts in remote sensing including radiometric resolution, reflectance, calculating surface temperature using Planck's law, and spectral reflectance and absorptance. It also describes a study applying linear spectral unmixing using MODIS data to map percentage tree cover in equatorial forests. Band 5 was omitted from the MODIS data and the remaining bands were resampled and used to generate a vegetation skewness image to identify pure and impure forest areas for analysis with a mix-unmix classifier to produce percentage tree cover maps.