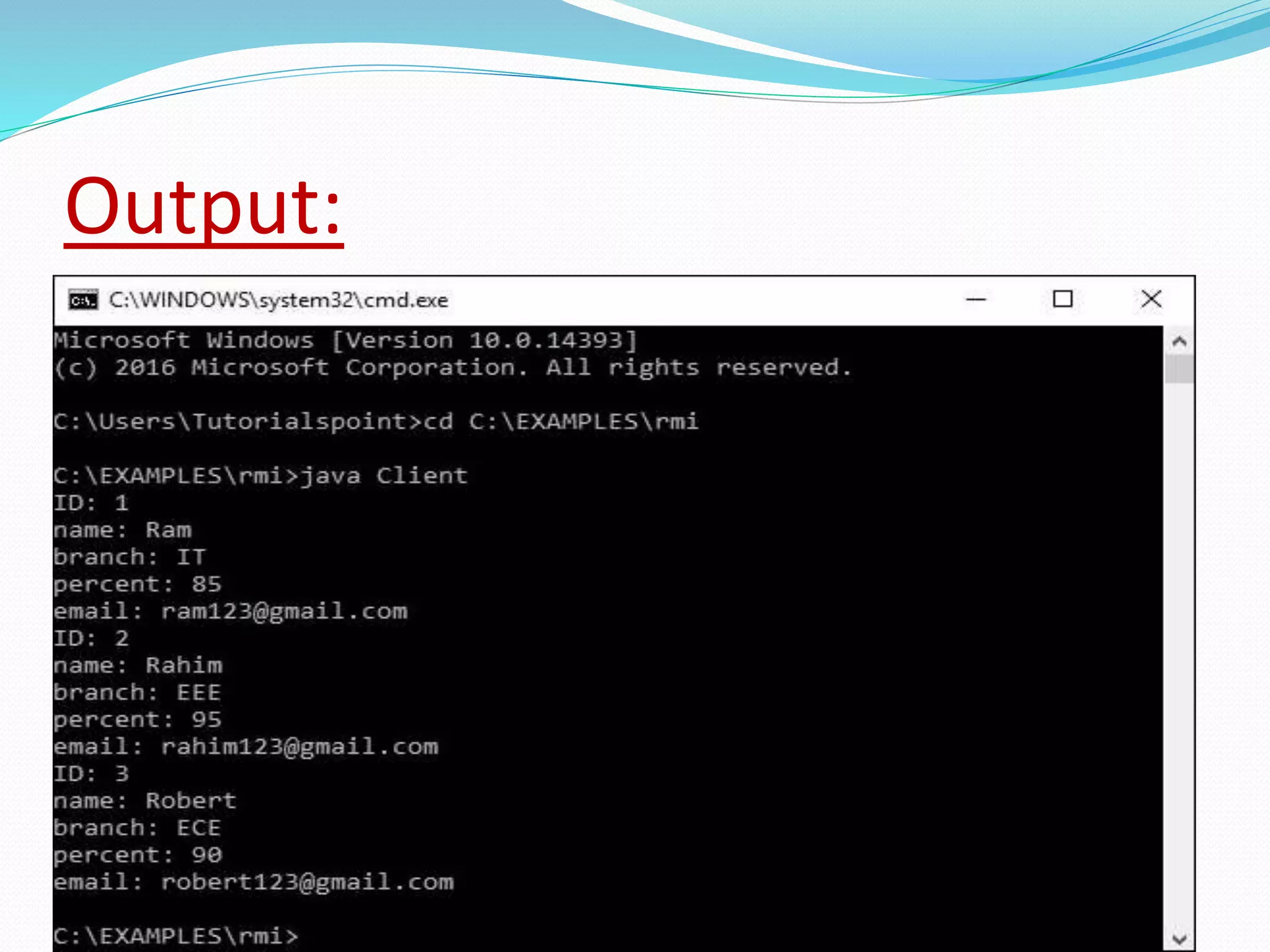
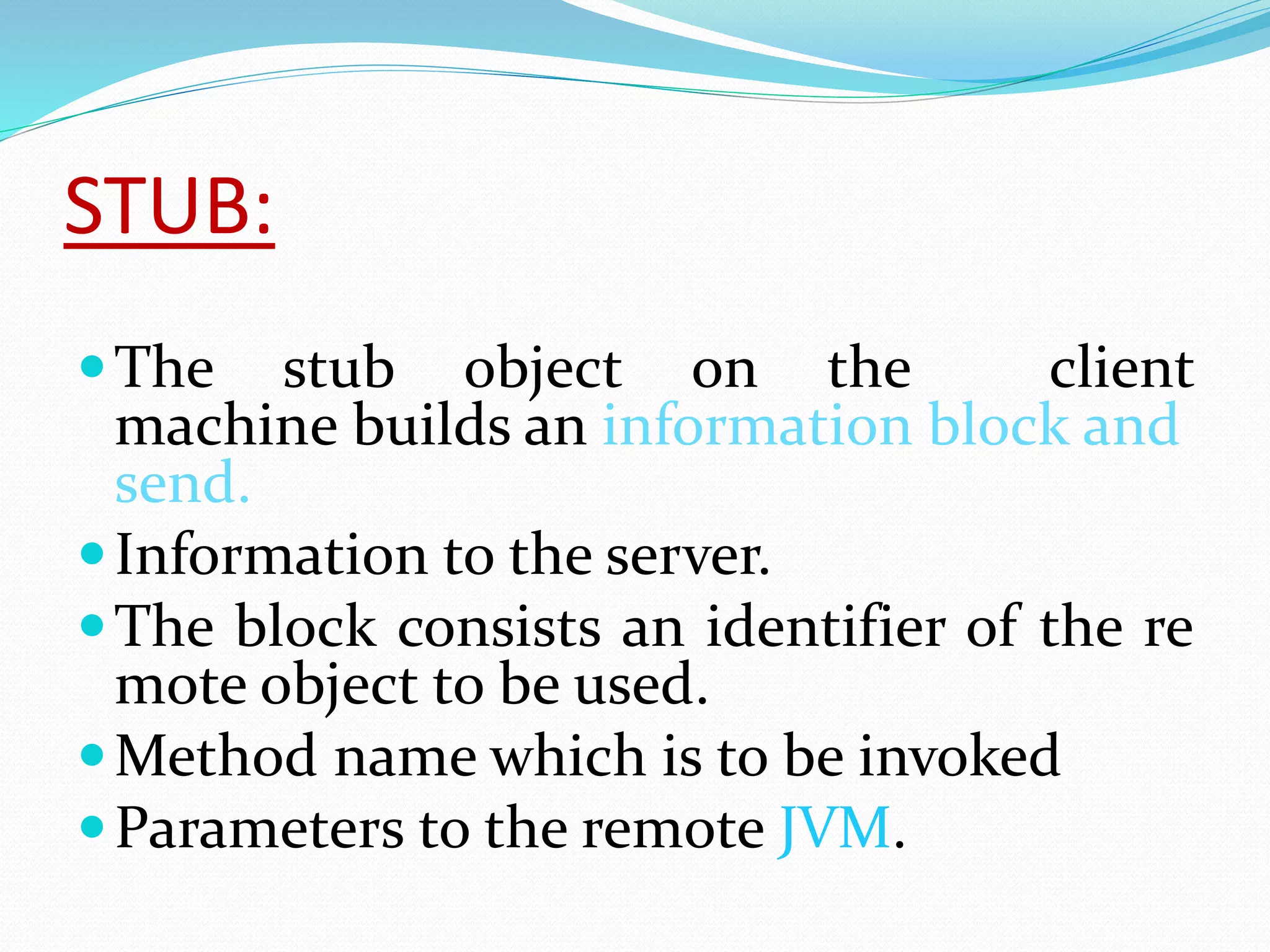
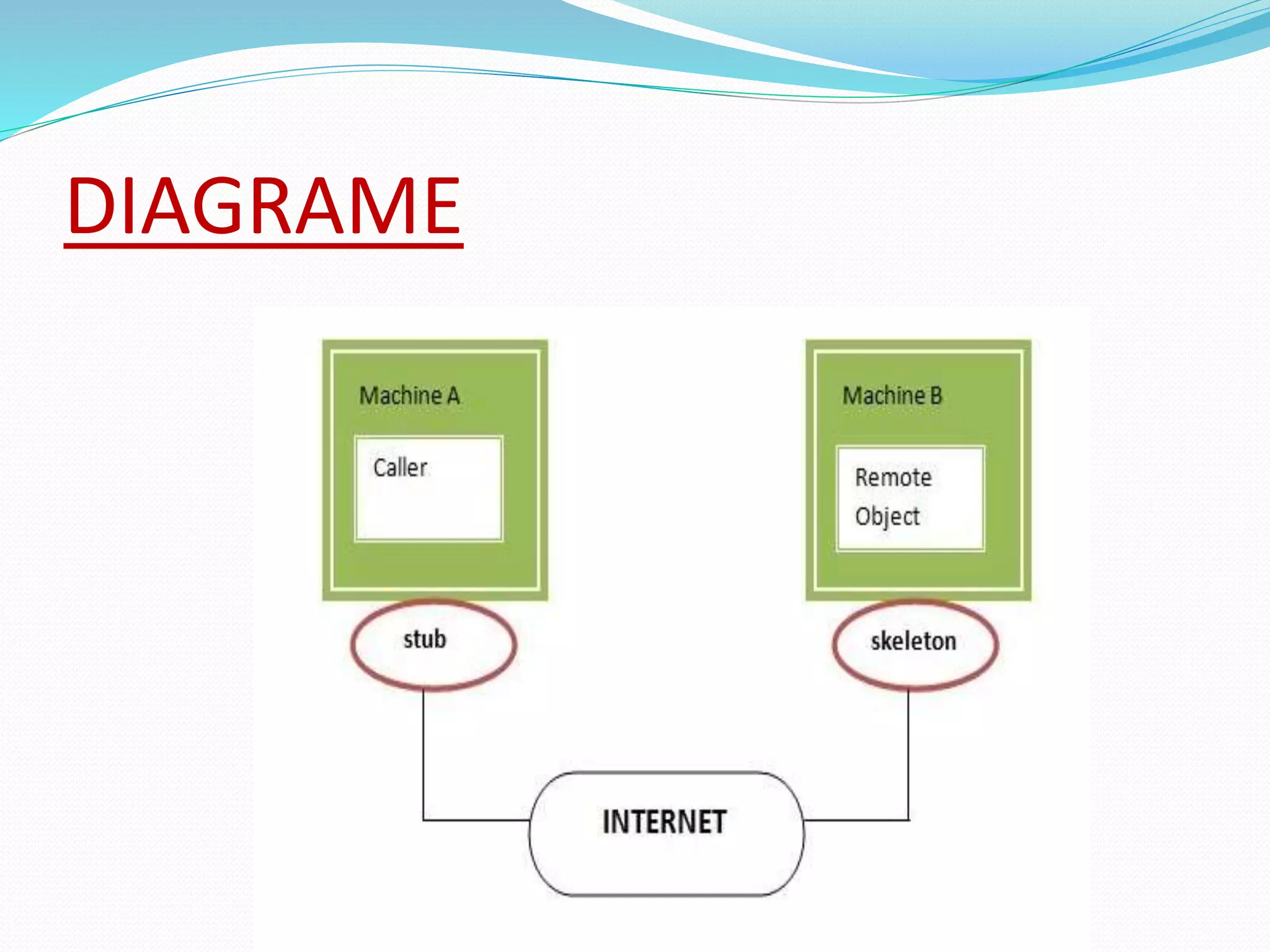
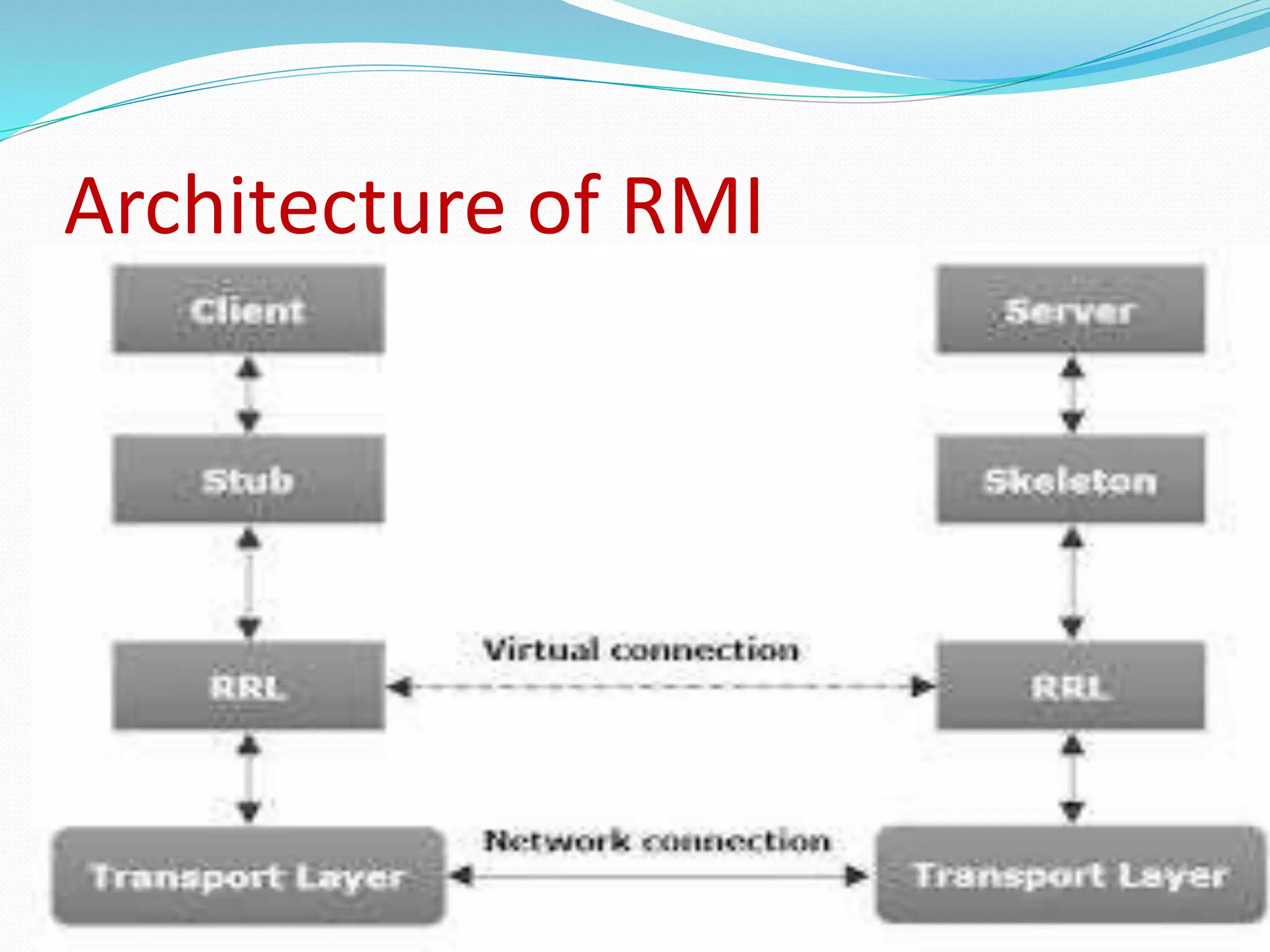
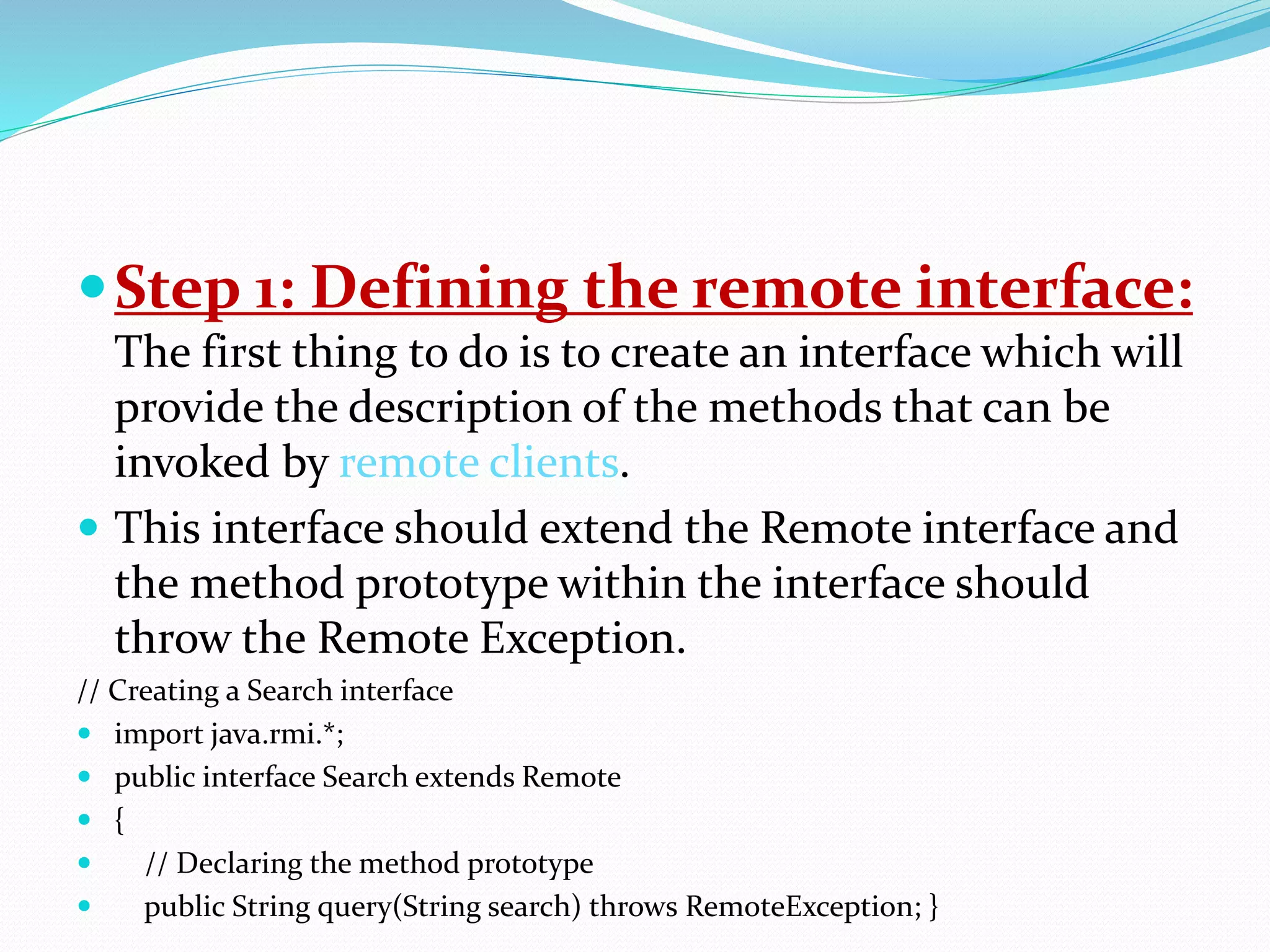
RMI allows objects in one Java Virtual Machine (JVM) to invoke methods on objects residing in another JVM. It uses stub and skeleton objects to enable remote communication between Java programs. The stub on the client side sends a call to the server-side skeleton, which then invokes the actual remote object. The key steps to build an RMI application are: defining the remote interface, implementing it, generating stub and skeleton objects, starting the RMI registry, running the server, and making calls from the client.












![ //program for client application
import java.rmi.*;
public class ClientRequest
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
String answer,value="Reflection in Java";
try
{
// lookup method to find reference of remote object
Search access =
(Search)Naming.lookup("rmi://localhost:1900"+
"/geeksforgeeks");
answer = access.query(value);
System.out.println("Article on " + value +
" " + answer+" at GeeksforGeeks");
}
catch(Exception ae) { system.out.println(ae);}}}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/remotemethodinvocatiomppt-201017081511/75/Remote-method-invocatiom-18-2048.jpg)

![Program:
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.util.*;
public class Client { private Client() {}
public static void main(String[] args);
{
try {
// Getting the registry Registry registry =
LocateRegistry.getRegistry](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/remotemethodinvocatiomppt-201017081511/75/Remote-method-invocatiom-21-2048.jpg)