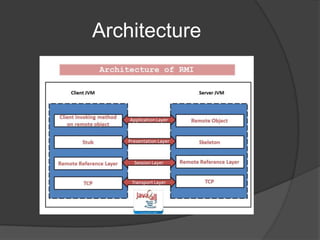
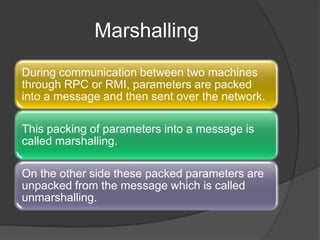
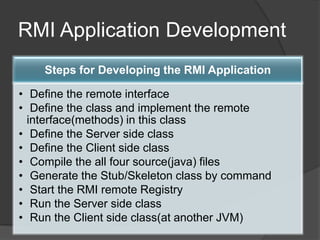
RMI allows Java objects to call methods on other Java objects running in a different JVM. It works by passing object references between JVMs using marshaling and unmarshaling. Developing an RMI application involves defining a remote interface, implementing that interface in a class, running an RMI registry, starting the server, and having the client lookup and invoke methods on remote objects.