This document discusses kernel modules and process management in Linux. It covers the following key points:
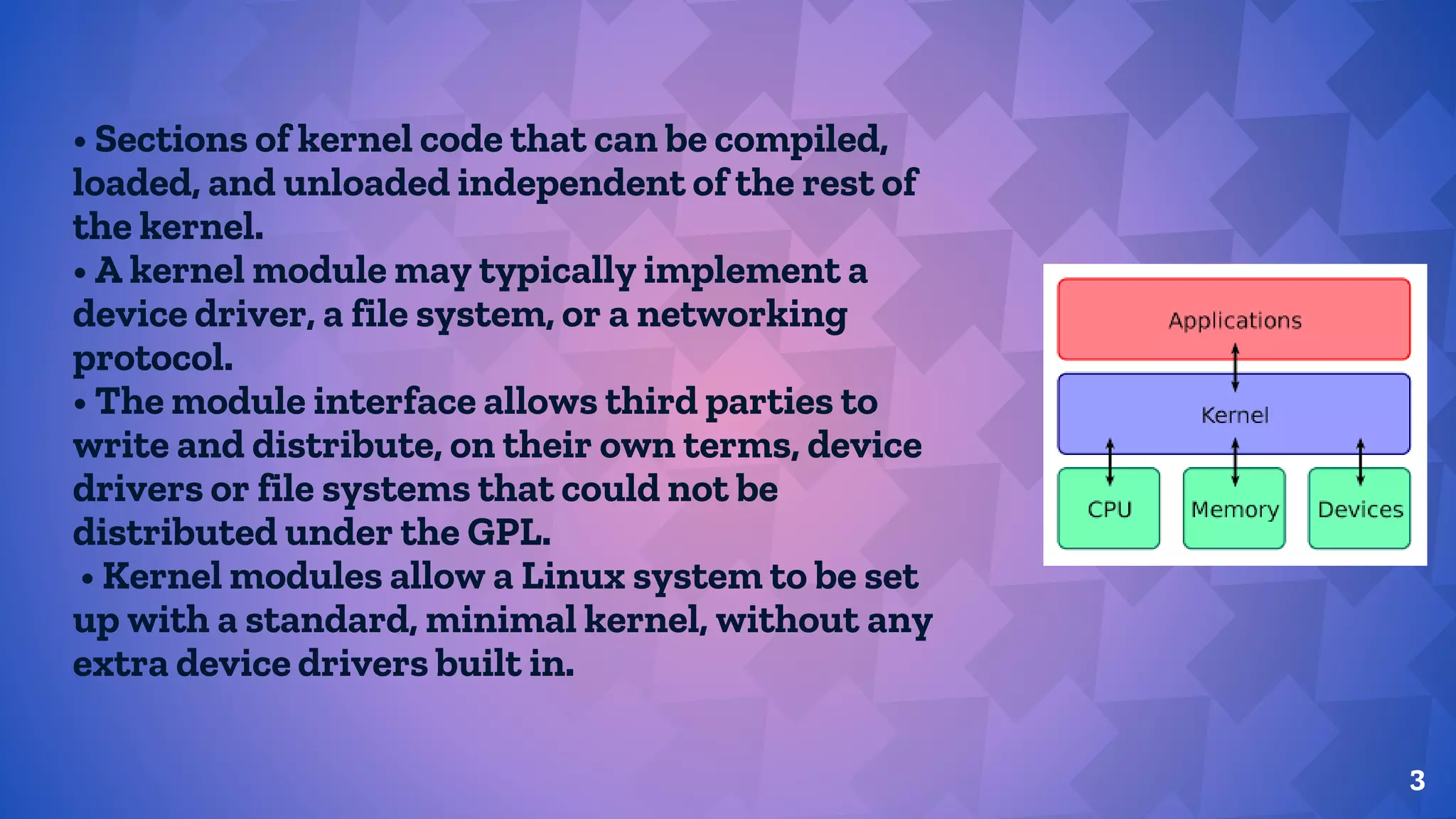
Kernel modules allow sections of kernel code to be loaded and unloaded independently. They implement drivers, file systems, or networking protocols. Process management in Linux uses fork to create new processes and execve to run new programs. A process encompasses the context needed to track a program's execution, including its identity, environment, and scheduling context. Linux represents both processes and threads internally but threads share the same address space as their parent process.