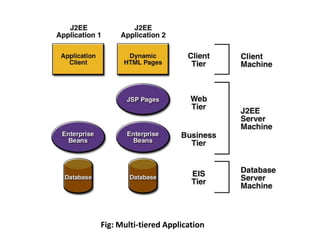
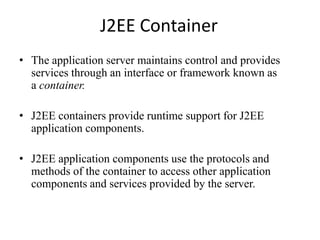
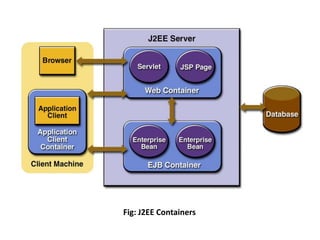
This document discusses the key components of the J2EE architecture. It describes how application logic is divided into client-tier, web-tier, and business-tier components that run on different machines. The business tier uses enterprise beans like session beans and entity beans to encapsulate business logic. These components communicate through well-defined J2EE containers that provide runtime services. The web container manages servlets and JSPs, while the EJB container handles enterprise beans and provides services like security and transaction management.