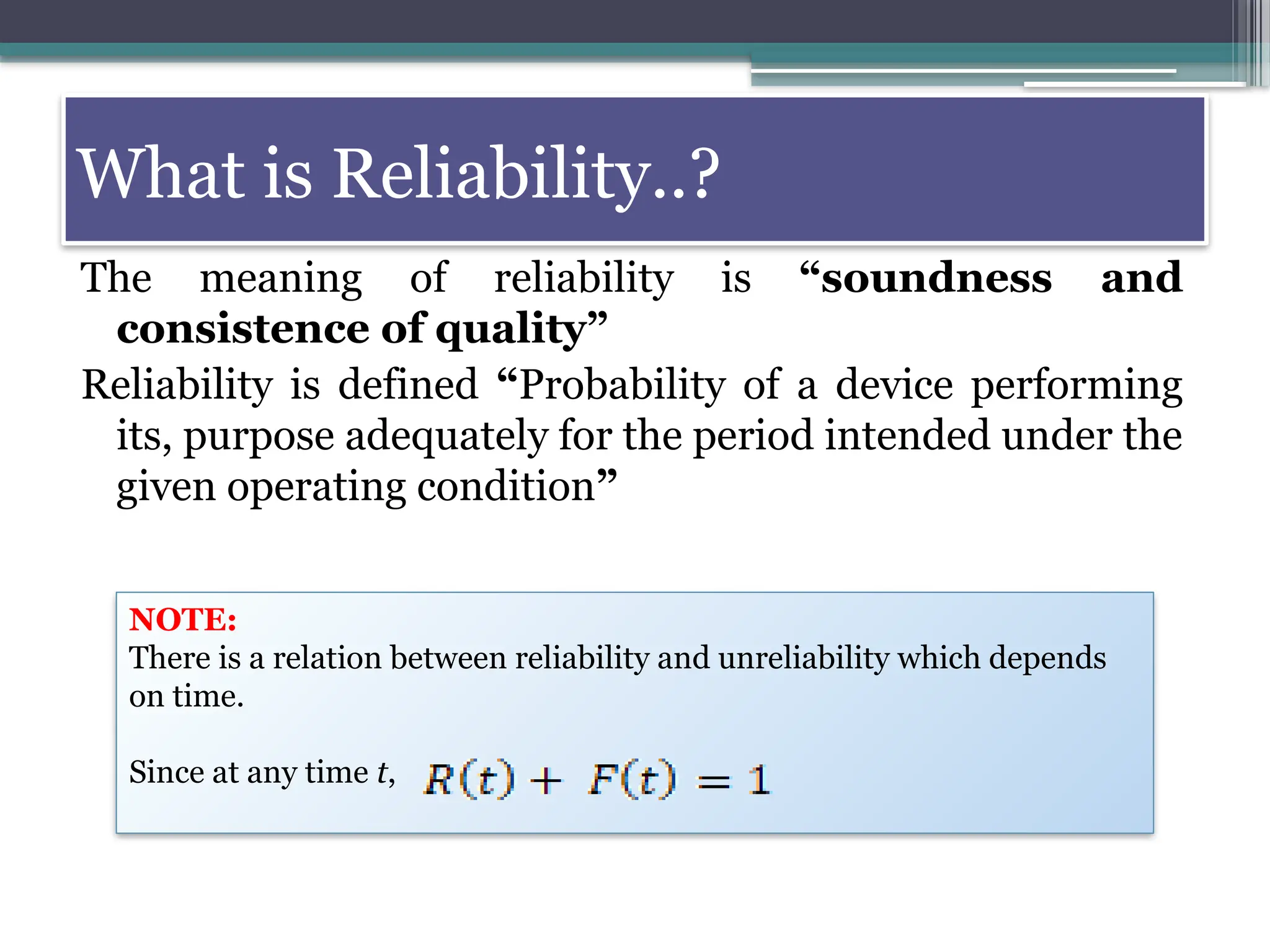
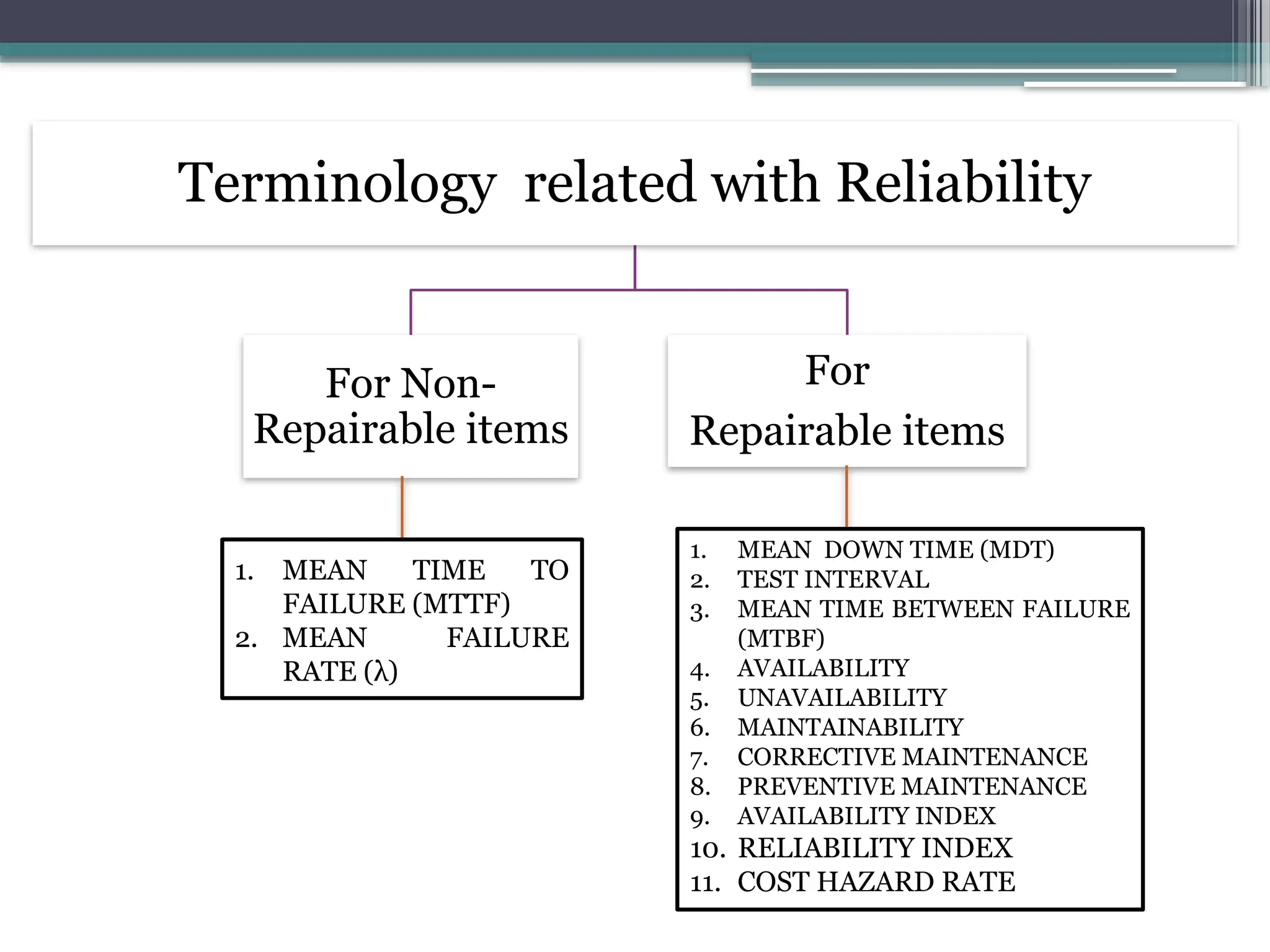
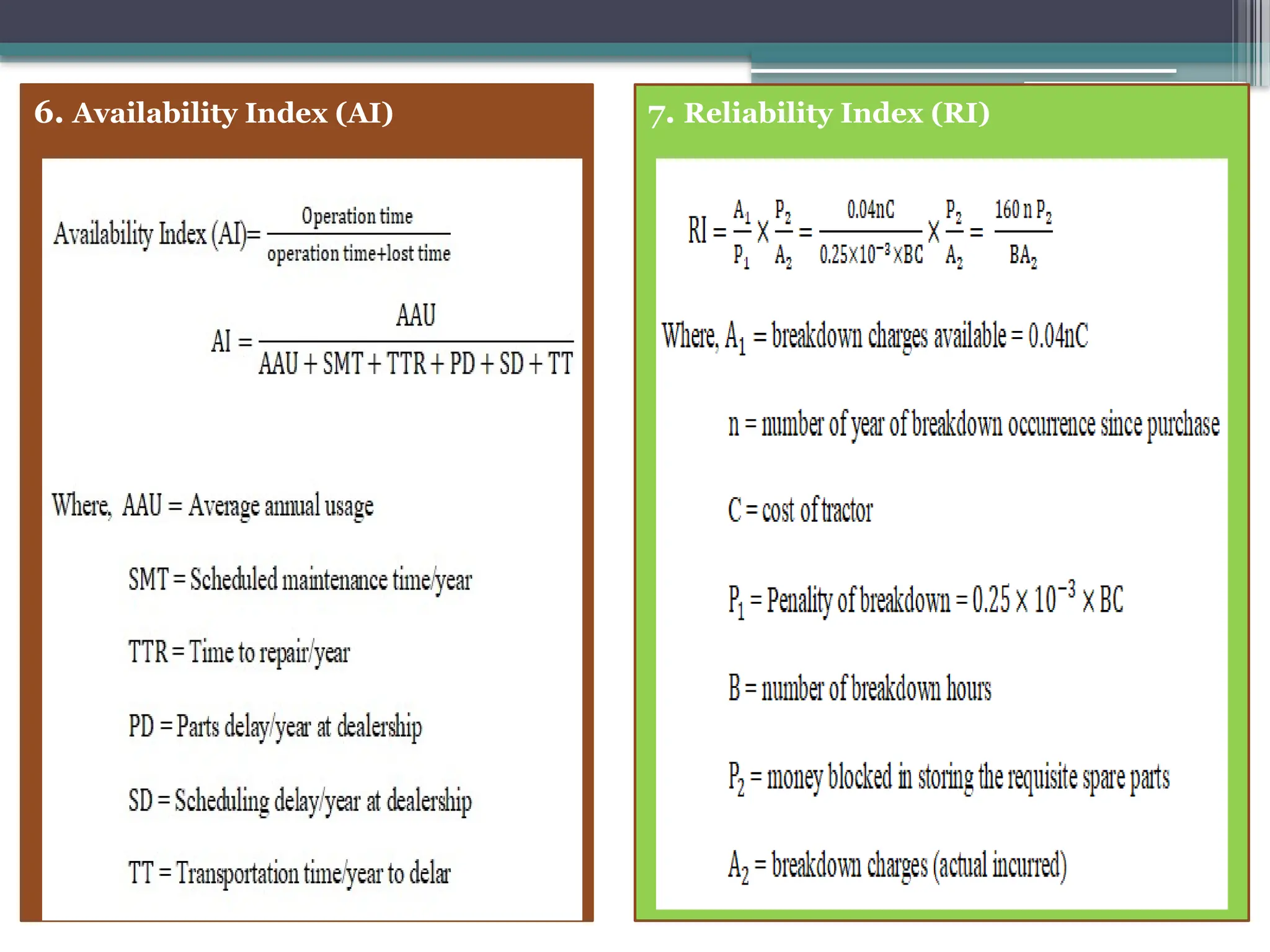
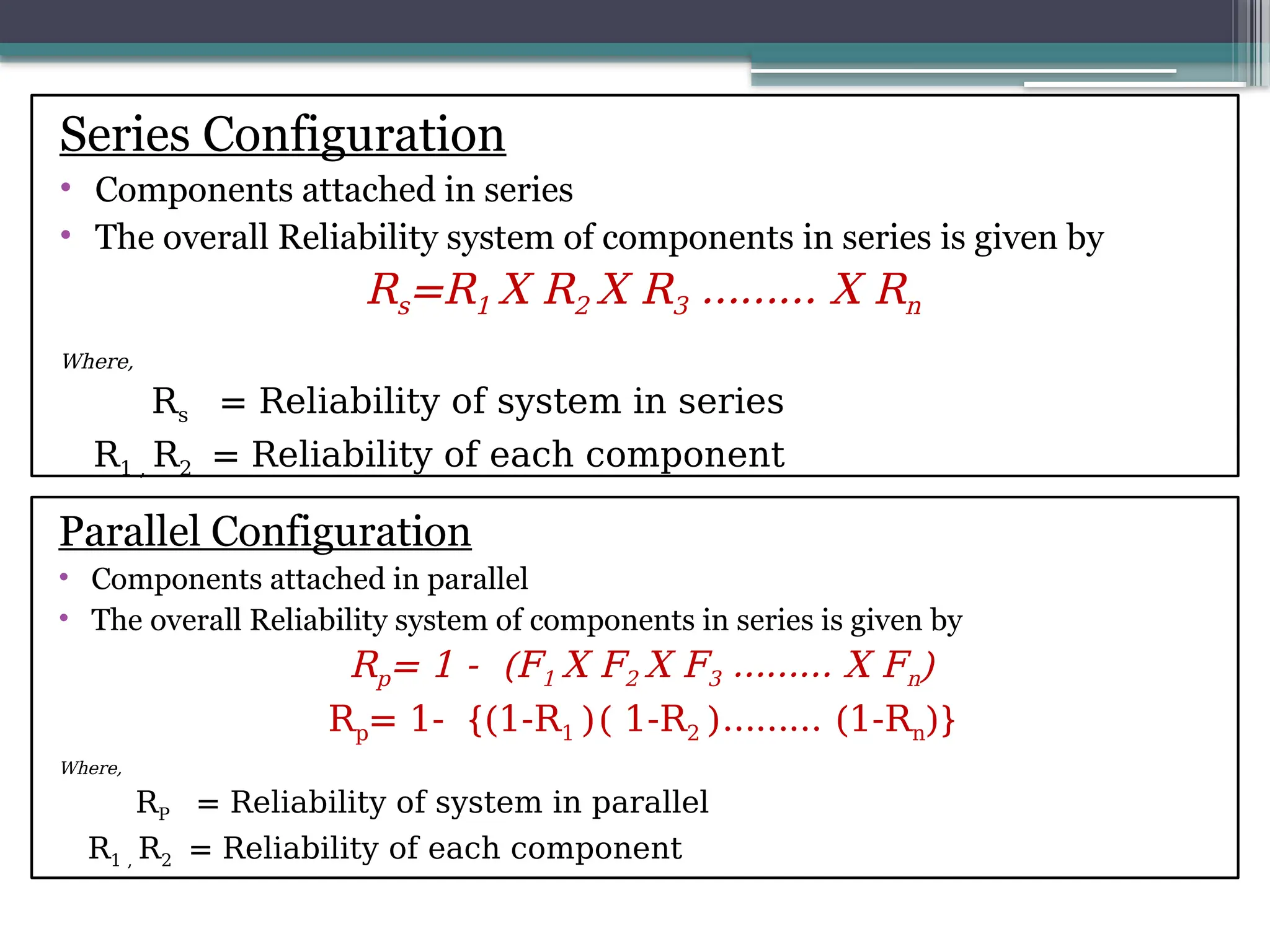
The document outlines reliability criteria in design, emphasizing its definition as the probability of a device performing adequately over time. It discusses the importance of reliability to manufacturers and customers, terminology related to both repairable and non-repairable items, and methods for developing product reliability. Additionally, it covers system reliability through configurations such as series and parallel, applying probability theory to calculate overall reliability factors.