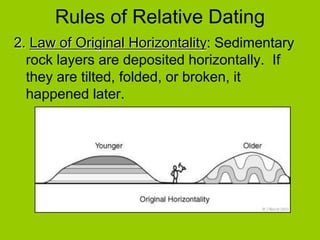
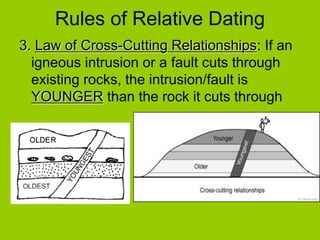
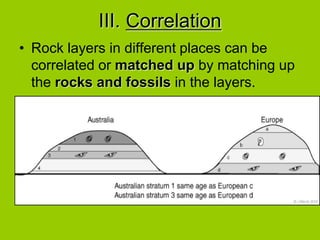
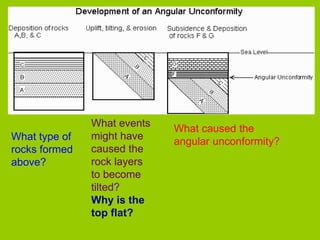
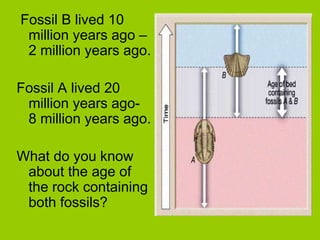
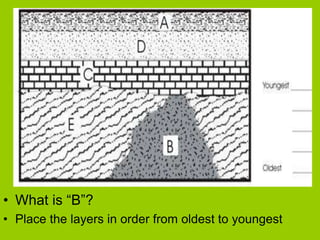
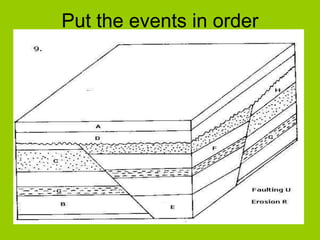
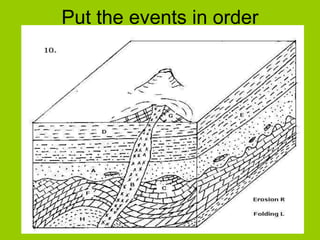
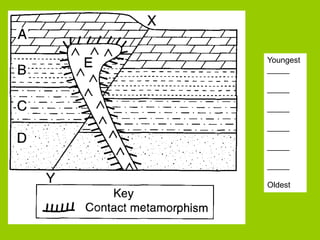
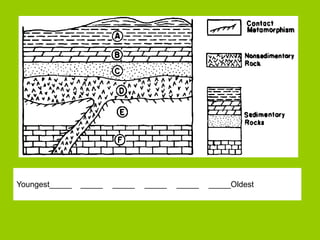
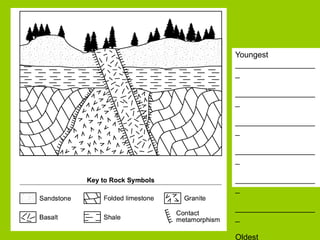
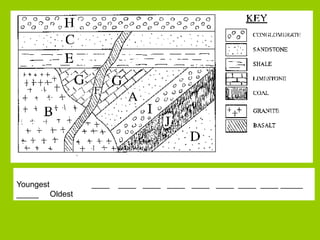
This document discusses key concepts in relative dating of geologic materials. It introduces important figures like James Hutton and Charles Lyell who were influential in developing theories of geology. The key principles of relative dating are described, including the law of superposition, law of original horizontality, and law of cross-cutting relationships. The document also discusses using index fossils and unconformities to correlate rock layers between locations and determine their relative ages.