This document discusses the respiratory cycle and mechanics of breathing. It defines respiration as the process of inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide. The principal muscle of inhalation is the diaphragm, while exhalation is passive. It describes the pressures involved in respiration, including alveolar pressure, pleural pressure, and atmospheric pressure. Obstructive and restrictive lung diseases can alter these normal pressure values and disrupt the inhalation to exhalation ratio.



![ORIGIN INSERTION NERVE
SUPPLY
FUNCTION
INSPIRATORY
MUSCLE
PRINCIPLE
MUSCLE
DIAPHRAGM LUMBAR
VERTEBRAE,COST
AL MARGIN AND
XIPHOID PROCESS
AS A CENTRAL
TENDON TO
COMBINE WITH
PERICARDIUN
PHRENIC
NERVE[
C3,C4,C5]
ABOUT 75%
WORK OF
BREATHING
INTERCOSTAL RIB 1-11 RIB2-12 INTERCOSTAL
NERVE
ELEVATE THE
RIBS,STABILIZ
E CHEST WALL
ACCESSORY
MUSCLE
STERNOCLEDO
MASTOID
B/L MANUBRIUM
AND MEDIAL END
OF CLAVICAL
MASTOID
PROCESS &
OCCIPLE BONE
CN 9,CERVIAL
PLEXUS
[C1,C2]
ELEVATE THE
FIRST RIB &
STERNUM
SCALENE LOER FIVE
CERVICAL
VERTEBRA
UPPER SURFACE
OF 1ST , 2ND RIB
CERVICAL
N,C6,C7,C8
FIXATION OF
RIB
PECTORALIS
MAJOR
CLAVICAL,STERNU
M & SIX COSTAL
CATILLAGE
HUMERUS MEDIAN
PECTORAL N.
LIFT RIBS &
CHEST
ABDOMINALS
EXPIRATORY
MUSCLE
PRINCIPLE
MUS LE
EXPIRATION IS
DONE
PASSIVELY BY
RECOILING
PROPORTY OF
LUNG & CHEST
WALL
ACCESSORY
MUSCLE
RECTUS
ABDOMINIS
PUBIC BONE COSTAL
CARTILAGE 7
ILIOINGUINAL DRIVE
DIAPHRAGM
UPWARD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rekhatopic1respiratorycycle-180714163931/75/Rekha-topic-1-respiratory-cycle-5-2048.jpg)





![Pressure at opening of airway [Pao] = Pressure at body
surface [Pbs]= 0
Alveolar pressure often reffered to intrapulmonary pressure
[Pav]
Pleural pressure is usually negative during quite breathing
[Ppl] ≈ -5
Difference between two pressure is called pressure gradient,
1. TRANSRESPIRATORY PRESSURE GRADIENT [Pts] =
difference in pressure between atmosphere and alveoli , Pts
= Pav-Pbs or Pts= Pav-Pao
2. TRANSPULMONARY PRESSURE GRADIENT [PL ] =
difference between alveoli and pleural space , PL =Pav-Ppl
3. TRANSTHORACIC PRESSURE GRADIENT = difference in
pressure between pleural space and body surface Pw= Ppl-
Pbs](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rekhatopic1respiratorycycle-180714163931/75/Rekha-topic-1-respiratory-cycle-11-2048.jpg)


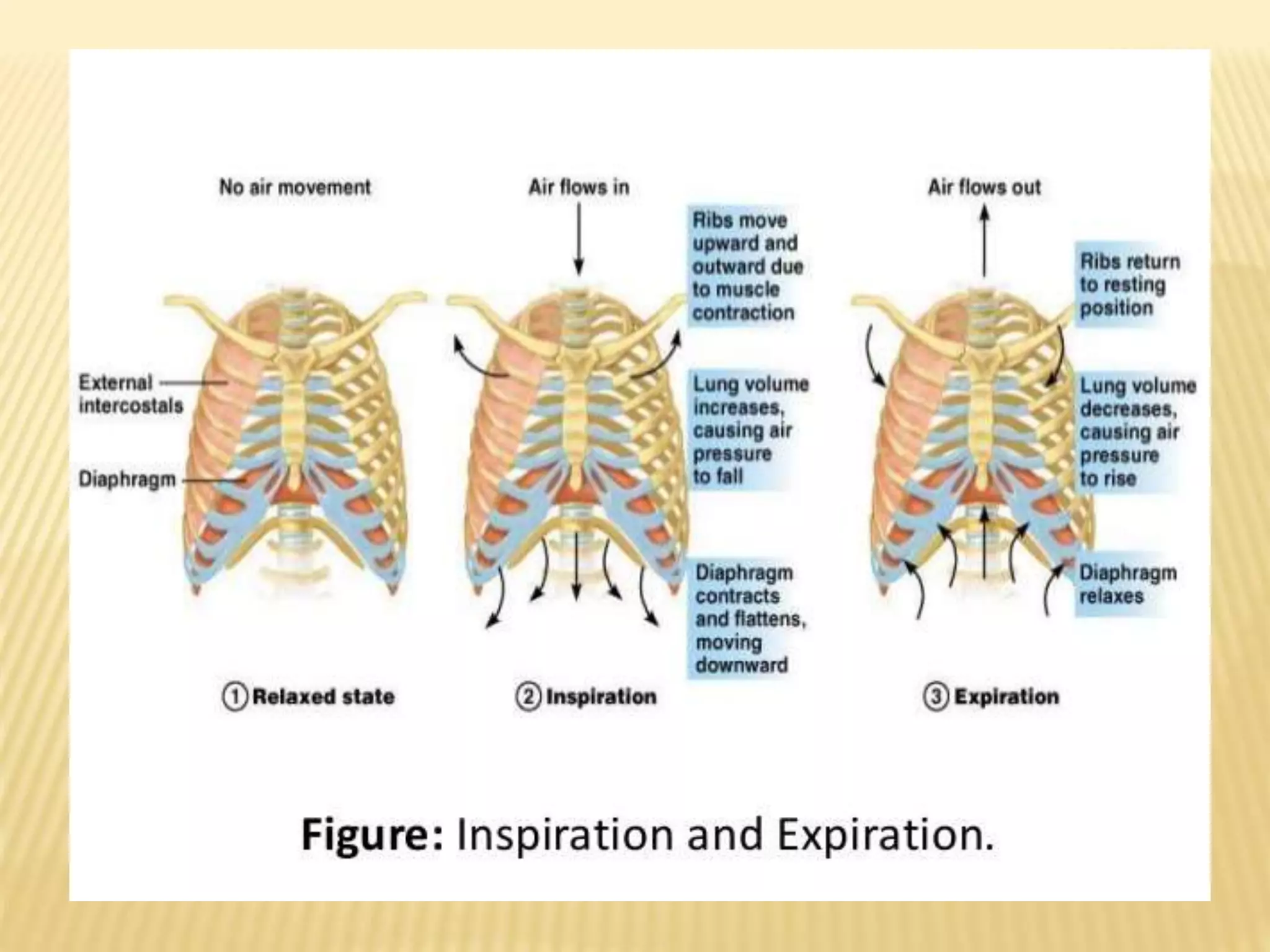
![Rekha topic[1]respiratory cycle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/rekhatopic1respiratorycycle-180714163931/75/Rekha-topic-1-respiratory-cycle-14-2048.jpg)