1. This document outlines the academic regulations for students pursuing a B.Tech degree from the 2009-2010 academic year onwards at JNTU.
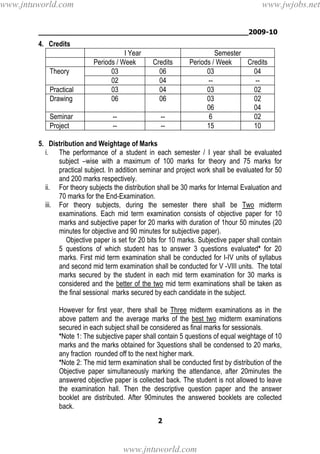
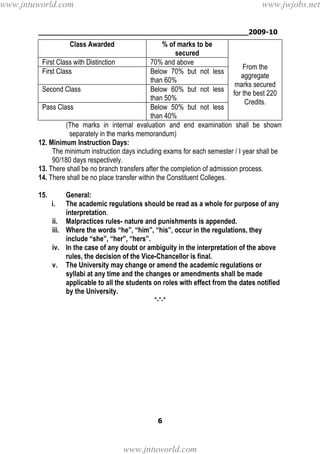
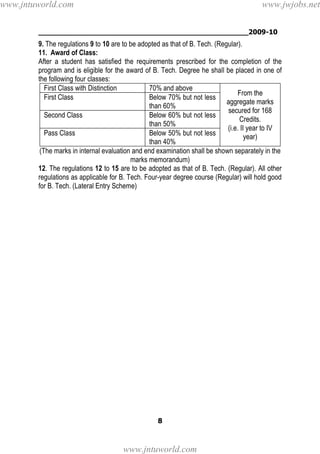
2. To earn a B.Tech degree, students must complete their course of study within 4-8 years, registering for 220 total credits and securing all 220 credits.
3. Coursework is offered in various engineering branches, including Aeronautical, Biotechnology, Civil, Computer Science, Electrical, Electronics, Information Technology, and Mechanical Engineering.