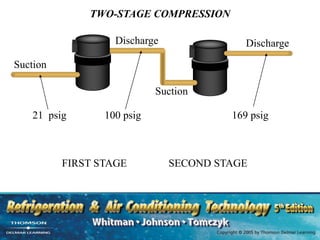
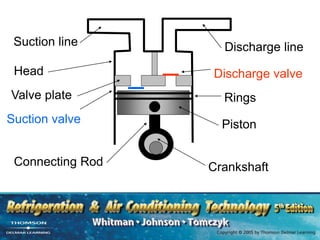
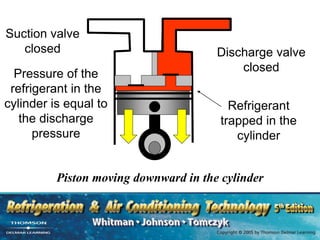
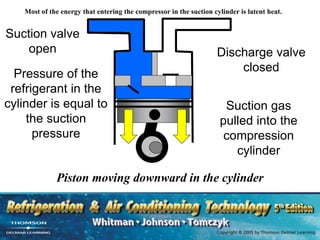
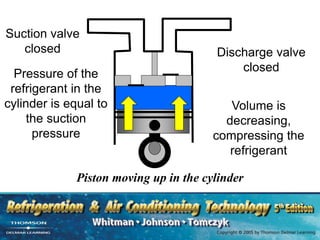
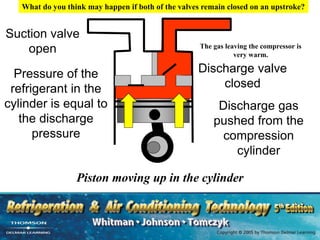
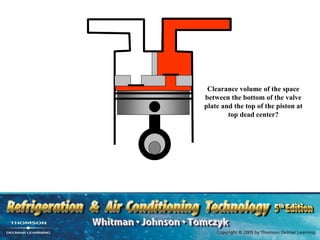
The document provides an overview of commercial refrigeration compressors, detailing their functions, types, and operational processes such as compression ratio, suction, and discharge. Key compressor types discussed include reciprocating, screw, rotary, scroll, and centrifugal compressors, along with their component parts and maintenance considerations. It emphasizes the importance of managing compression ratios and preventing liquid slugging to maintain system efficiency and prevent damage.