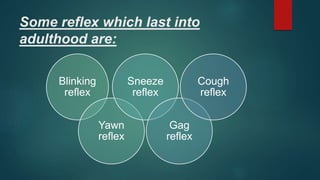
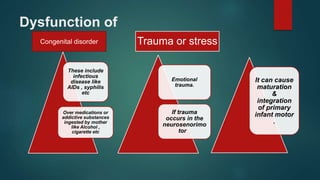
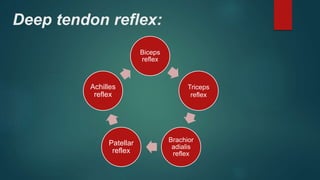
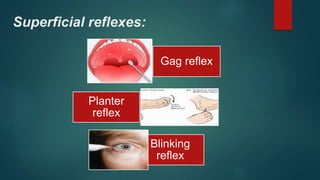
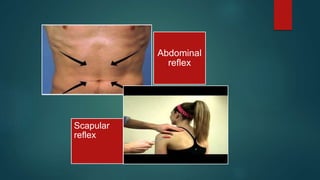
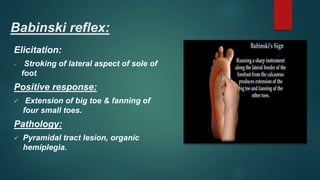
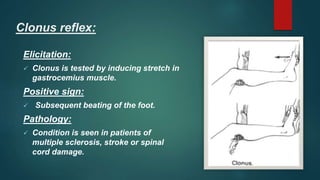
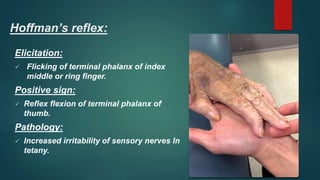
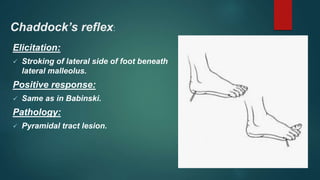
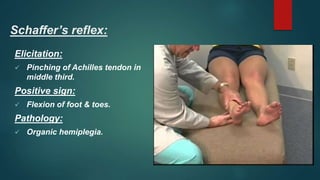
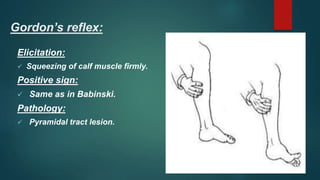
1. The document discusses various reflexes and cranial nerves in the human body. It provides details on different types of reflexes including infant, superficial, deep tendon and pathological reflexes.
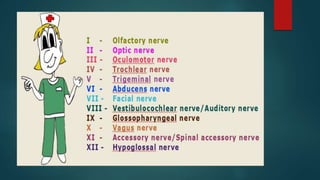
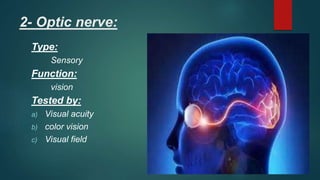
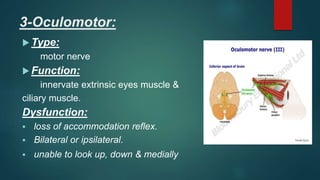
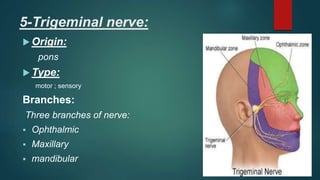
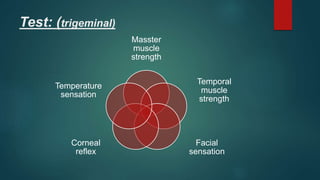
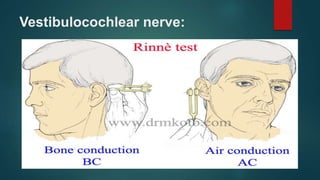
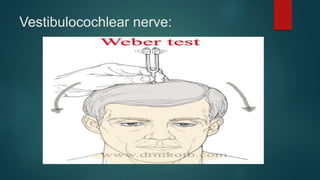
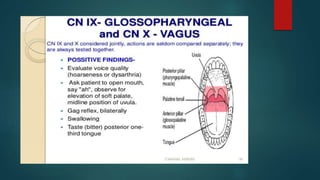
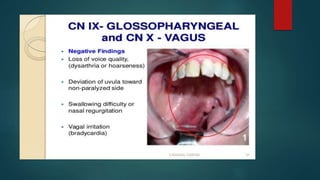
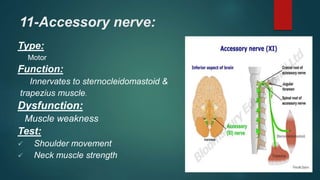
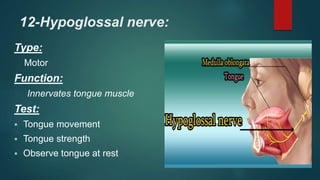
2. It then describes the 12 pairs of cranial nerves, their origin, function and how to test for dysfunction. The cranial nerves discussed are olfactory, optic, oculomotor, trochlear, trigeminal, abducens, facial, vestibulocochlear, glossopharyngeal, vagus, accessory and hypoglossal nerves.
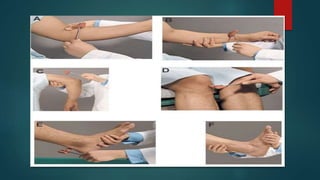
3. The document provides guidance on clinically evaluating various reflexes and testing different cranial nerves to identify any abnormalities.