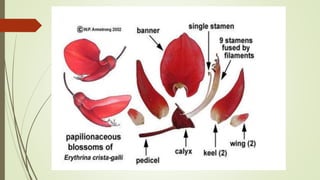
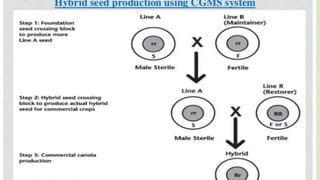
The document discusses hybrid seed production techniques for red gram. It describes using male sterile lines as female parents that are crossed with male parents that produce pollen. The key steps involve emasculation of the female parent's flowers before pollination with pollen from the male parent. New high yielding hybrids and varieties have been developed by ICRISAT and IIPR that provide 30-40% greater yields than traditional varieties through genome sequencing and other innovations.