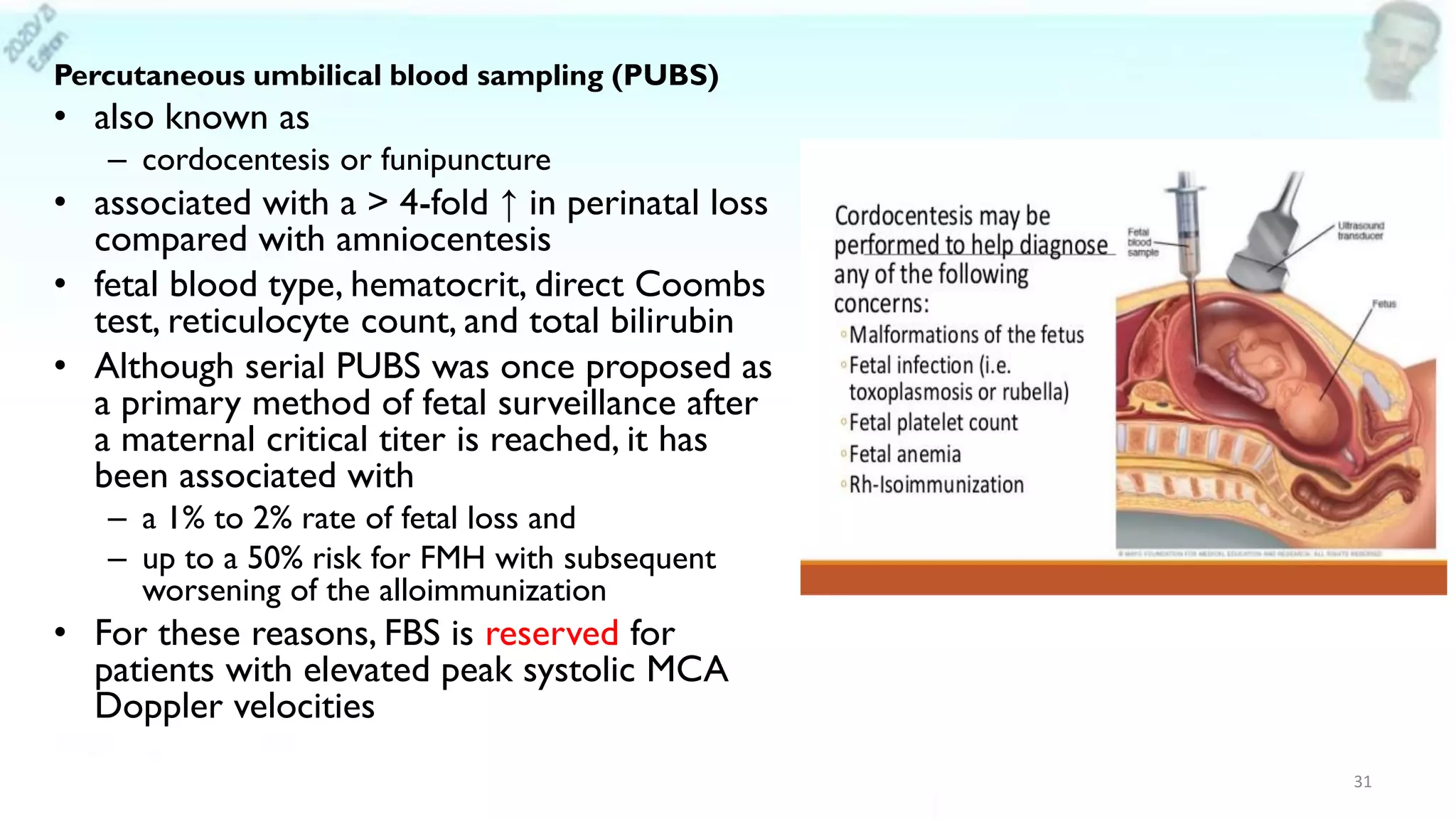
Red cell alloimmunization, also known as Rh disease, occurs when a woman develops antibodies against the Rh factor in her baby's blood. This can cause hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn if she has a subsequent Rh-positive pregnancy. Screening involves testing the mother's blood type and performing an antibody screen and Kleihauer-Betke test if needed. Diagnosis may involve ultrasound to check the fetus for signs of anemia like increased blood flow in the middle cerebral artery. Treatment depends on the severity and includes monitoring the pregnancy, intrauterine fetal transfusions if indicated, or early delivery. Noninvasive prenatal testing using cell-free fetal DNA in the mother's blood can also determine the baby's




![The Rhesus System
• The International Society of BloodTransfusion currently recognizes
– 33 different blood group systems & 339 red cell antigens
• Any individual who lacks a specific red cell antigen may produce an antibody when exposed to that antigen
• Two important antigens are common as a cause of transfusion reaction
• OAB
– most important blood group system
– immediate spontaneous agglutinin response
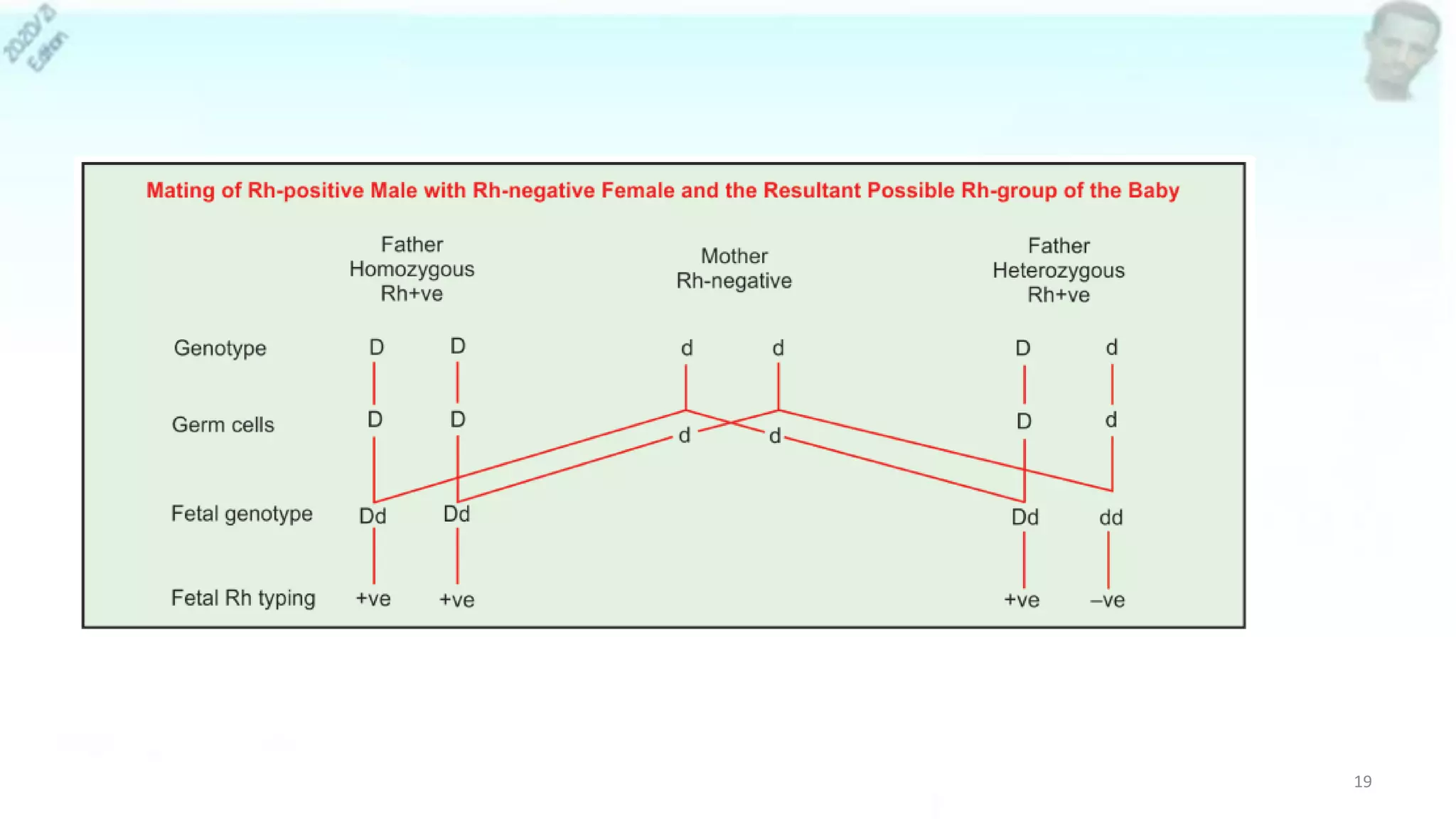
• Rh system (6 Rh antigens : C,c,D,d,E,e)
– Second most important blood group system
– No immediate spontaneous agglutinin response from serum
– Two separate genes for the Rh system are found on short arm of chromosome 1
• RHD gene - encodes for D antigen
– Rh(D) status described - positive or negative [no d antigen]
– Rh Positive—95% (black American), 85% (whites), 100% (in Africans)
• RHCE gene, encodes for a combination of CE or ce antigens
– Severe fetal anemia requiring antenatal transfusion are due to anti-D, anti-Kell, anti-c, or anti-E
alloimmunization
5](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/redcellalloimmunization-210611062214/75/Red-cell-alloimmunization-JUNE-2021-5-2048.jpg)














![Screening Vs Diagnosis
• Screening
– Blood type: ± D antigen?
– Antibody screen:
• Coombs test ( maternal blood & fetal/neonatal blood)
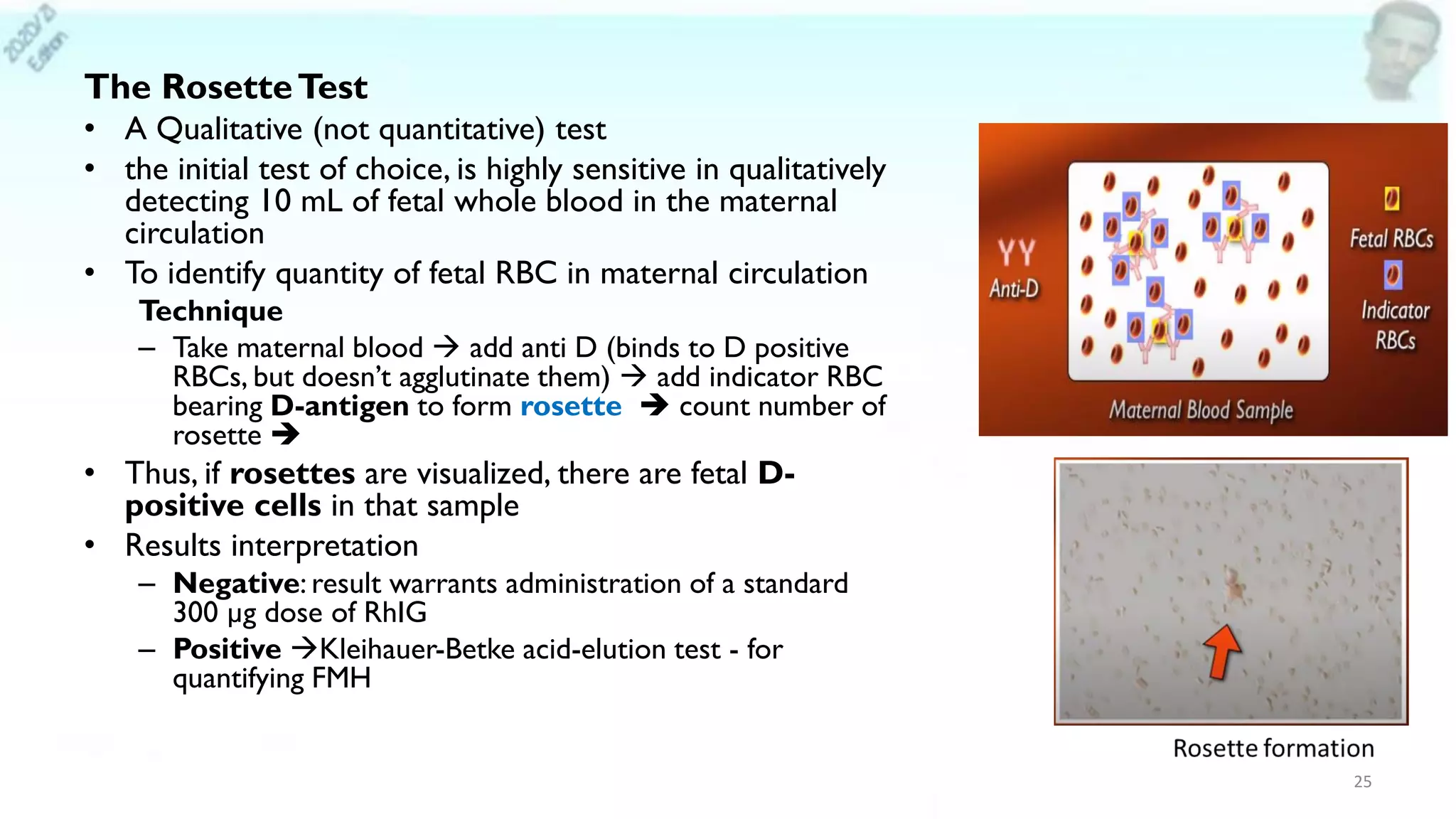
– Rosette Test (Fetal RBC Screen [Qualitative])
– Kleihauer-Betke test
• Diagnostic
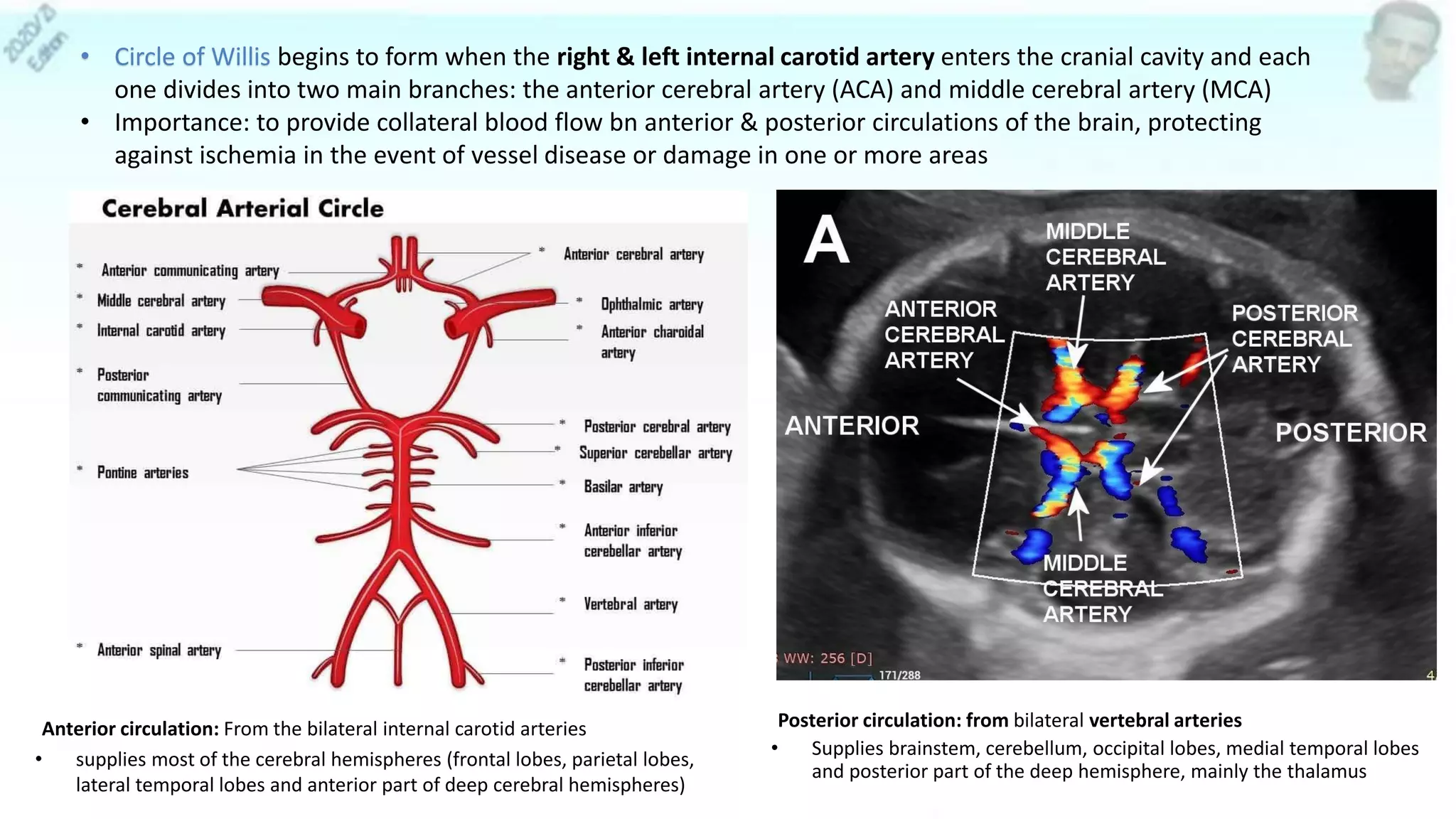
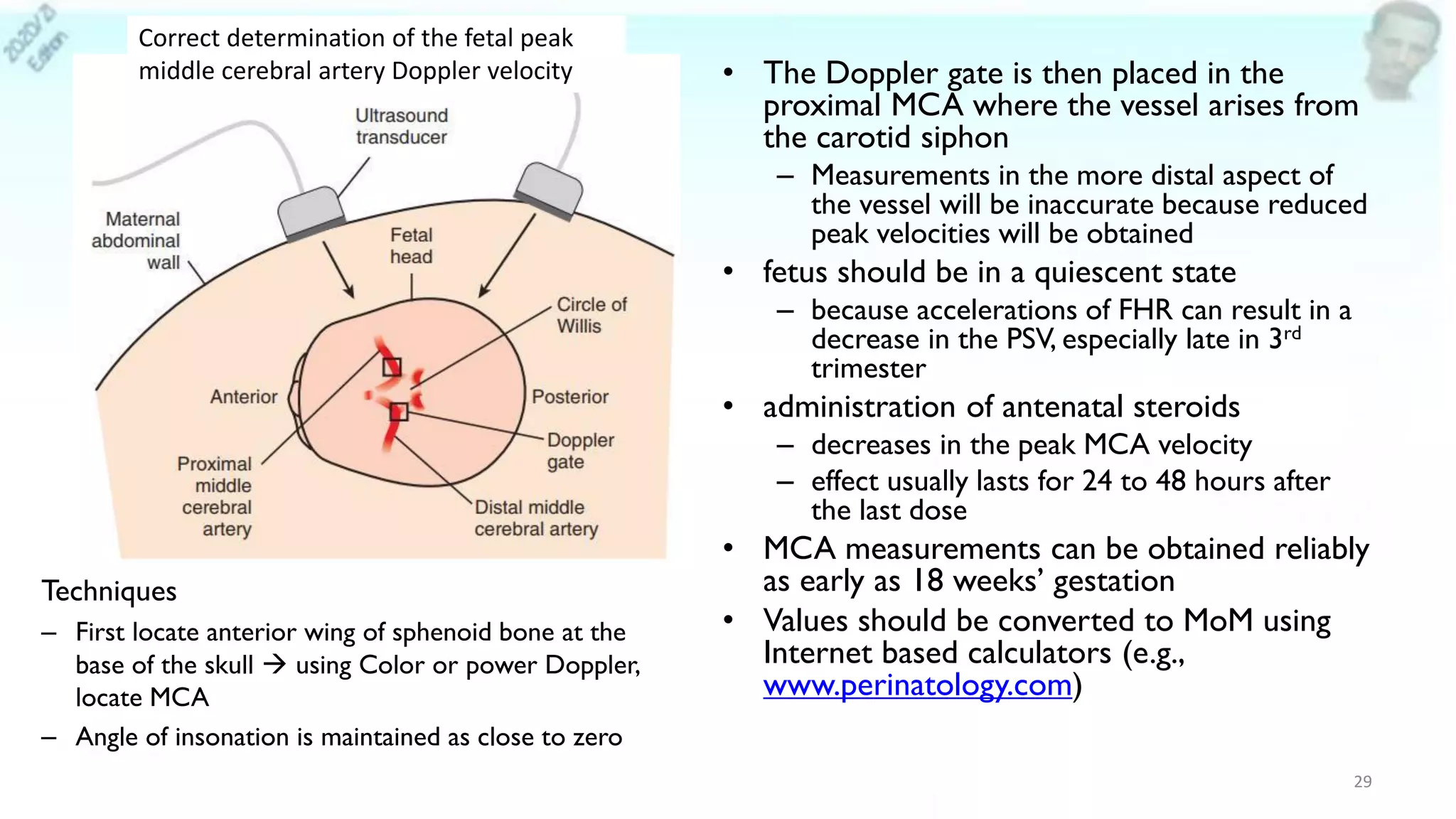
– Sonography:
• MCA peak systolic velocity (most accurate predictor)
• Hydrops (ominous finding)
– CTG: sinusoidal FHR pattern
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/redcellalloimmunization-210611062214/75/Red-cell-alloimmunization-JUNE-2021-23-2048.jpg)







![1st Dose: at approximately 28 weeks’ gestation: 300 µg
• 1 full dose = 300 µg (1500 IU): Covers fetal 30 ml of fetal blood (15 ml of
fetal RBC, since Hct is 50%)
• Reduces risk from 16% (ABO compatible newborn) to 2% or from 2%
(ABO incompatible newborn) to 0.1%
• If both antepartum & postpartum: risk of alloimmunization is reduced to
0.1% [Current 12th]
• repeat antibody screening is recommended to identify individuals who have
become alloimmunized (AAP, 2017).
• Duration: Suppression of Rh isoimmunization: ~ 12 weeks
• If > 12 weeks have elapsed since anti-D immunoglobulin administration,
consideration should be given to administering 300 µg of anti-D
immunoglobulin at 40 weeks of gestation
35](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/redcellalloimmunization-210611062214/75/Red-cell-alloimmunization-JUNE-2021-35-2048.jpg)