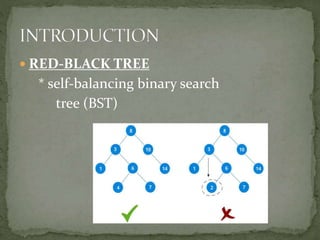
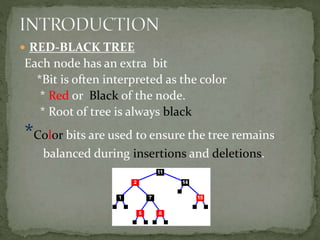
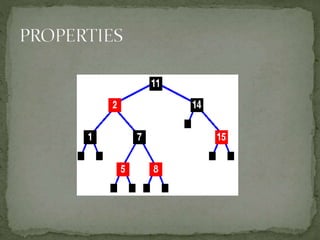
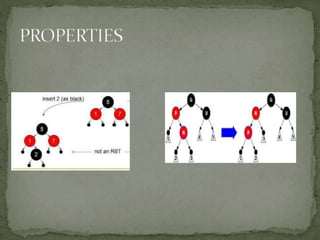
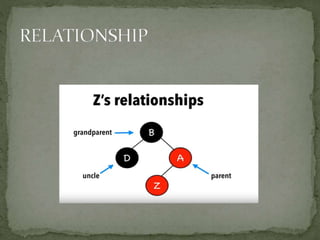
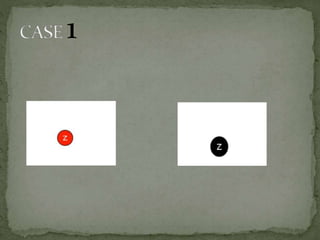
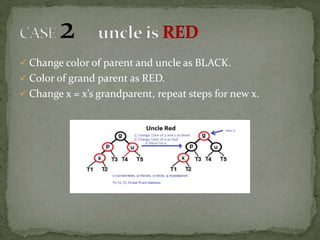
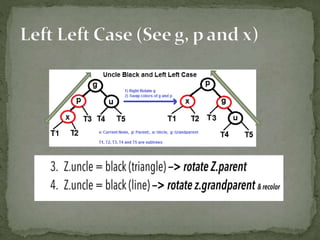
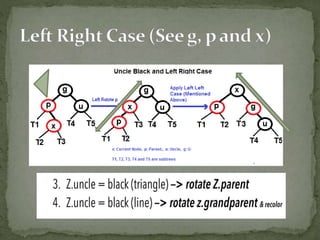
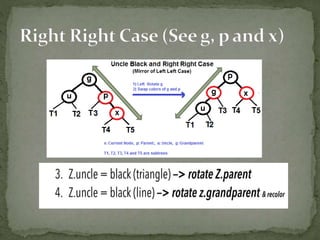
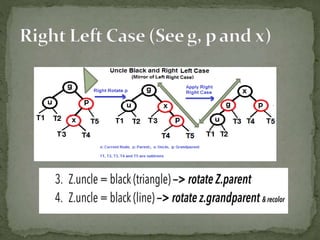
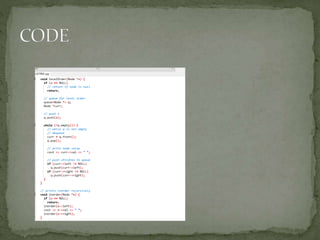
This document discusses red-black trees, which are self-balancing binary search trees. Each node of a red-black tree has an extra bit denoting its color, either red or black. Operations like insertion, lookup, and deletion can be performed in O(log n) time due to rebalancing techniques and restrictions on how nodes are colored. Some examples of using red-black trees include implementing maps and sets in libraries, organizing virtual memory, and CPU scheduling. Code examples and references are provided.